It becomes like this when it visualizes the overwhelming difference of “the company which introduces the industrial robot” and “the company which does not”

By
' Industrial robots ' are mechanical devices that perform assembly work, etc. Many of the products that we usually see are manufactured by industrial robots. Industrial robots have made remarkable progress in recent years, but some companies have not introduced industrial robots. 'There is a possibility that robots will steal people's work, ' but by introducing industrial robots, 'the number of workers will increase, the business results will be strong, and the productivity will be high.' Research has been published
Robots and firms | VOX, CEPR Policy Portal
https://voxeu.org/article/robots-and-firms
Since the advent of industrial robots, many researches have been published, 'How did the industrial robots affect the manufacturing industry?' In one example, industrial robots contribute about 15% of the overall economy's production rate, according to a survey of industries in 17 countries ( Graetz, G and G Michaels, “Robots at work” ) in 14 years from 1993 to 2007. Is shown.
However, it is said that such research was mostly conducted on a national basis on the premise that all companies introduced the same amount of industrial robots. In response to this problem, a research team led by Associate Professor Michael Koch of the Faculty of Economics at Bayreuth University in Germany conducted a survey on 'the difference between companies that introduced industrial robots and those that did not.' The

By
It was to provide data that is the source of the study, an annual survey on the country's manufacturing industry about 1900 company that Spain is doing ESEE is. According to the research team, Spain is one of the highest proportion of industrial robots per worker in Europe among the countries, and ESEE contains data such as the utilization rate of industrial robots in each company's production line It was thought that it was suitable for this research.
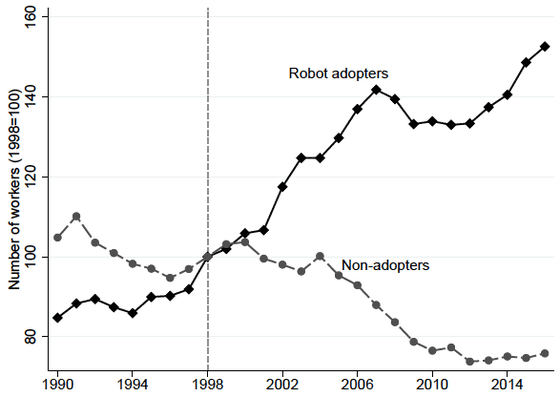
From the ESEE data, the graph below shows the change in the number of workers every year for companies that have introduced industrial robots and companies that have not. The graph connecting the plots represented by ◆ is the average number of workers of companies that introduced industrial robots before 1998, and the graph linking the plots represented by ● is the industrial robot over the entire period The average number of workers in companies that did not introduce The number of workers in introduced companies has been steadily increasing since 1998, but on the contrary, it can be seen that the number of workers in non-introduced companies has decreased since 1998.
In addition, the graph below shows the difference in “
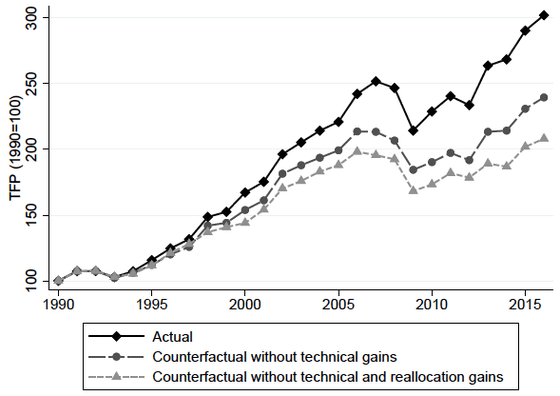
According to the research team, companies that introduced industrial robots saw an increase in output of 20% to 25% within five years. Furthermore, contrary to the general concern 'Why robots do not take work?', It has also been found that the introduction of industrial robots will increase total employment by about 10%.
In addition, the manufacturing industry that requires high skill does not introduce industrial robots, the effect of industrial robots is low in such companies, and the export industry has more industrial robots than other industries. It is also known that the introduction rate is high.
By Besjunior
As the conclusion of this research, 'The company which introduced the industrial robot has a good performance and the workers are increasing, while the company which has not introduced it has the negative output and can not compete with the high-tech company, and the employment situation Will be worse. '
In addition, in this research, 'Artificial intelligence, robots and employment: Analysis by personal survey' by Mr. Masayuki Morikawa, Deputy Director of the Research Institute of Economy, Trade and Industry, was introduced as a similar research in Japan.
RIETI-Artificial Intelligence, Robots and Employment: Analysis by Individual Survey
Related Posts:
in Hardware, Posted by darkhorse_log