A movie "How do hard drive work?" That shows how the hard disk physically records data

A hard disk drive (HDD) that can store an enormous amount of data on a compact fuselage has penetrated the lives of modern people, such as being built in a PC or being used as external storage. Such a hard disk will know how to read and write data "Movie"How do hard drives work?"Published by TED Ed, who has produced many educational movies.
How do hard drive work? - Kanawat Senanan - YouTube
Please imagine an airplane that is 1 mm high from the ground and that makes one round of the earth in 25 seconds.

What shrinking this earth into the palm size is "the world of HDD".

How do you store massive amounts of data on a small aircraft?

Inside the HDD, many disks (platter) rotating at high speed overlap.

At the surface of each disk, a magnetic head for reading and writing data is running.

The disk is covered with a thin film of a minute magnetic metal, and grains of magnetic metal gather to form a block (magnetic domain).
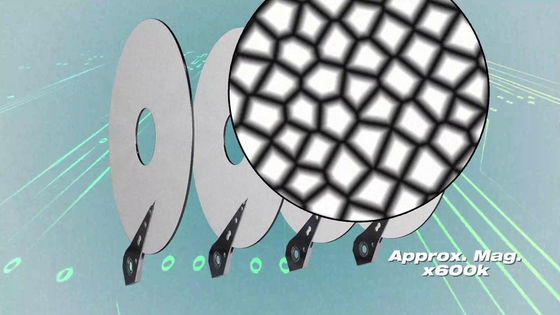
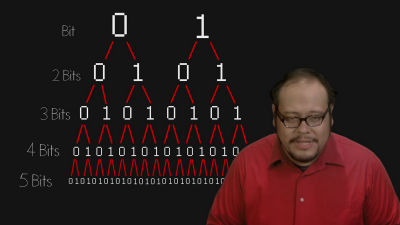
Each block becomes "1 bit" which is the basic unit of computer information volume.

For each block the direction of magnetism is determined ......
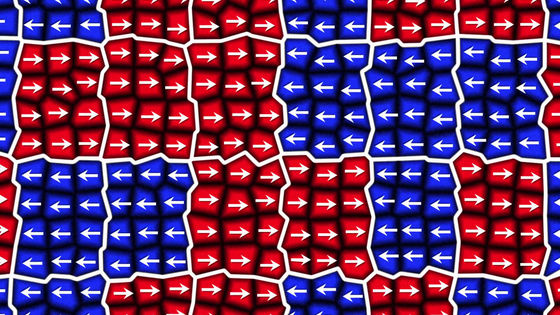
One indicates "0", the other indicates "1".
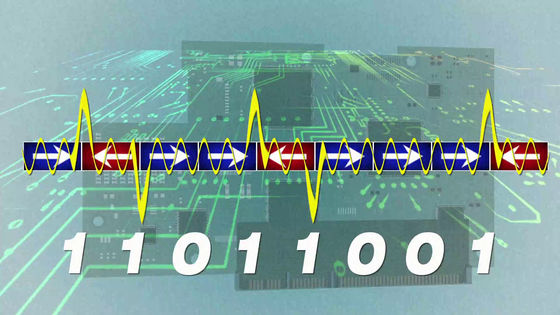
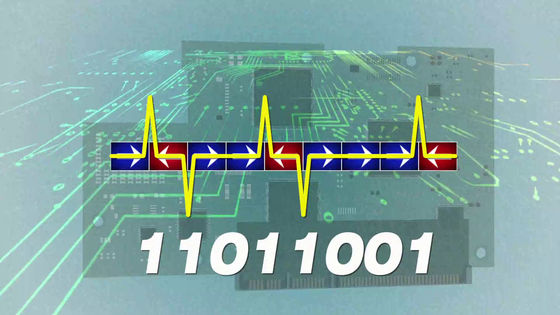
When writing data to the disk, the bit string is converted to current.
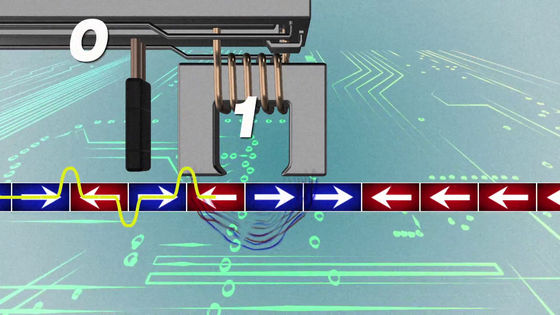
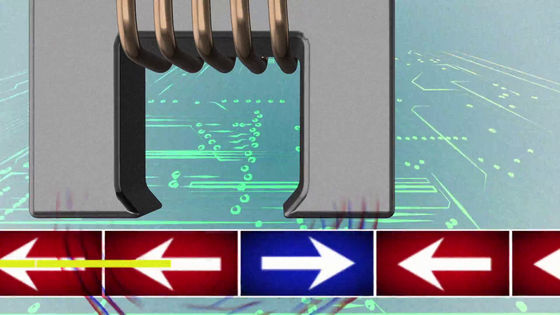
The electromagnet attached to the tip of the magnetic head creates a magnetic field that is strong enough to change the magnetic direction of the block on the surface of the disk and magnetizes the disk to write the data.
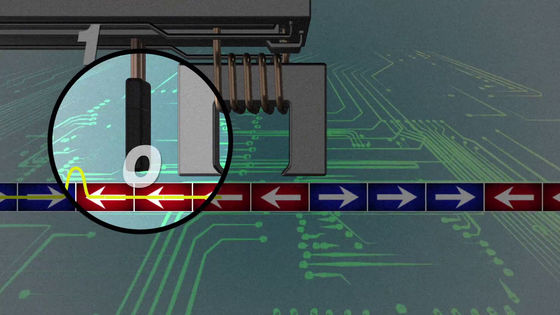
The data written to the disk can be read out by converting it to the bit string again through the magnetic reader. This mechanism is very similar to that of a record player playing music by placing a needle in the groove of the record.
Then, how do we represent huge volumes of data with only two types of "0" and "1"?

The answer is "to arrange a number of 0s and 1s". The smallest unit representing information on a computer is 1 byte (8 bits), and 8 bits indicating 0 or 1 are lined up. For example, 256 kinds of data can be represented with 8 digit combination such as "01000001" for alphabet "a" for 01100001, "01000010" for lower case "a".

For photographs, on average, one megabyte (8 million bits) of data is required per piece.

In order to record as much information as possible on one disk,Recording densityHas been developed to increase the amount of data per 1 inch square. The recording density of hard disks in recent years is about 600 gigabits per square inch.

Compared to the world's first HDD made in IBM made in 1957, it boasts approximately 300 million times the recording density.

Due to the miniaturization of magnetic heads and readers, HDD size itself has gradually become smaller.
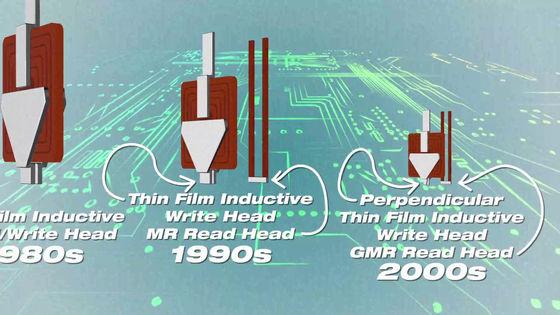
With the evolution of algorithms for numerical calculation to reduce noise of radio waves, it became possible to write more data in the same area by bringing the distances between bits closer.
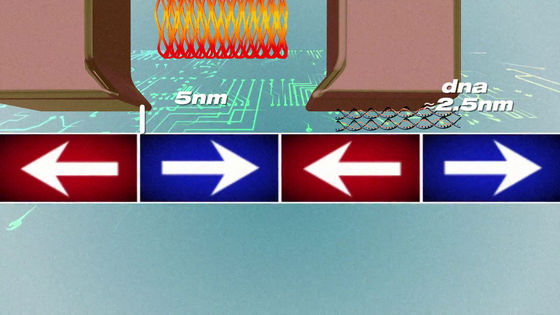
In addition, a heater for controlling the thermal expansion of the electromagnet is attached to the magnetic head, and the clearance between the disk and the head has been reduced to 5 nm or less for two human DNAs.
Thanks to such technological progress, over the past few decades, the recording densityMoore's lawWe have doubled every two years according to the record density per 1 inch square exceeded 100 gigabits, the hard diskSuperparamagnetismWe faced a problem called.
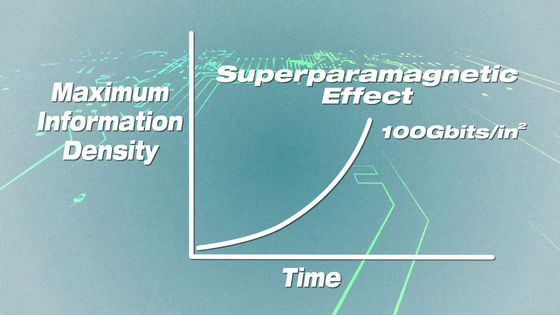
Superparamagnetism is the problem that the direction of magnetization of the disk surface is unintentionally reversed due to temperature change and data is lost.
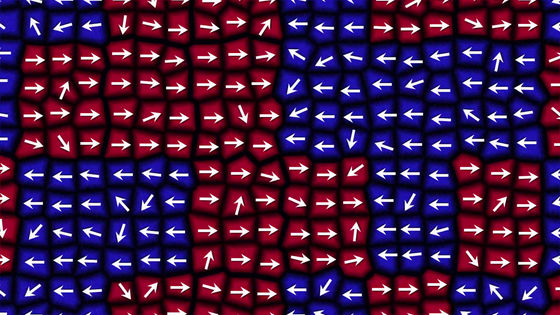
This problem was solved by making the direction of recording magnetism perpendicular, and succeeded in further increasing the recording density to 1 terabit per square inch. Finally in 2014 the hard disk capacityReached 10 TBdoing.
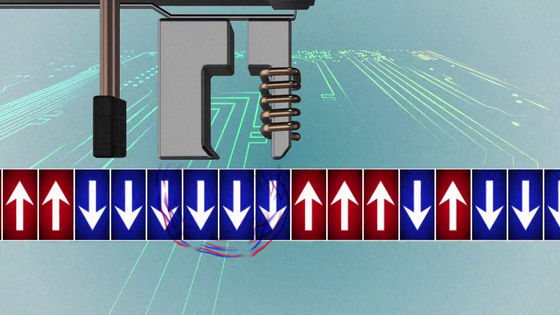
In addition, a technology called "heat assisted magnetic recording (HAMR)" that writes data by giving pinpoint heat to the disk surface using a laser is under development for practical use.

Besides, by machining the uneven pattern on the surface of the magnetic media, it is possible to reduce the magnetic field which leaks to the adjacent bit by making each one bit independentBit Pattern Media(Bit Pattern Media) has also been developed and it is possible to create an ultra-high capacity storage device of more than 20 terabits per square inch if realized.

Related Posts: