How will AI change the way we work? Is it possible that AI will steal your job?

ChatGPT, which can generate natural conversations and advanced sentences, Stable Diffusion and Midjourney, which can generate high-quality images simply by inputting words, have appeared, and 80% of all occupations are affected by generative AI.
AI and the automation of work—Benedict Evans
https://www.ben-evans.com/benedictevans/2023/7/2/working-with-ai
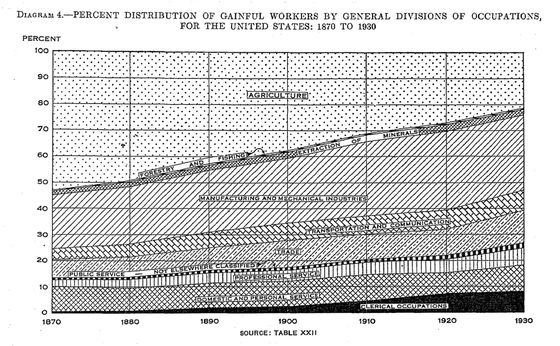
According to Evans, in the wave of automation in labor work for 200 years, all kinds of jobs disappeared, but new kinds of jobs were created instead. The following figure shown by Mr. Evans is a graph showing changes in the `` distribution rate of paid workers by general occupational sector in the United States '' released by the US Census in 1930, and the number of distributions of `` AGRICULTURE (agriculture) '' is It has greatly decreased from about 50% in 1870 to about 20% in 1930, and the proportion of 'MANUFACTURING AND MECHANICAL INDUSTRIES' is increasing. In this way, instead of reducing old jobs, new jobs will increase, and there will be more than a few troubles along the way. ',' said Evans.
It is possible to predict what kind of jobs will disappear due to automation, but it is difficult to predict what new jobs will become, and there are cases where new jobs have not yet been created. It is natural to worry that There is a term in economics called the ' labor mass fallacy ', and it is sometimes viewed that there is only a certain amount of work in the world and that workers are competing for it. , which is economically erroneous. If the amount of work to be done is fixed, if machines and AI take some of it away, there will be no jobs for humans, but in reality it will lead to new prosperity and new employment. , it is considered that the amount of work will not be violated.
However, even so, there are many opinions that AI has actually taken away jobs and that there are many areas that will be affected by automation. For that reason, Evans says, 'I think what's really happening in automation over the past 200 years is that we've scaled up human capabilities.' Since humans became able to automate their legs and move at high speeds, they have automated their arms to enable them to perform powerful tasks, automated their fingers to enable them to perform delicate tasks, and have automated their brains with AI. In economics, we think that we can reduce the consumption of resources by improving the consumption efficiency of resources through the advancement of technology. There is a notion of the ' Jevons Paradox ' that usage increases as a result. This is the same as thinking of resources as human labor, and as a result of making work more efficient by automating even limbs and brains, workers may be diverted in various ways and become more busy.
“Before spreadsheets were invented, investment bankers worked very long hours,” Evans previously said. Deep learning means you only have to work one day a week,' he tweeted, giving an example of how technology makes it easier to do things. On the other hand, he also says that technology can mean doing the same thing with fewer people, or it can mean doing more with the same people.
Younger people may not believe this but before spreadsheets investment bankers worked really long hours. It's only thanks to Excel that Goldman Sachs associates can get everything done and leave the office at 3pm on Fridays. Now LLMs mean they'll only have to work one day a week!
—Benedict Evans (@benedictevans) May 5, 2023
Even if the number of people required for one job is reduced and the same person will be able to do a wider range of jobs, ``automation allows people to do 10 times more work'' means that ``people'' are needed to do that job. means to be However, Evans points out that there are two types of objections to this idea. First, the changes caused by AI are the same kinds of changes we have seen with the development of the Internet and PCs, and they may not have the same long-term impact on net employment. Still, some argue that AI is developing so rapidly that the friction it creates will be high and difficult to coordinate. It took about 10 years to ship 100 million PCs, but ChatGPT has achieved '100 million monthly users' in just two months.
It is reported that ChatGPT has achieved ``100 million monthly users'' in just two months and is growing the fastest ever - GIGAZINE

Also, in order to introduce ChatGPT and image generation AI, there is almost no need for special network construction or specific devices, and it can be made to function as a simple website on existing equipment. However, according to Mr. Evans, it should take some time to complete it as a 'product' or 'work tool' that is ready for actual work.
Also, unlike machines that are basically made for a specific purpose, ChatGPT and LLM (Large Scale Language Model) are general-purpose technologies that can answer anything, so they not only take away specific jobs, but also have an impact. There is also the idea that power is far-reaching. However, Evans points out that professional parameters are required to make it work as an actual job, so a training set for that should be needed to invade as a job.
In conclusion, the idea of whether AI can significantly encroach on human work comes down to the field of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). If there is no error rate, no hoax, and there is a system that can really do anything that humans can do, even ``one person'' that ``automation makes it possible for one person to do more'' AI is necessary instead lose. However, Evans says that there is no magical AGI here now, and that the waves of automation that have been experienced in the past 200 years will only occur again.
Related Posts:
in Software, Web Service, Web Application, Posted by log1e_dh