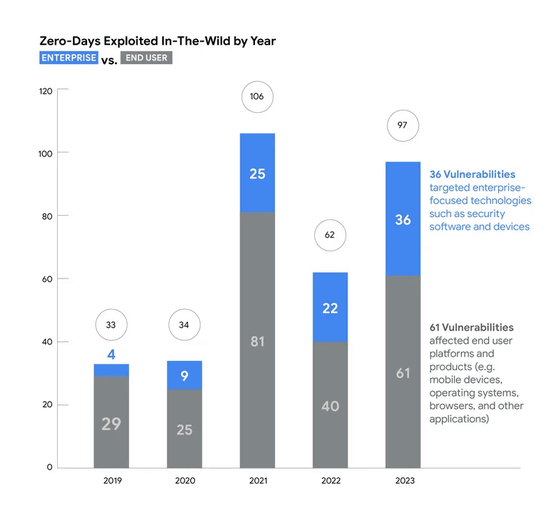
Google reports that 97 cyber attacks using zero-day vulnerabilities were observed in 2023, an increase of 50% compared to the previous year, and attacks for companies are on the rise

Google's threat analysis team, TAG, and cybersecurity firm
A review of zero-day in-the-wild exploits in 2023
https://blog.google/technology/safety-security/a-review-of-zero-day-in-the-wild-exploits-in-2023/
Trends on Zero-Days Exploited In-the-Wild in 2023 | Google Cloud Blog
https://cloud.google.com/blog/topics/threat-intelligence/2023-zero-day-trends/
Zero-days exploited in the wild 50% of 2023, fueled by spyware vendors
https://therecord.media/zero-day-exploits-jumped-in-2023-spyware
Google: Spyware vendors behind 50% of zero-days exploited in 2023
https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/google-spyware-vendors-behind-50-percent-of-zero-days-exploited-in-2023/
Attackers increasingly exploit enterprise tech zero-days • The Register
https://www.theregister.com/2024/03/27/surge_in_enterprise_zero_days/
The following graph summarizes the results of Google's investigation into zero-day vulnerabilities and exploits that were actually exploited. The number of zero-day vulnerabilities detected in 2023 was 97, of which 36 were enterprise zero-day vulnerabilities (blue) and 61 were end-user zero-day vulnerabilities (gray). The total number of zero-day vulnerabilities detected in 2023 is more than 50% higher than in 2022, but 9 fewer than the 106 detected in 2021.
Google wrote, 'Analyzing this data shows clear progress in the fight against zero-day vulnerabilities. End-user platform vendors such as Apple, Google, and Microsoft have made notable investments that have had a clear impact on the types and number of zero-day vulnerabilities available to attackers. Vulnerabilities that were common in past years are now virtually non-existent,' praising the efforts of end-user platform vendors.
Focusing solely on zero-day vulnerabilities targeting enterprises shows that the range of targeted vendors and products is expanding, and that the number of enterprise-specific technologies being exploited is increasing. 'Over the years, we've learned that the faster we find and patch attacker bugs, the shorter the lifespan of their exploits becomes, and the higher the cost to attackers of maintaining their capabilities. As an industry, we must apply these lessons and learn how to patch the broader ecosystem of vendors under attack,' Google wrote.
Google listed the following six key findings in its report on zero-day vulnerabilities:
Vendor investments are driving change
Big changes driven by vendor investments include Google's
Attackers will shift their focus to third-party components and libraries in 2023
The leading attack surface in 2023 was zero-day vulnerabilities in third-party components and libraries, which, when exploited, can impact multiple products.
Attacks targeting businesses will continue to increase and become more diverse by 2023
Attackers are increasingly exploiting enterprise-specific technologies in 2023, with the total number of vulnerabilities increasing by 64% year-over-year. Enterprise vendors have been clear targets of cyberattacks since at least 2019.
Commercial monitoring vendors (CSV) are leading the way in browser and mobile device exploitation
CSV was behind 75% of known zero-day exploits (13 of 17 vulnerabilities) targeting Google products and Android ecosystem devices in 2023. Of the 37 zero-day vulnerabilities in browsers and mobile devices exploited in 2023, Google noted that more than 60% were attributable to CSV, which sells spyware capabilities to government customers.
-The People's Republic of China (PRC) continues to lead the way in government-sponsored exploitation
The number of confirmed exploits of zero-day vulnerabilities by Chinese cyber espionage groups has increased from seven in 2022 to 12 in 2023. This is more than any other nation state, and Google noted that this 'continues a trend we have observed for several years.'
Exploitation involving financially motivated actors has decreased proportionately
Ten zero-day vulnerabilities exploited in 2023 were by financially motivated attackers, but the overall percentage was lower than observed in 2022. The threat group FIN11 exploited three separate zero-day vulnerabilities, and at least four other ransomware groups were also observed exploiting four vulnerabilities separately.

In recent years, cyber attacks leveraging zero-day vulnerabilities have been on the rise, and advances in exploit technology have made it easier for more attackers around the world to take advantage of these nasty threats. Google has listed the following six security recommendations for individuals and organizations:
1: One of the biggest ways the industry can help resolve the crisis is to embrace transparency and disclosure, and release lessons learned and patches as quickly as possible.
2: Organizations need to develop defensive strategies that prioritize the threats most likely to harm themselves or others.
3: Build a strong security foundation. While Google's report focuses on zero-day vulnerabilities, it is also important to make it impossible for attackers to succeed with simpler cyber attacks. By building a strong security foundation, Google claims that 'forcing attackers to take advantage of zero-day vulnerabilities leads to stronger security.'
4: Software and product vendors must be prepared at the design stage for how to respond when brute-force zero-day vulnerabilities are discovered targeting their products. The recommendations for patching and responding that have been made so far remain valid responses.
5: For high-risk users, iPhone users are recommended to enable Lockdown mode. For Pixel 8 users, Arm Memory Tagging Extension (MTE) is recommended to be enabled.
6: For high-risk Chrome users, it is recommended to enable HTTPS-first mode and disable the v8 optimizer.
Research into zero-day vulnerabilities is critical to protecting users and the online ecosystem, which is why Google remains committed to ongoing efforts in this area, with TAG and Mandiant discovering 29 of the 97 zero-day vulnerabilities discovered in 2023.
Related Posts: