North Korea's cyber crime group 'APT37' turned out to be attacking Internet Explorer's zero-day vulnerability

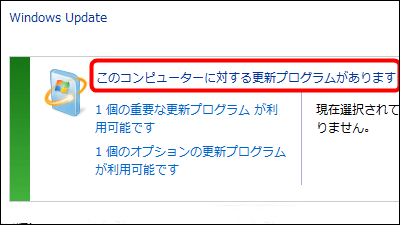
According to Google's Threat Analysis Group (TAG), a North Korean cyber crime group codenamed 'APT37' and 'Reaper' exploited Internet Explorer's zero-day vulnerability in October 2022 to attack. announced that it had been discontinued. The attack is said to target machines with Windows 7 or later or Windows Server 2008 or later that have not installed the November 2022 security update.
Internet Explorer 0-day exploited by North Korean actor APT37

Google found North Korea used a tragedy to exploit Internet Explorer vulnerability - The Verge
https://www.theverge.com/2022/12/7/23498226/google-north-korea-exploited-internet-explorer-vulnerability-security
According to the security company FireEye's (PDF file) report , APT37 has been confirmed to be making full use of spear phishing and social engineering so far. Specifically, in addition to exploiting a vulnerability in Hangeul word processing software widely used in South Korea, in 2018, an attack was conducted using a zero-day vulnerability ( CVE-2018-4878 ) in Adobe Flash. has also been confirmed.
This time, APT37 seems to have exploited the zero-day vulnerability ' CVE-2022-41128 ' in Internet Explorer's JavaScript engine 'jscript9.dll'. According to Google TAG, Internet Explorer reached its end of support on June 16, 2022, but Microsoft Office still uses Internet Explorer's JavaScript engine, and the security update delivered in November 8, 2022. It was working on a machine with Windows 7 or later or Windows Server 2008 or later that was not installed.
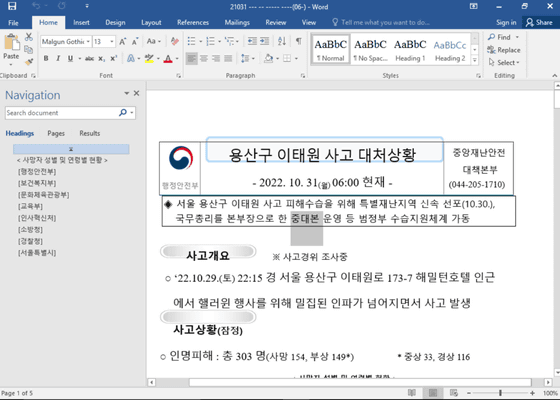
On October 31, 2022, Google TAG noticed that a Microsoft Office document titled '221031 Seoul Yongsan Itaewon accident response situation (06:00).docx' was uploaded online. This document is about a crowd accident that occurred in Itaewon, Seoul, South Korea on October 29, 2022. When opened, it downloads a rich text file template and acquires HTML content. When rendering this HTML content, Internet Explorer's JavaScript engine is used, and arbitrary code may be executed.
While Google TAG was unable to recover the final payload of this attack, we expect this document to carry out similar attacks, as APT37 has previously caused various malware to be downloaded onto the victim's machine. doing.
Google TAG said, ``I have to say that it is careless not to recognize the prompt response and patch application to CVE-2018-4878 by the Microsoft team,'' urging immediate patch application and caution. I'm here.
Related Posts: