A device that can produce drinking water from seawater cheaper than tap water has been completed

Engineers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and Shanghai Jiao Tong University have devised a new freshwater generation system that captures seawater and is powered by sunlight. This system achieves higher water production and salt recovery rates than existing systems.
Desalination system could produce freshwater that is cheaper than tap water | MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology
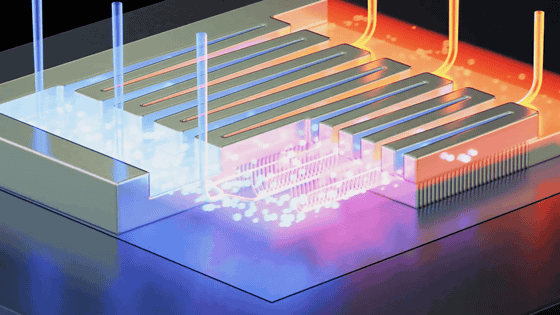
The desalination device developed by the research team is an improved version of the system designed in previous research, which consists of multiple layers called 'stages.' This system uses solar heat to separate salt from water, but the problem is that the remaining salt quickly forms crystals and accumulates, causing the system to malfunction after a few days. did. This would require periodic replacement of stages, which would significantly increase costs.
MIT researchers have improved the system described above and evolved it into a new convection -inspired structure.
The new system uses a thin, box-like stage with two internal layers, top and bottom. The seawater sent to the evaporation layer in the upper half is evaporated by the heat of the sun hitting the ceiling of the box, and only the water vapor is sent to the condensation layer in the lower half, where it is air-cooled and turned into drinkable water. The upper half is connected to a tube that takes in seawater from the outside.

by Jintong Gao and Zhenyuan Xu
In this configuration, water is naturally pushed up through the tube into the box, and the combination of the box's tilt and the heat energy from the sun causes the water to swirl and flow. This is a vortex caused by differences in salinity, and takes advantage of the fact that water with higher salinity tends to flow downward. The small vortices prevent salt from settling and guide water to the evaporation layer while maintaining circulation.
The researchers built several one-, three-, and 10-stage prototypes and tested their performance in a variety of waters, including natural seawater and water with seven times the natural salinity. As a result, it has achieved higher water production and salt recovery rates than any existing seawater desalination concept.

by Jintong Gao and Zhenyuan Xu
Researchers estimate that if the system was scaled up to the size of a small suitcase, it could produce about 4 to 6 liters of potable water per hour and last several years before parts need to be replaced. I am. With this scale and performance, it is said that drinking water can be produced at a lower price than tap water.
Zhenyuan Xu, who was involved in the research, said, ``This device is characterized by its long service life. This opens up the possibility of desalination.' In the future, they aim to expand the system to a scale of several kilometers.

In addition, Mr. Xu and his colleagues are also known for having once created a ``desalination device that cost about 500 yen''. The current system was a further improvement on this device.
What is the mechanism of 'a device that makes drinking water from seawater using only sunlight' that can be made for only 500 yen? -GIGAZINE

Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1p_kr