CERN publishes a site that can experience the world's first web browser 'WorldWideWeb' in the browser
The HTML editor " WorldWideWeb " developed by Tim Bernards-Lee et al., A European nuclear research institute (CERN) technical consultant and others, is said to be the world's first web browser. A site that completely reproduced such WorldWide Web on a web browser has been published on CERN's server that produced WorldWideWeb.
CERN 2019 WorldWide Web Rebuild
https://worldwideweb.cern.ch/
Adactio: Journal-WorldWide Web
https://adactio.com/journal/14821
Go to the public page of CERN and click "Launch WorldWideWeb".
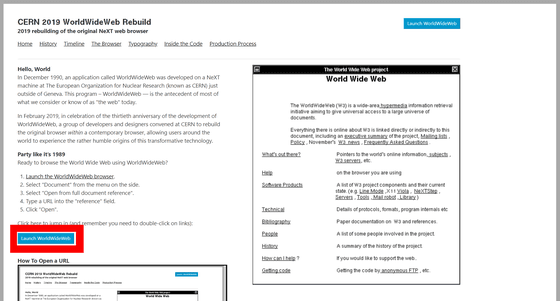
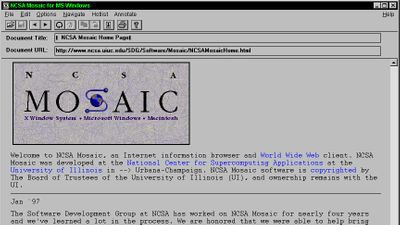
WorldWideWeb looks something like this. WorldWide Web, which appeared as an HTML editor of NeXTSTEP, NeXT computer 's computer , was known as the world's first web browser, and its source code was released as a public domain in 1993. This time WorldWide Web published on CERN server seems to have been reorganized by Remy Sharp in JavaScript within just 5 days.

To actually display the website on WorldWide Web, click "Document" from the "WorldWideWeb" window on the left side of the screen and select "Open from full document reference".
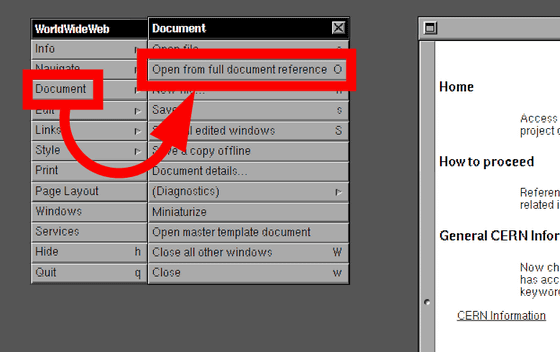
Then a window named "Open using hypertext reference" is displayed. Enter the URL in the "Reference" field and click "Open". This time I will display GIGAZINE .
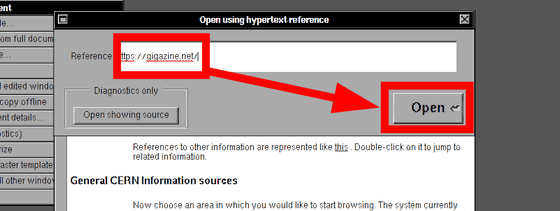
The displayed top page of GIGAZINE looks something like this. HTML is originally a tool born to solve the problem "how to share research content and various information ongoing in CERN among many scientists", and it is a tool by CSS which became common in modern times We do not expect modification of pages, so colors, images and site styles are not reflected. However, as hyperlinks work, of course, it seems possible to read articles.

I tried to display the article by double clicking from the top page and the image below. Only the title · body · header and link remain, it is a very simple appearance.

WorldWide Web was not only a browser, it was also an HTML editor. Click "Document" from the "WorldWideWeb" window on the left and click "New file ...".

Since the file management window will be launched, enter the file name with ".html" extension together in the Name column and click "OK".

The editor window will be displayed. "Heading" is the title of the document, "Text" is the content of the document, "Author" is the column describing the author of the document, and you can edit it by clicking on it.

In HTML, the accessibility of being able to refer to necessary information from within a document in one shot was revolutionary, by creating a hyperlink in the document, without having to locate the document from the data bank one by one . Of course, even on WorldWide Web you can create hyperlinks in the document. This time, let's try to skip the link to the top page of GIGAZINE from the character "GIGAZINE" in "test.html". First, click "Links" from the "WorldWideWeb" window on the left to display the "Links" window.

With the window displaying the top page of GIGAZINE active, click "Mark all" in "Links" window.

Then, drag and select "GIGAZINE" in test.html and click "Link to marked" in "Links" window.

It is a bit hard to understand, but I understand that underline has been added to GIGAZINE, and a hyperlink was created.

Double click on the link, the top page of GIAGZINE is displayed.

By experiencing WorldWideWeb, the world's first web browser on the current web browser, you can touch a page of the history of the Internet, but there is also a topic that CERN that produced WorldWide Web has opened up, At the time of writing the article, there were several times that it was not possible to connect to the server of CERN.
Related Posts:
in Review, Software, Web Application, Posted by log1i_yk