Google announces that it sent 40,000 hacking alerts in 2019
Google has a team called the Threat Analysis Group (TAG) that prevents government-sponsored hacking attacks from targeting Google and its users. The TAG has analyzed the trends of hacking attacks in 2019, and has announced the trends of attacks against zero-day vulnerabilities.
Identifying vulnerabilities and protecting you from phishing

Google alerts users when it detects that a user's account is targeted for malware or government-driven phishing attacks. Google has announced that this warning was 40,000 in 2019. The number of 40,000 is down 25% in 2018, which means that Google's protection was working. Attackers are believed to be slowing down and attacking more cautiously.
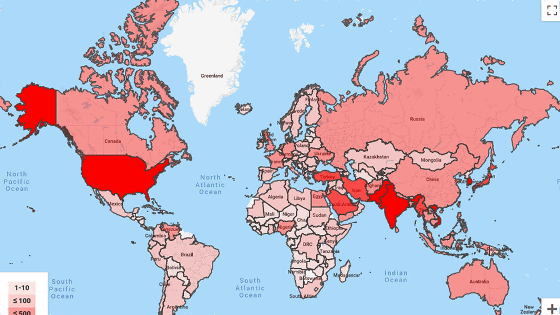
From the map published by Google, you can see that the countries where the citizens collectively received more than 1000 warnings are the United States, India, Pakistan, Japan, Korea, etc. In addition, Microsoft reports that more than 10,000 customers are under hacking attack with the support of states such as Iran, North Korea and Russia in 2019.
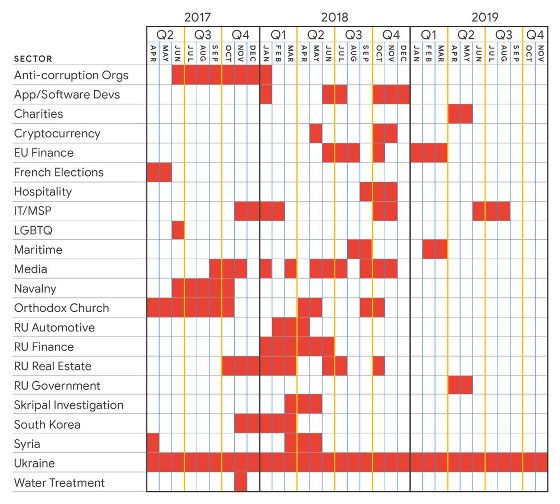
Among the hackers that work with government support, the most prominent is the 'Sandworm,' which is supported by the Russian government. Sandworm is believed to have been involved in hacking at the 2018 Winter Olympics and features malware attacks disguised as fake apps.

Google publishes a graph of what countries and industries Sandworm has been targeting from 2017 to 2019. Ukraine in particular has been under continuous attack for three years.
TAG also found a zero-day vulnerability in 2019 that affects Android, iOS, Windows, Chrome, and Internet Explorer.
According to Google, one attack group exploits five unpatched vulnerabilities, and 'it is extremely rare for the same attacker to make multiple zero-day attacks in a relatively short timeframe.' thing. The attack hacks legitimate websites and links to malicious websites and phishing emails. Many of the targets were individuals living in North Korea or engaged in matters related to North Korea.
Zero-day attacks are considered more dangerous because they target vulnerabilities that have not yet been detected and fixed, and have a high success rate. When Google detects an attack using the zero-day vulnerability, it sends a notification to the vendor, gives a 7-day grace period for the patch creation period, and if no action is taken during the grace period, Google itself will make its own recommendation Announced.
In addition, Google also mentions that in the phishing attacks that occurred in the past few years, accounts using an account protection program using multi-factor authentication etc. have never been taken.
Related Posts:
in Security, Posted by darkhorse_log






