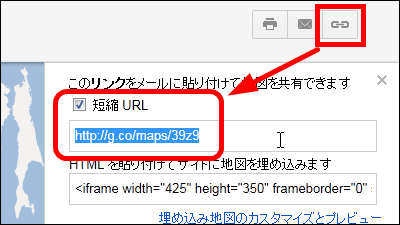
Why you shouldn't use URL shortening services?
Link shorteners: the long and short of why you shouldn't use them - GCS
https://gcs.civilservice.gov.uk/blog/link-shorteners-the-long-and-short-of-why-you-shouldnt-use-them/
Common misconception #1: You need to use a URL shortening service to share links on social media
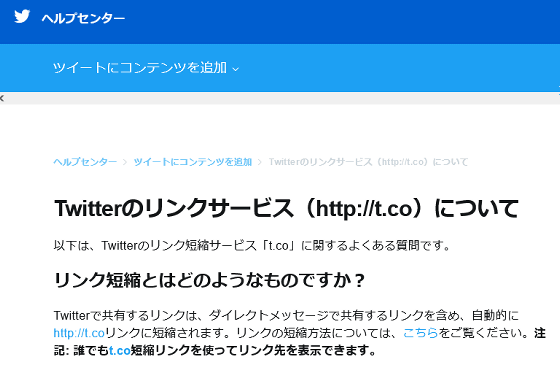
According to GCS, many people believe that when sharing links on social media, they need to use a URL shortening service to shorten the URL in order to avoid character limits.
However, at the time of writing, many social networking sites, such as
◆Common Misconception #2: URL shortening services analyze the number of clicks, etc.
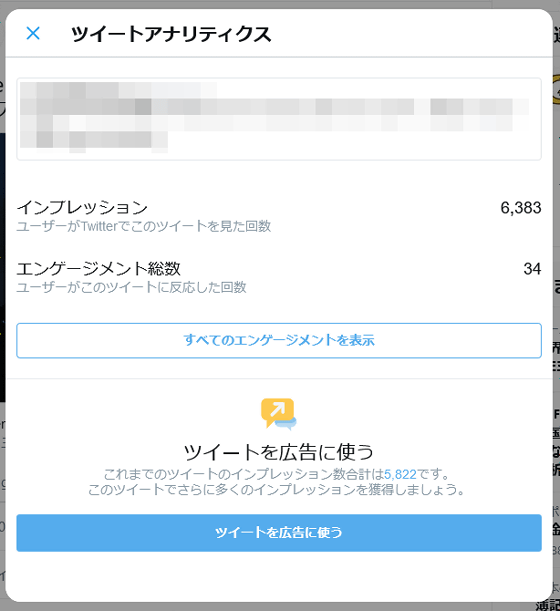
Some URL shortening services advertise to users that they have analytical features, such as the number of link clicks.
However, since social media sites such as Twitter and Instagram provide their own analysis tools, there is no need to use the analysis tools of URL shortening services. GCS also states that 'If you want to enhance your analysis, please use a dedicated analysis tool such as
Risk 1: Privacy cannot be protected
Each URL shortening service has its own privacy policy, and it is impossible for users of the URL shortening service to control the privacy policy. Therefore, if a visitor to a website clicks on a link created using a URL shortening service, the visitor's privacy may be compromised.
Risk 2: Reduced accessibility
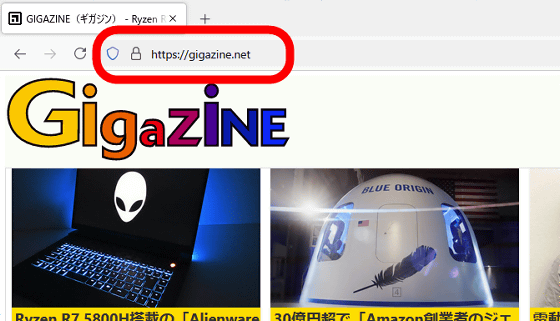
URLs also play a role in indicating the content of the web service being accessed. For example, when a user sees the URL ' https://gigazine.net/ ', they can guess that they can access the GIGAZINE homepage. However, if a URL shortening service is used to generate a URL such as 'https://○.○/○○○/', the user cannot guess the web page being accessed.
Risk #3: Damaging brand trust
As mentioned above, users can guess the web page they are accessing from the URL. Therefore, for example, if the URL contains the domain 'gov.uk', users can trust the destination and click the link, thinking 'I can access a reliable source of information from the UK government.' However, if you use a URL shortening service, users will lose trust in you.
Risk #4: There is a possibility that the risk may spread
GCS pointed out that 'if GCS used external URL shortening services too much, it could lead users to believe that it is safe to click on shortened URLs. ' In light of this, GCS has declared that it will not use external URL shortening services in order to spread the awareness among users that 'URLs containing domains such as 'gov.uk' and 'nhs.uk' are URLs for official government information.'
Related Posts:
in Web Service, Posted by log1o_hf