Apple announces results of collaboration with NVIDIA to accelerate performance of large-scale language models

On December 18, 2024, Apple announced the results of a joint research project with NVIDIA to accelerate inference processing of large-scale language models (LLMs). By integrating Apple's proprietary '
Accelerating LLM Inference on NVIDIA GPUs with ReDrafter - Apple Machine Learning Research
https://machinelearning.apple.com/research/redrafter-nvidia-tensorrt-llm
NVIDIA TensorRT-LLM Now Supports Recurrent Drafting for Optimizing LLM Inference | NVIDIA Technical Blog
https://developer.nvidia.com/blog/nvidia-tensorrt-llm-now-supports-recurrent-drafting-for-optimizing-llm-inference/
Apple collaborates with NVIDIA to research faster LLM performance - 9to5Mac
https://9to5mac.com/2024/12/18/apple-collaborates-with-nvidia-to-research-faster-llm-performance/
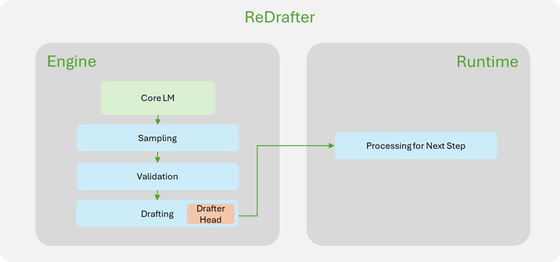
In March 2024, Apple announced a new inference acceleration technology called 'ReDrafter' and released it as open source. This technology uses a recurrent neural network (RNN) as a draft model and combines two techniques: a search algorithm called ' beam search ' to find the optimal output sequence and 'dynamic tree attention' to efficiently process options, which can significantly speed up text generation in LLMs.
The core of this technology is the efficiency of a process called 'inferential decoding.' Conventional LLMs require processing each token in turn when generating text. In contrast, ReDrafter uses an RNN draft model to predict the next token that is likely to appear, and speeds up processing by evaluating multiple candidates simultaneously.
Apple claims that by applying ReDrafter to the open source model, it is possible to process up to 3.5 tokens per generation step, significantly outperforming previous inference decoding techniques.
In addition, this announcement also stated that they have worked with NVIDIA to put this technology to practical use for GPUs. In the integration, NVIDIA implemented a feature called in-flight batching (IFB) to efficiently process requests in the context and generation phases. They also succeeded in reducing processing overhead by performing token validation and path acceptance within the engine.
In actual performance evaluation, a 2.7x speedup was confirmed for a practical model with tens of billions of parameters using the NVIDIA H100 GPU, with particularly notable benefits in specific tasks such as code completion and low-traffic scenarios with small batch sizes.
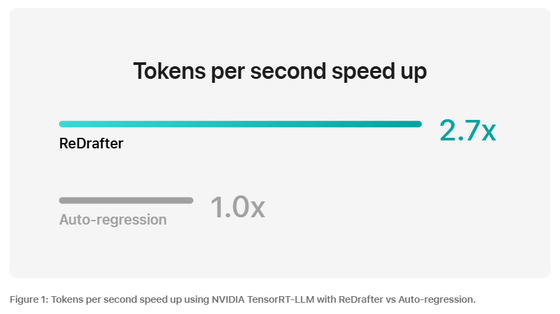
Apple's machine learning research team says that this acceleration technology will significantly reduce user wait times while also reducing GPU usage and power consumption, marking an important step forward in the practical application of LLM.
Related Posts:
in Software, Posted by log1i_yk