Snowflake Arctic, a large-scale language model optimized for enterprise tasks such as SQL generation, coding, and instruction following that can be used for free and commercially, is now available

Snowflake, a company that develops cloud-based data warehouse services, has released ' Snowflake Arctic ' as a top-level enterprise large-scale language model (LLM). It is an open model provided under
Snowflake Arctic - LLM for Enterprise AI
https://www.snowflake.com/blog/arctic-open-efficient-foundation-language-models-snowflake/

According to Snowflake's survey, enterprise users often want to use AI to create chatbots that mainly perform data assistance, code assistance, and search augmentation generation (RAG). Therefore, Snowflake created a single metric called 'Enterprise Intelligence' by taking the average of 'coding ability,' 'SQL generation ability,' and 'command following ability.'
Snowflake Arctic, the LLM released by Snowflake this time, is said to have the best enterprise intelligence capabilities among open LLMs. In addition, the cost of training is less than $2 million (about 310 million yen), and it is said to be very efficient compared to other models.
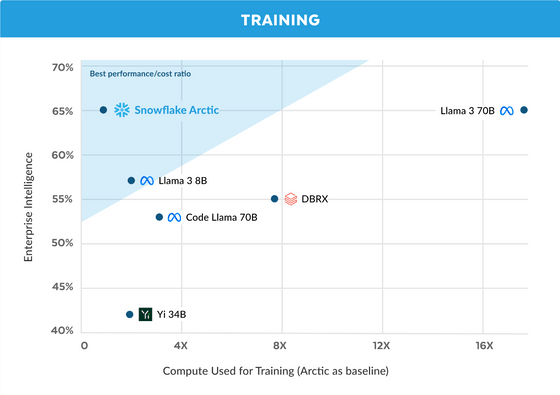
The graph below compares several LLMs, with the vertical axis representing enterprise intelligence score and the horizontal axis representing computing resources required for training. We can see that Snowflake Arctic delivers high performance at low cost.
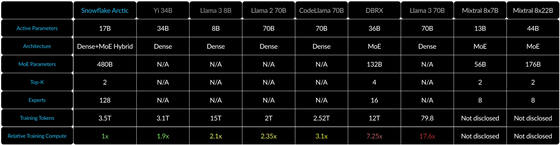
The figure below is a table for calculating the specific computing resource usage. The amount of calculation required for training is proportional to the product of the number of active parameters and the training tokens. A model with high training efficiency has the advantage that users can create custom models at an affordable price.
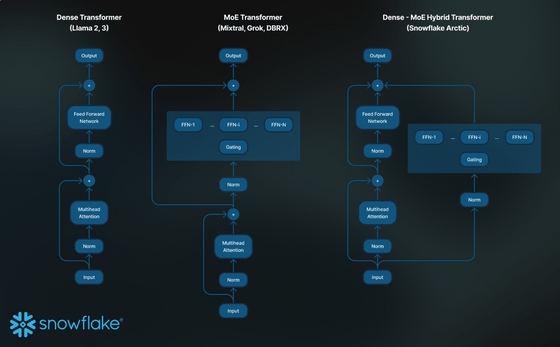
To achieve good training efficiency, Snowflake Arctic uses a proprietary Dense-MoE hybrid transformer architecture. MoE stands for 'Mixture of Experts,' and in Snowflake Arctic, a total of 480 billion (480B) parameters are allocated to a total of 128 'experts,' and only a total of 17 billion (17B) parameters are used from the experts for training and inference.
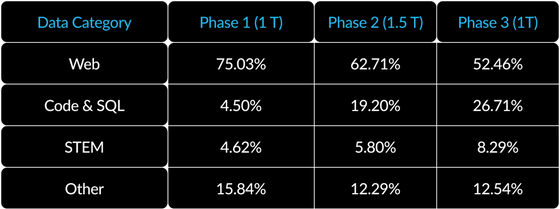
In addition, the training content changes for each phase, with Phase 1, which is the first 1 trillion (1T) tokens, teaching general skills such as common sense reasoning, and Phases 2 and 3 teaching more complex content such as coding and mathematics.
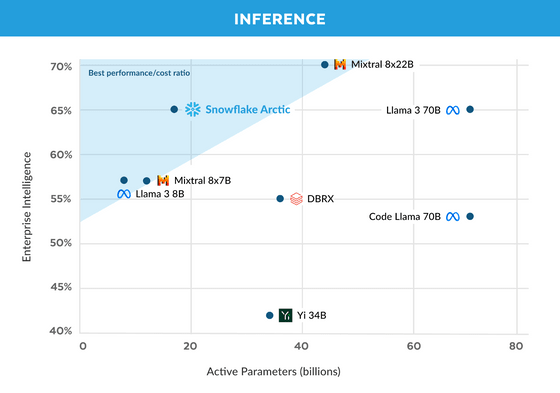
Through these adjustments, Snowflake Arctic has become more efficient not only in training but also in inference. If we plot various LLMs with enterprise intelligence on the vertical axis and the number of active parameters, which is an indicator of inference efficiency, on the horizontal axis, as shown in the figure below, we can see at a glance that Snowflake Arctic achieves high performance with a small amount of calculation.
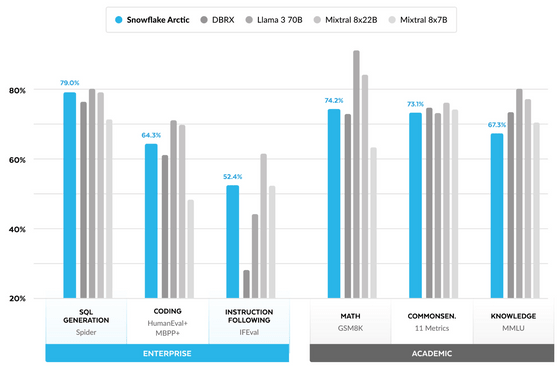
Snowflake Arctic can perform at the highest level against large open models with active parameters that exceed Snowflake Arctic in enterprise intelligence such as 'SQL generation,' 'coding,' and 'command following,' and it can perform at the same level as models of the same size in indicators common in the academic world such as 'mathematics,' 'common sense reasoning,' and 'knowledge.'
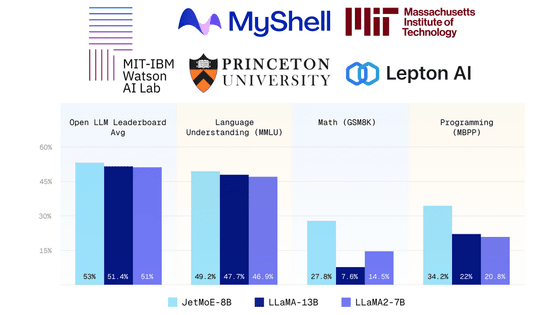
The specific benchmark figures are as follows:
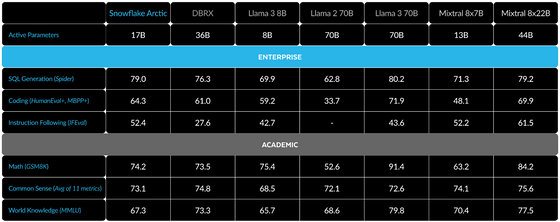
There is
The Snowflake Arctic model is available on Hugging Face and is expected to appear on AWS, Lamini, Microsoft Azure, NVIDIA API Catalog, Perplexity, Replicate, Togetter AI, and more within the next few days.
Related Posts:
in Software, Posted by log1d_ts