North Korean hackers exploit Internet Explorer zero-day vulnerability to launch malware attack

Although support for Internet Explorer (IE) ended in 2022, it remains standard on operating systems up to Windows 10 for compatibility, and continues to exist as the IE mode of Microsoft Edge in Windows 11. South Korean cybersecurity authorities have announced that a North Korean hacker group has newly confirmed an attack that exploited a zero-day vulnerability in IE.
AhnLab and NCSC Release Joint Report on Microsoft Zero-Day Browser Vulnerability (CVE-2024-38178) - ASEC
Malicious ads exploited Internet Explorer zero day to drop malware
https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/malicious-ads-exploited-internet-explorer-zero-day-to-drop-malware/
On October 16, 2024, South Korea's National Cyber Security Center (NCSC) and the country's security company AhnLab released a joint report on the Internet Explorer zero-day vulnerability 'CVE-2024-38178.'
The attack exploiting this vulnerability was carried out by the North Korean hacker group 'APT37,' also known by the names 'ScarCruft,' 'RedEyes,' and 'TA-RedAnt.' According to the joint report, APT37 has previously targeted North Korean defectors and human rights activists who advocate for North Korea issues by exploiting vulnerabilities in hacking emails and Android app files (APK files).
In 2022, Google's Threat Analysis Group (TAG) discovered that APT37 had carried out attacks exploiting the IE vulnerability 'CVE-2022-41128.'
North Korean cybercrime group 'APT37' revealed to be attacking Internet Explorer zero-day vulnerability - GIGAZINE

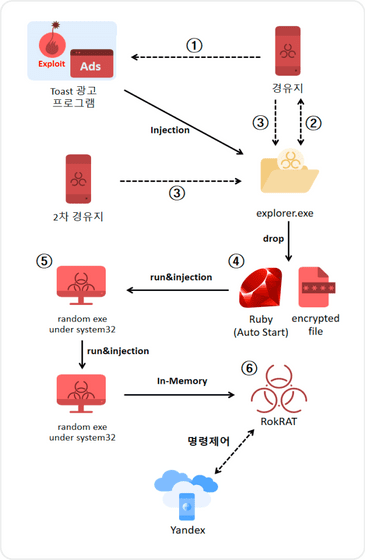
In this attack, the malware 'RokRAT' was used, which targets programs for 'toast ads' that are installed with free software. Toast ads are pop-up ads that are displayed at the bottom or bottom right of the screen. This attack is classified as a zero-click attack because the malware is infected when the ad is displayed even if the user does not click on it.
The main modus operandi was as follows: APT37 first infiltrated the server of an advertising agency in South Korea and tampered with the Toast advertising program, a free software widely used by South Koreans.
The ads in question contain a malicious iframe element that, when rendered by IE, results in a JavaScript file called “ad_toast” that executes remote code via a vulnerability in IE’s JavaScript engine, “JScript9.dll.”
RokRAT then exfiltrates files with 20 different file extensions, including .xls, .doc, and .txt, from the infected device to a Yandex cloud instance, as well as stealing data by performing keylogging, clipboard monitoring, and screenshot capture.
Following the report by NCSC and AhnLab, Microsoft fixed CVE-2024-38178 in an update in August 2024. However, even if Microsoft fixes Windows, free software that was a direct infection route for the malware may not have been fixed yet.
BleepingComputer, an IT news site that covered this incident, pointed out that 'Microsoft fixed the IE flaws in August, but there is no guarantee that the fixes will immediately apply to tools that use older IE components. Therefore, free software that uses older IE components will continue to put users at risk.'
BleepingComputer has contacted AhnLab to find out the specific name of the free software in question, and will provide an update as soon as more information becomes available.
Related Posts:
in Security, Posted by log1l_ks