Scientists warn that ``summer without sea ice'' may occur in the Arctic by 2035

In recent years, global warming has progressed, and
Projections of an ice-free Arctic Ocean | Nature Reviews Earth & Environment
https://www.nature.com/articles/s43017-023-00515-9

Ice-free summers in Arctic possible within next decade, scientists say | Arctic | The Guardian
https://www.theguardian.com/world/2024/mar/05/ice-free-summers-in-arctic-possible-within-next-decade-scientists-say
Sea ice in the Arctic has been decreasing significantly since satellite observations began in 1978, and it has been found that the pace of decrease in sea ice has particularly rapidly increased in recent years. The decrease in sea ice not only has a negative impact on marine animals such as polar bears, seals, and walruses, but also has an impact on the lives of people along the coast by increasing waves that would normally be suppressed by sea ice. .
If global warming continues at this rate, it is thought that eventually there will be almost no sea ice in the Arctic during the summer. Therefore, the research team defined an ``ice-free Arctic'' as a state in which the area of sea ice in the Arctic Circle is less than 1 million km2, and investigated when an ice-free Arctic would occur.
Below is a diagram showing the sea ice area in September, when there is the least amount of sea ice in the Arctic during the year. The letter 'a' on the far left represents the Arctic Circle in the 1980s, when it was covered with sea ice even in summer, and the typical sea ice area during this period was 5.5 million km2 . However, between 2015 and 2023, the sea ice area decreased to about 3.3 million km2 . This is the 'b' in the middle. Furthermore, looking at 'c' on the right, where the sea ice area has fallen further to less than 1 million km2 , it can be seen that sea ice has disappeared except for the coastal areas of Greenland and the Arctic Islands of Canada. This is what the research team predicts an ``ice-free Arctic.''

In addition, the figure below is a graph that shows the annual trends in sea ice area from 1980 to 1999 in red, and the blue range in the 10 years during which an ``ice-free Arctic'' will occur. In the future, sea ice extent is expected to decrease in all months of the year, but the research team predicts that the decline will be greatest in September.
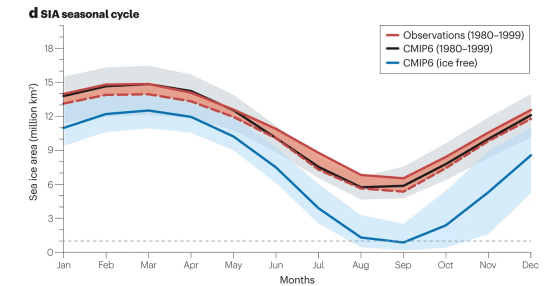
According to the research team, the first ice-free Arctic could occur as early as the 2020s, or by 2050 at the latest. It is also predicted that the Arctic will remain ice-free throughout September from 2035 to 2067.
The duration of an ice-free Arctic depends on how much humans can reduce their use of fossil fuels. In a scenario with high greenhouse gas emissions, the Arctic could remain ice-free from May to January of the following year, and in a scenario with low greenhouse gas emissions, it could be ice-free from August to October.
However, unlike the Greenland ice sheet, which took thousands of years to form, sea ice is formed by freezing due to annual temperature changes. Therefore, even if an ice-free Arctic occurs, it is possible to increase the extent of summer sea ice again by reversing climate change.
Alexandra Jahn, associate professor of atmospheric and ocean sciences at the University of Colorado Boulder and lead author of the paper, said, ``In this case, summer in the Arctic changes from a ``white Arctic'' to a ``blue Arctic,'' a completely different environment. Therefore, even if an ice-free Arctic cannot be avoided, we need to reduce emissions as much as possible to avoid prolonging that state.'

Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1h_ik







