What are the three problems that were found by analyzing 'Why are Google projects failing and Meta projects succeeding?'

Major IT companies such as Google and Meta are promoting many large-scale projects, but these projects do not always succeed. Jeffrey Liu, who consults on AI-related products and used to work on machine learning at Meta, analyzes the question, 'Why do Google's projects fail but Meta's projects succeed?'
Google's Lost Moonshots · Jerry Liu
Liu pointed out that Google was once a company that not only made products but also 'defined the future,' and that the innovations and slogans that Google created have had a huge impact on the world. For example, Google Maps revolutionized the world of navigation, Gmail made previous email services obsolete, Chrome redefined the possibilities of browsers, and Android contributed to 'democratizing' smartphones.
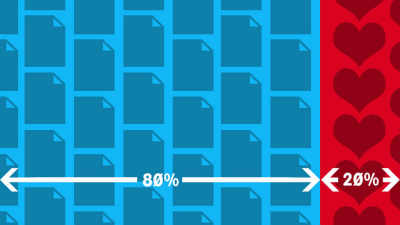
Also, the ' 20% rule ,' which states that 20% of your working time can be spent on anything you like, is known as an initiative started by Google, and it was said that this free time would lead to the creation of bold new businesses.
'BASEDEF' is a little technique to make full use of the '20% rule' that allows you to use your work time for what you like - GIGAZINE
But over the past few years, Liu said, Google seems to have lost some of its luster: Its multimodal AI, Gemini , for example, came later than its competitors' AI and is what Liu calls a 'follower product.'
Google's acquisition strategy has also been unsuccessful in recent years. Although it acquired fitness tracker Fitbit for approximately $2.1 billion (approximately 230 billion yen at the time) in 2021, it has yet to release a groundbreaking healthcare product. In addition, Motorola 's smartphone business, which it acquired for $12.5 billion (approximately 960 billion yen at the time) in 2011, was later sold for $2.91 billion (approximately 296 billion yen at the time). Other recent examples of failure include the closure of products such as smart glasses Google Glass and cloud gaming service Stadia .
On the other hand, Meta has made Instagram and WhatsApp , which were initially viewed with skepticism, a huge success, and both services are now indispensable to Meta. In addition, in recent years, the company has been investing billions of dollars (several hundred billion yen) annually in the AR/VR field, and continues to move forward even after suffering huge losses.
After analyzing these differences between Google and Meta, Liu argues that Google has three systemic problems:
◆1: Imperfect incentives
The careers of Google's innovation-driving playing managers (PMs) are determined by regular performance reviews. For PMs, it is more stable to release a small product that looks good in a performance review than to spend years on a large-scale project that may fail, so there is less incentive to spend resources on ambitious projects.
'It's like trying to work on a 10-year climate change project with a politician who is term-limited to four years and needs to win the next election,' Liu said of the problem.

◆2: Moonshot Budget
A moonshot (great project) requires a certain amount of resources to succeed, but in recent years, Google's budget has been limited to 'well-funded experiments,' while Meta is investing resources on a scale commensurate with its ambitions. In fact, Meta's VR/AR research division, 'Reality Labs ,' continues to receive more funding than any other company has ever spent before.
In the fourth quarter of 2023, Reality Labs' revenue reached a record high of $1.07 billion (approximately 156.5 billion yen), but its costs exceeded that, reaching $5.72 billion (approximately 837 billion yen).
Meta's VR division, Reality Labs, achieves record revenue of over $1 billion, thanks to the success of Meta Quest 3 - GIGAZINE

◆3: Learning as a company
Although both Google and Meta have failed projects, Liu believes that the difference is whether they can learn from their failures and use them in the future. For example, at Google, after Google Glass was discontinued, the team was disbanded and the context was lost except for some internal documents, and even after the social networking service Google+ was discontinued, its legacy was not well utilized.
On the other hand, Meta was strongly conscious of working on AR and VR when it acquired Oculus in 2014, and pointed out that it has had a clear learning curve from the Meta Quest to the smart glasses Ray-Ban Meta . 'In most cases, the team or organization will continue in some form and the context will be maintained. Every failure will directly reflect on the next attempt,' Liu said.

First of all, managing a moonshot project requires a long-term belief, which is difficult for a typical company whose leaders change regularly. In contrast, Liu argues that Meta's CEO Mark Zuckerberg has consistently maintained leadership and stuck to his beliefs even when criticized, which allows the organization to continue to learn and progress. Liu said, 'In the end, I think the biggest risk at this scale is not failure, but being afraid to commit.'
Related Posts:
in Note, , Posted by log1h_ik