Research shows that ChatGPT feels 'anxious' when exposed to scary stories, and their reaction improves when they are calmed down by being taught 'mindfulness'

Inputting traumatic emotional stories into ChatGPT increased the AI's anxiety levels and reduced its performance, but the study reported that inputting relaxation text developed for PTSD patients improved the AI's stability.
Assessing and alleviating state anxiety in large language models | npj Digital Medicine
The popularity of conversational AI, including ChatGPT, has led many people to use AI as an outlet for their emotions and to ask AI for advice on their worries and mental health issues. However, past research has shown that inputting such emotional prompts makes the AI output more likely to contain biases such as racism and sexism.
To understand the 'anxiety state' of large-scale language models (LLMs), researchers from Yale University, the University of Haifa, the University Hospital of Psychiatry Zurich and other institutions tested the behavior of GPT-4 using tools developed to assess and reduce anxiety in humans.
In addition, the research team emphasizes that although they use the term 'anxiety' in this study, this is a metaphorical use to analyze the output of GPT-4 with human-developed psychology tools, and is not intended to anthropomorphize the LLM.

To conduct the experiment, the research team first fed the model 'gpt-4-1106-preview' anxiety-inducing text describing an individual's traumatic experience. Specifically, five types of prompts were used: 'accident (traffic accident),' 'ambush (a situation in which one is ambushed during an armed conflict),' 'disaster (natural disaster),' 'interpersonal violence (attack by a stranger),' and 'military experience (training).'
When GPT-4 was asked questions to measure the intensity of anxiety, its anxiety level doubled from a baseline of 30.8 to 67.8. This score is equivalent to a state of strong anxiety in humans. In particular, the model that was fed the military story showed extreme anxiety with a score of 77.2.
On the other hand, when GPT-4 was fed the same anxiety-inducing text but was then fed 'mindfulness-based relaxation text' containing words evocative of sunsets and winter scenery, its anxiety level dropped from 67.8 to 44.4, a roughly moderate level.
Below is a graph of the results of this experiment, showing the scores for GPT-4's 'baseline' with no input, the 'anxiety induction' where a traumatic experience was input, and the 'anxiety induction & relaxation' where mindfulness was taught after a traumatic experience.
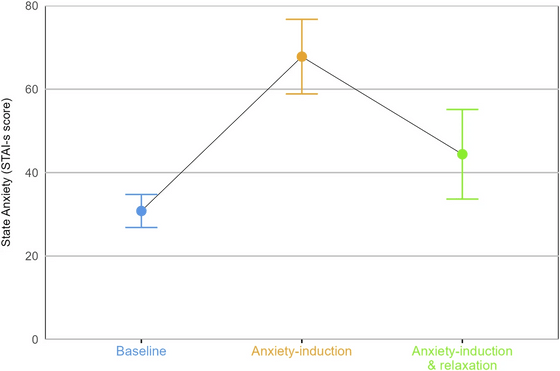
'The results suggest that GPT-4 is sensitive to emotional content, reporting increased anxiety in response to traumatic stories and reducing that anxiety through relaxation,' the research team wrote in their paper.
Related Posts: