What is the mechanism of `` a device that makes drinking water from seawater using only sunlight '' that can be made with only 500 yen?

Researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and Shanghai Jiao Tong University are developing a device that can turn seawater into freshwater simply by putting it in and illuminating it with sunlight. The cost of the device is only $ 4 (about 520 yen), and one boasts the ability to supply the drinking water that a family of four needs a day.
Highly efficient and salt-rejecting solar evaporation via a wick-free confined water layer |
Solar-powered system offers a route to inexpensive desalination | MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology
https://news.mit.edu/2022/solar-desalination-system-inexpensive-0214
Two-thirds of the earth is covered by water, 97% of which is seawater. Seawater has a high salt concentration, so drinking it straight will cause dehydration. Therefore, it can be said that the technology to produce fresh water from seawater is very important.
There are two methods of desalinating seawater, one is evaporating seawater and cooling it again to make it freshwater, and the other is desalinating seawater by passing it through a filtration membrane. In particular, the method of desalinating seawater by evaporating it using sunlight does not require electricity or complicated equipment. In the long run, the durability of the equipment becomes a problem.
Therefore, the research team of MIT and Shanghai Jiao Tong University developed a device with the concept of 'using natural convection '.
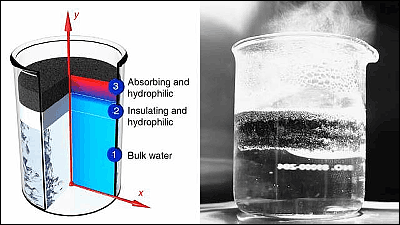
The key points of this device are the highly insulating polyurethane and the black cover. When polyurethane with many 2.5mm diameter holes is floated in a seawater storage tank, seawater collects in the depressions on the top of the polyurethane. And the seawater storage tank is covered with a black cover to store heat energy from sunlight. This heat energy evaporates the water from the seawater on top of the polyurethane.
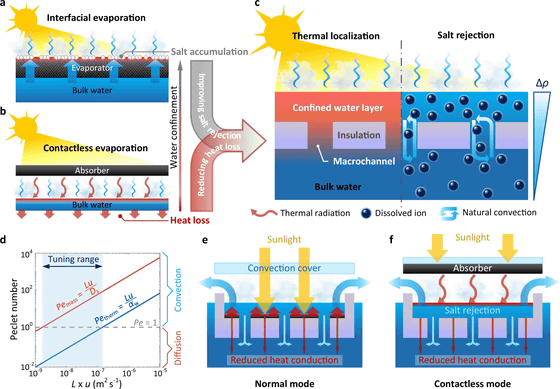
Then, as the water evaporates and the salt concentration increases, the seawater becomes denser, so it flows under the polyurethane through the holes in the polyurethane. At the same time, the seawater that was under the polyurethane flows over the polyurethane. In other words, natural convection occurs due to the difference in seawater density between the upper and lower layers of the tank with polyurethane sandwiched between them.
The advantage of this mechanism is that when the evaporated seawater with high salinity flows to the lower layer, it mixes with the lower layer seawater and dilutes the salinity. It solves the problem of salt precipitation if seawater with a high salt concentration remains as it is, so the durability of the equipment is greatly improved. When the research team actually manufactured and experimented with this device, the device functioned continuously for a week and no salt accumulation was observed.

According to the research team, it took only $ 4 to make a device with a size of 1 square meter. And it seems that this one-square-meter device can provide a family of four with the drinking water they need every day for at least a week.
Although it is a proof of concept on a laboratory scale to the last, the research team says that commercialization is also being considered in the future. They are also considering the possibility of using it for disaster relief in areas where the supply of fresh water has been cut off due to typhoons and earthquakes.
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1i_yk