North Korean hacker group Kimski's malware 'Gold Dragon' is a clever trick to attack only the target?

Kimsuky's GoldDragon cluster and its C2 operations | Securelist
https://securelist.com/kimsukys-golddragon-cluster-and-its-c2-operations/107258/
Early in 2022, we detected activity from the #Kimsuky hacking group targeting entities in South Korea. In its latest attack, the #APT actor initiated the infection chain by sending a spear-phishing email containing a macro-embedded Word doc.
— Kaspersky (@kaspersky) August 25, 2022
Know more ???? https://t.co/cS09EoOrET pic.twitter.com/Bz8lo1DgWx
How 'Kimsuky' hackers ensure their malware only reaches valid targets
https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/how-kimsuky-hackers-ensure-their-malware-only-reach-valid-targets/
According to Kaspersky, Kimsky's 'Gold Dragon' launched a new operation against various South Korean companies in early 2022, which employed new techniques to filter invalid download requests. About. This Gold Dragon method is very powerful, and it seems that even after the researcher can successfully connect to the attacker's C2 server , it is not possible to acquire the payload that is the part that behaves maliciously.
The Kimski attack sends phishing emails containing malware-embedded Word documents to North and South Korean politicians, diplomats, university professors, and journalists. The first email sent contains a link that directs the victim to the C2 server, which is the stepping computer for the first stage, and this server determines ``whether the person who accessed the link is a target.'' How it works. If the visitor's email address belongs to the target, it will additionally send the malicious document, and if the visitor is not on the target's list, the link will only deliver the harmless document.
The first-stage C2 server contains information such as the victim's email address, OS (valid only for Windows), whether it is the first access, etc. The victim's IP address is an additional check item on the second-stage C2 server will be forwarded to If this two-step check is passed, the victim gets a payload containing a malicious macro and executes it as an attack. Ultimately, malware can steal local file lists, user keystrokes, stored browser login credentials, and more.
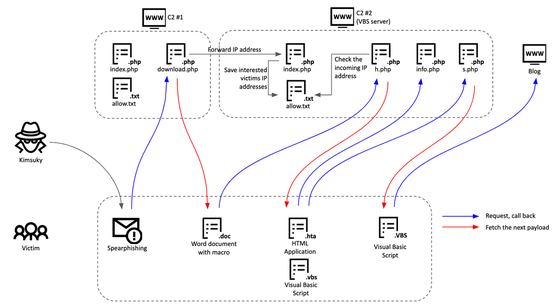
Regarding the details of the Gold Dragon malware, Kaspersky said, ``Interestingly, this C2 script uses the victim's IP address to generate the blog address. , which reduces malware exposure.'
Kaspersky said it was only able to obtain the payload up to the second stage, so it was not known whether it was the final stage of the malware mechanism or whether it included further victim identification methods.
Related Posts:
in Security, Posted by log1e_dh