A programmer explains the once widely used 'floppy disk'

JP's Website · 2023-08-28 · Everything I know about floppy disks
https://thejpster.org.uk/blog/blog-2023-08-28/
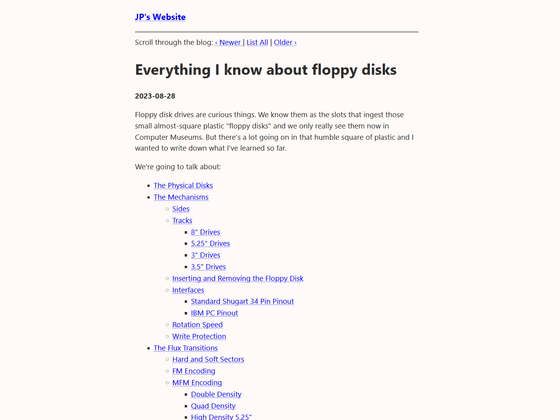
There are three main sizes of FD: 8 inches, 5.25 inches, and 3.5 inches. In addition to this, there were also '3 inches', '2.5 inches', '2 inches', etc.

The 8-inch FD was the first FD to appear and was developed in the early 1970s. A thin plastic disk was covered by a thin plastic case, and the read/write head of the drive accessed the disk through a hole in the case. As the name suggests, the size is 8 inches (about 200 mm) square, and the capacity was 80 KB when it first appeared, but later products have 1.6 MB.
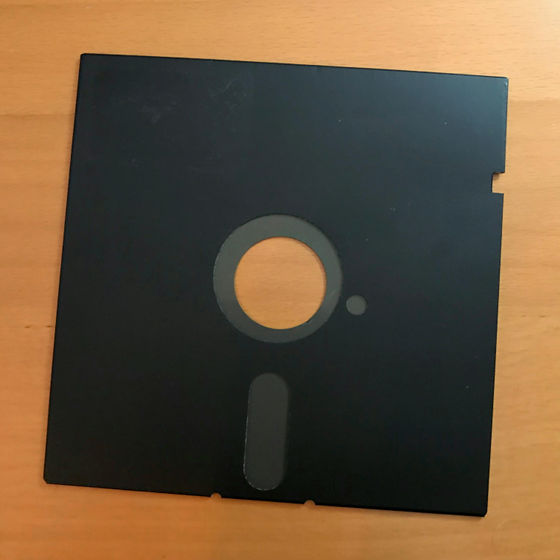

The 5.25-inch FD is a structure similar to an 8-inch FD reduced to 5.25 inches (approximately 130 mm) square, and first appeared in 1976. The miniaturization enabled the drive to be built into computers, replacing the 8-inch FD. The capacity was in the 100KB range when it first appeared, but later products have a capacity of 1.2MB.

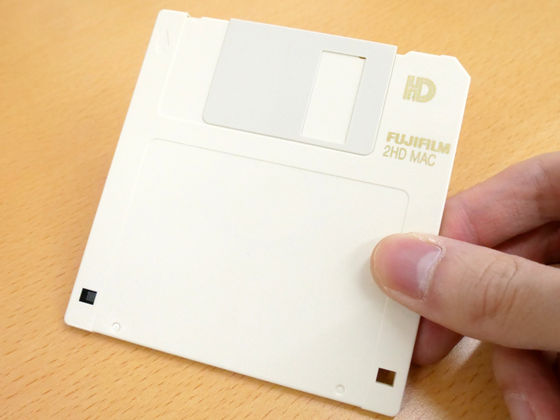
The most popular type of FD was the 3.5-inch one that appeared in 1980, and its outer case was made of a hard material to improve durability. The standard capacity was 1.44MB, which was introduced in 1985, and there was also a 2.8MB version, although it was not very popular. A movable shutter was provided in the part accessed by the drive, and it was possible to move it by hand to check the internal disk.

There are two types of FDs: 'single-sided disks,' which have one read/write head that can only access one side of the disk, and 'double-sided disks,' which have two read/write heads, one on each side of the disk. was doing. By inserting the disc upside down into the drive, the information was recorded in the opposite direction, but it was possible to read the back side even with a single-sided disc. In addition, some single-sided discs had cutouts that made it impossible to read the back side.
Most FD drives operate the magnetic disk inside at 300 revolutions per minute. On the other hand, 8-inch disks, some 5.25-inch disks, and 3.5-inch drives were said to be running at 360 revolutions per minute. Also, the early Apple Macintosh was equipped with a mechanism that changed the rotation speed of the magnetic disk inside depending on the track being accessed.
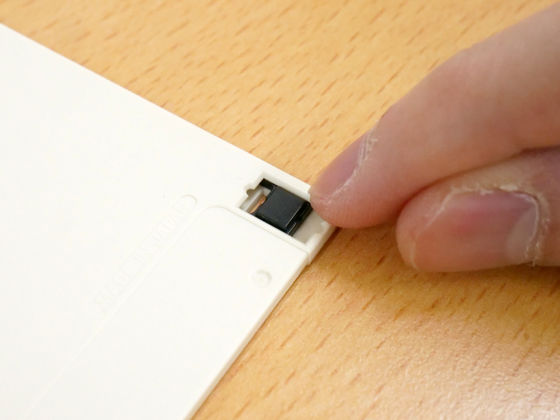
In addition, these FDs are equipped with a mechanism to prevent writing; 8-inch FDs are prohibited from writing if there is a hole in a specified position, and writing is possible if the hole is covered, while 5.25-inch FDs are , writing was possible if there was a hole in the specified position, and writing was prohibited if the hole was blocked. The 3.5-inch FD is equipped with a plastic switch, and by moving this switch it was possible to switch between prohibition and permission of writing.

Basically, FDs operate based on electrical signals generated by the magnetic field that changes as a magnetic disk inside rotates. As technology progressed, the amount of information about changes in the magnetic field that could be stored per inch, called 'bit density,' gradually increased, from an early 8-inch disk that could store about 1594 bits per inch. Later 3.5-inch FDs can store approximately 35,000 bits per inch.
In addition, 8-inch FDs and 5.25-inch FDs had holes called 'index holes' that marked the start of each sector and specified the exact timing for reading and writing data. However, as technology advances, reliable data processing is now possible without an index hole.
Early FDs used a technique called '

In addition, Apple II and Commodore FD drives ' Comodore 2040 ' and ' Comodore 1541 ' apparently used a method called ' group encoding recording ' for encoding.
◆Forum now open
A forum related to this article has been set up on the GIGAZINE official Discord server . Anyone can write freely, so please feel free to comment! If you do not have a Discord account, please create one by referring to the article explaining how to create an account!
• Discord | “When was the last time you used a floppy disk?” ' | GIGAZINE
https://discord.com/channels/1037961069903216680/1217766127564754996
Related Posts:
in Hardware, Posted by log1r_ut