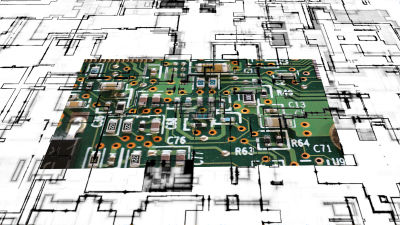
X-raying suspicious USB cables: Which ones are genuine?

Today's society is full of security risks. While we can be careful not to install suspicious software like malware, there have also been reports of suspicious chips embedded in hardware like USB cables, making their dangers obvious from their appearance alone. Security solutions company Eclypsium explains in a blog post whether X-ray technology can be used to identify dangerous USB cables.
We X-Rayed A Suspicious FTDI USB Cable - Eclypsium | Supply Chain Security for the Modern Enterprise
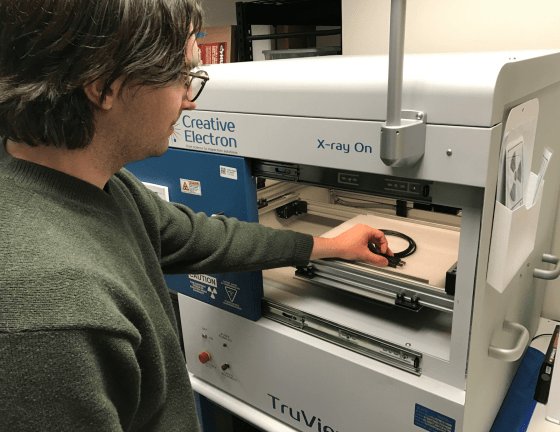
Eclypsium recently purchased an industrial X-ray machine to conduct cybersecurity research. Its main purpose is to perform X-ray inspections on behalf of large corporations, but the company also uses its time between schedules to conduct various verification experiments.

One of the tests Eclypsium conducted in the past was an X-ray inspection of an
What is the difference between a 'suspicious cable' and a 'genuine product'? FTDI has publicly announced the problem of counterfeit devices and has even released drivers to disable counterfeit chips , so it seems possible that the 'suspicious cable' contains a counterfeit FTDI chip.
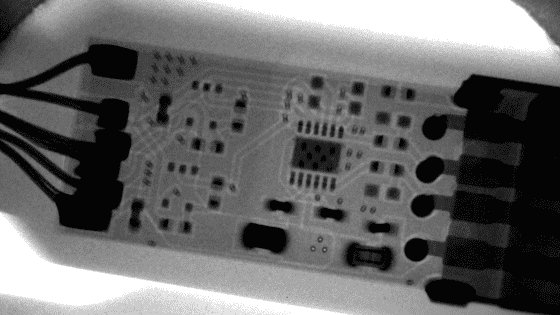
To the naked eye, the two cables look the same, but what about under X-ray?

Here's the second cable. So which one is the 'genuine' one?
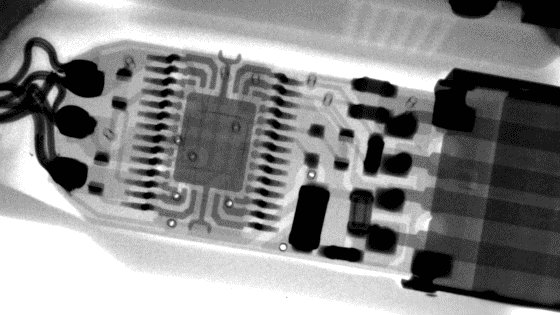
The blog lists the following clues to help you tell the difference:
Ground pour
Ground pores are a design technique in which empty spaces on the signal layer of a printed circuit board are filled with copper foil at ground (GND) potential, and are effective in reducing impedance and earth loops, as well as improving noise and heat dissipation. Although there is some debate about their actual effectiveness, reputable manufacturers install ground pores.
・Ground stapling
Ground stapling is a design technique that uses multiple vias (through holes) to connect the GND planes on different layers of a multi-layer printed circuit board, and has the effect of maintaining a uniform GND potential.
・Decoupling capacitor
Decoupling capacitors placed near integrated circuits (ICs) stabilize the voltage supplied to the IC's power pins, and are effective in stabilizing the voltage level of the entire IC and reducing noise.
・Passive isolation of USB data pins
The data pins on a USB cable are susceptible to noise, so the pins must be physically and electrically isolated from each other.
- Thermal pad under the IC
A thermal pad is a pad made of a material with high thermal conductivity and is used to efficiently dissipate heat from heat-generating components such as ICs. Placing a thermal pad under an IC will cool the IC, improving its stability and lifespan.
・Strain relief
Strain relief is a structure designed to relieve stress caused by pulling or bending on a cable, and strain relief designed for wiring connections improves the reliability, durability, and safety of the cable.
-Metal tab on USB Type-A connector
The large metal tab on the USB Type-A connector ensures both a mechanical and electrical ground connection to the board. Proper soldering of the tab to the board significantly improves the reliability and durability of the connection.
・Silicon process
Miniaturization of silicon processes leads to increased operating speed and reduced power consumption, but also increases production costs and technological barriers.
・Passive alignment
Passive alignment is a method of accurately aligning components on a board using only structures, guides, and jigs. Passive alignment is suitable for mass production because it does not require real-time power supply or monitoring.
To reveal the secret, the first of the two X-ray images is of the 'genuine product' and the second is of the 'suspicious cable.' However, it's important to note that even if you know how to spot a counterfeit product, it's not easy to actually detect it. While a suspicious USB cable alone isn't that serious, there's also the possibility that companies could introduce counterfeit network equipment equipped with backdoors or servers storing suspicious data, making supply chain security risk prevention increasingly important. The blog concludes that supply chain security risks could become an even more serious issue, especially considering that AI data centers now require massive amounts of hardware such as chips, memory, and storage.
Related Posts: