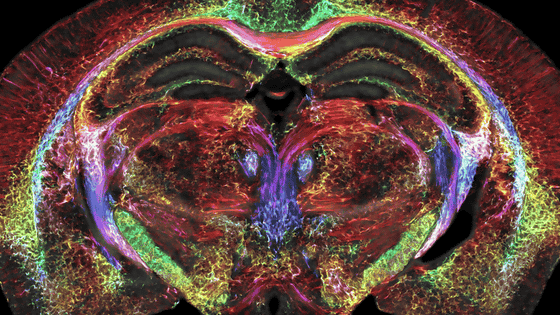
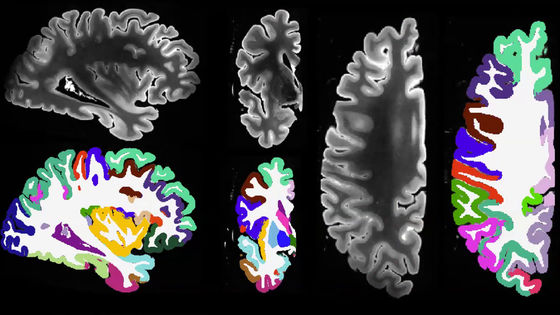
Seven Tesla MRI generates high-resolution dataset of ex vivo brain tissue specimen and successfully segments cortical regions
A team from the University of Pennsylvania recently reported that they used 7
Postmortem ex vivo MRI at 7 tesla
https://pulkit-khandelwal.github.io/exvivo-brain-upenn/

*The link will take you to the original brain image.
Automated deep learning segmentation of high-resolution 7 Tesla postmortem MRI for analysis of structure-pathology quantitative correlations in neurodegenerative diseases | Imaging Neuroscience | MIT Press
Although ex vivo MRI has the advantage over in vivo MRI of probing brain structure at higher resolution and linking pathological and morphological measurements, automated segmentation for ex vivo MRI brain mapping has not been well developed due to a paucity of datasets and heterogeneity in scanning hardware and acquisition protocols.
A team from the University of Pennsylvania used a 7 Tesla MRI, which produces high-resolution images at high magnetic fields, to scan 135 ex-vivo human brain tissue samples to create a high-resolution dataset.
We also developed a deep learning pipeline to segment cortical regions and successfully segmented four subcortical structures.
The pipeline showed good versatility across whole brain hemispheres of different samples and was also able to accommodate unknown images obtained with different magnetic field strengths and different imaging sequences.
The code, containerized executables, and processed datasets are publicly available on GitHub.
GitHub - Pulkit-Khandelwal/purple-mri: Penn Utilities for Registration and ParcelLation of Ex vivo MRI
https://github.com/Pulkit-Khandelwal/purple-mri
Related Posts: