The world's first active cooling chip 'XMC-2400' that prevents smartphones from overheating has been released, and is scheduled to start shipping in 2026

In recent years, there has been a growing trend to integrate large-scale language models and personal AI into smartphones, such as Google's
xMEMS | Active Micro Cooling | XMC-2400
https://xmems.com/products/microcooling/
1st-of-its-kind 'cooling chip' could prevent AI smartphones from overheating — with 1st devices launching in 2026 | Live Science
https://www.livescience.com/technology/electronics/1st-of-its-kind-cooling-chip-could-prevent-ai-smartphones-from-overheating-with-1st-devices-launching-in-2026
Unlike devices such as laptops, many smartphones do not use active cooling systems such as fans, but rely on a passive cooling system that dissipates heat from a heat sink. In fact, Samsung's Galaxy S24 uses a technology called a ' vapor chamber ,' and the iPhone 15 Pro uses a large heat spreader to address heat issues.
In addition, by equipping smartphones in recent years with a large number of processor cores and on-board memory, it is possible to integrate AI, play heavy 3D games, edit videos, use 5G networks, etc. However, while smartphones are becoming more powerful, they are also more prone to 'throttling,' which limits functionality when they reach a certain temperature. Therefore, scientists have been developing 'active cooling system' technology that can cool smartphones more powerfully rather than 'passively.'
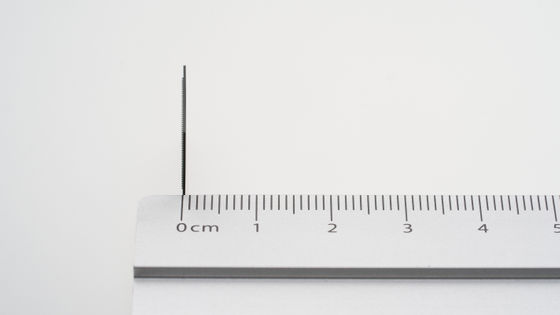
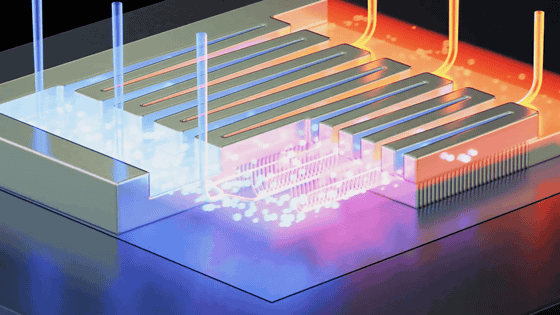
The 'XMC-2400' chip developed by xMEMS is only 1mm thick and can be installed in devices such as smartphones and tablets. According to xMEMS, the XMC-2400 has vents on the side or top, and can replace 39 cubic centimeters of air per second using minimal power. In addition, unlike conventional fans, it uses a 'piezoelectric MEMS transducer' that utilizes the ' piezoelectric effect ,' in which a material changes volume when power is applied. The piezoelectric MEMS transducer vibrates at ultrasonic frequencies to generate air pulses and create airflow.
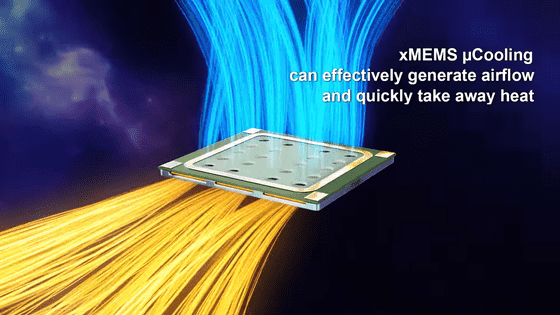
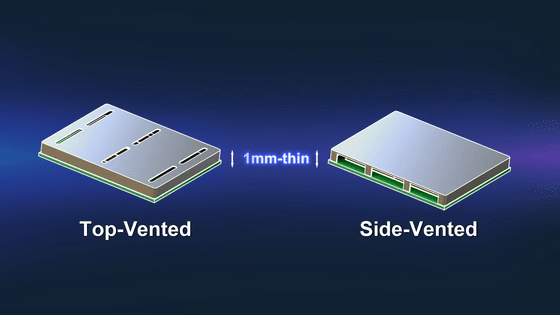
There are two types of XMC-2400: 'XMC-2400-S 'Side Venting'' with vents on the side and 'XMC-2400 'Top Venting'' with vents on the top. 'XMC-2400-S 'Side Venting'' takes in heat released by the passive cooling system and releases it to the outside. On the other hand, 'XMC-2400 'Top Venting'' sucks in air from slits in the main body and blows cold air directly onto heat-generating components such as processors and memory to cool them.
'The inclusion of the XMC-2400 will reduce the probability of throttling in core components, lowering the surface temperature of the smartphone and improving app performance,' xMEMS said.

'Our revolutionary XMC-2400 comes at a critical time in mobile computing,' said Joseph Jiang, CEO of xMEMS. 'With the increasing integration of processor-intensive AI applications in modern devices, thermal management has been a major challenge for manufacturers and consumers. Because modern devices are so small and thin, active cooling solutions for smartphones and tablets had not been developed until the release of the XMC-2400.'
According to xMEMS, sample shipments of the XMC-2400 to smartphone manufacturers will begin in early 2025, with the chip being installed in commercially available smartphones in 2026.
Related Posts:
in Video, Hardware, Smartphone, Posted by log1r_ut