Vectara releases open source evaluation model that can objectively verify the risk of large-scale language models causing 'hallucinations'

The phenomenon in which AI outputs careless content that looks very similar to the input content is called 'hallucination.' AI company Vectara has announced the open source Hallucination Evaluation Model (HEM).
Measuring Hallucinations in RAG Systems - Vectara
Sometimes a large-scale language model answers a question accurately, and sometimes it outputs sloppy information contained in the training data. Large-scale language models only output words statistically, and do not understand the meaning of what they are outputting, so they may return answers that make it seem like you have no idea what they are saying. Generating large-scale language models, such as ``creating answers to the user's questions by making up completely non-existent content'' and ``outputting specific biases based on training data.'' For companies considering the introduction of AI, errors caused by 'hallucinations' are one of the risks of greatest concern.
Although many companies have put off implementing generative AI due to the risk of hallucinations, the current situation is that the risk of hallucinations has not been quantified, so although it is a concern, it has not been possible to specifically consider the risks.

Vectara argues that the real power of large-scale language models in the enterprise comes from search-enhanced generation (RAG). RAG allows AI to interact with external knowledge sources to supplement the internal representation of knowledge held by large-scale language models, and is said to have the effect of reducing hallucinations.
The HEM developed by Vectara is capable of evaluating the accuracy and hallucination rate of large-scale language models, just as banks' credit ratings function to account for financial risk. Vectara publishes the results of evaluating the hallucination rate of large-scale language models such as OpenAI's GPT and Meta's Llama on GitHub.
GitHub - vectara/hallucination-leaderboard: Leaderboard Comparing LLM Performance at Producing Hallucinations when Summarizing Short Documents
https://github.com/vectara/hallucination-leaderboard
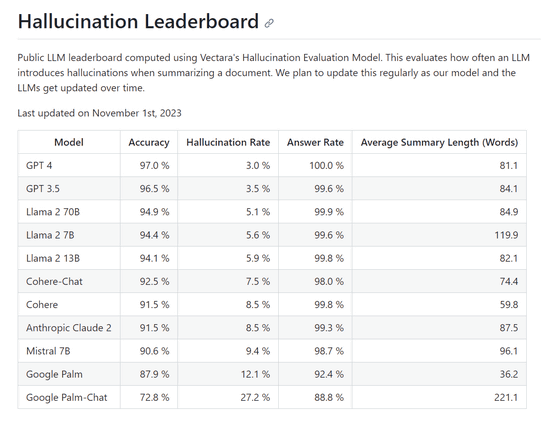
In Vectara's evaluation, they input 1,000 short documents into a large-scale language model via a public API and instructed it to summarize each document using only the content contained within the document. Then, for 831 out of 1000 cases that all large-scale language models successfully summarized, we calculated the ``Accuracy'' of the summary and the ``Hallucination Rate'' where the summary became inaccurate due to hallucinations. has been calculated. In addition, the proportion of summaries out of 1000 documents is summarized as ``Answer Rate'', and the average number of words in summarized sentences is summarized as ``Average Summary Length''.
At the time of article creation, OpenAI's GPT-4 was the least likely to cause hallucinations, with a hallucination rate of 3.0%. On the other hand, Google's Palm-Chat had the highest hallucination rate at 27.2%.
HEM released by Vectara is Hugging Face, an AI-related library platform, and is open source.
vectara/hallucination_evaluation_model · Hugging Face
https://huggingface.co/vectara/hallucination_evaluation_model
'For organizations to effectively deploy generative AI, including chatbots, they need a clear understanding of the risks and potential downsides,' said Simon Hughes, engineer at Vectara. Anyone can measure the risk of hallucinations produced by scale language models. As part of Vectara's commitment to industry transparency, we have published this HEM as open source so that anyone can make this assessment. , we provide leaderboards that are accessible to everyone.”
Related Posts:
in Software, Posted by log1i_yk