A 12,000-year-old magnificent mural depicting extinct giant animals is found in the Amazon rainforest

by Marie-Claire Thomas / Wild Blue Media
A huge number of indigenous murals were discovered in the Amazon rainforest in southeastern Colombia about 12,000 years ago. Researchers report that there are a total of tens of thousands of mural paintings that span the three archaeological sites, including the figures of giant animals that have already become extinct.
Colonisation and early peopling of the Colombian Amazon during the Late Pleistocene and the Early Holocene: New evidence from La Serranía La Lindosa --ScienceDirect
Research news --Newly discovered Amazon rock art show the rainforest's earliest inhabitants living with giant Ice Age animals --University of Exeter
https://www.exeter.ac.uk/news/research/title_829032_en.html
Sprawling 8-mile-long'canvas' of ice age beasts discovered hidden in Amazon rainforest | Live Science
https://www.livescience.com/ice-age-rock-art-amazon.html
'Sistine Chapel of the ancients' rock art discovered in remote Amazon forest | Archeology | The Guardian
https://www.theguardian.com/science/2020/nov/29/sistine-chapel-of-the-ancients-rock-art-discovered-in-remote-amazon-forest

A joint research team from England and Colombia investigated the site at the northern end of the Amazon River in Chiribiquete National Park in southeastern Colombia. The area of Chiribikete National Park is home to the armed rebel guerrilla- Columbia Revolutionary Armed Forces (FARC) , which has been closed for a long time due to danger, but in 2016 the Colombian government and FARC agreed to end the civil war. In response to this, he started investigating the ruins in 2017.
The ruins discovered by the research team are rock shelters that use overhanging bedrock as a roof, and from the bones and plant debris found in the excavation, the indigenous people who lived in the ruins are palms, fruits, piranha, crocodile, etc. We know that we ate snakes, frogs, capibaras, and armadillos. The indigenous people are believed to be the early people who arrived at the Amazon and are believed to have lived a hunter-gatherer life.
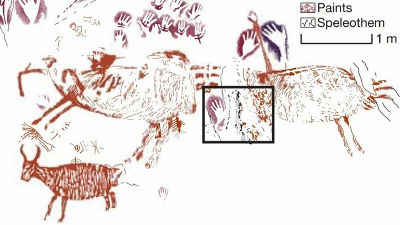
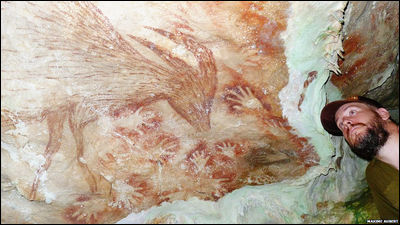
It is also known that the indigenous people painted tens of thousands of mural paintings using ocher as a pigment, using a rock wall with a total length of about 8 miles (about 13 km) that spans three rock shelters as a canvas. Due to the large scale of the murals, the research team expects the murals to be drawn over several to dozens of generations.
The patterns confirmed in previous surveys are extremely diverse, including geometric patterns, figures, handprints, plants, and small animals such as deer, tapir, crocodile, bat, monkey, turtle, snake, and porcupine. In addition, giant animals such as extinct camelids, giant sloths, horses, and mastdons were also depicted. The mural painting is believed to have been painted between 12,600 and 11,800 years ago, as it depicts Mastodon, which is said to have become extinct 12,000 years ago in South America.

by Ella Al-Shamahi
Mark Robinson, an archaeologist at the University of Exeter and a participant in the mural survey, said, 'This is a truly wonderful painting by the early people who lived in the western Amazon. They see changes in vegetation and forest composition. I moved to the area during the period of extreme climate change that caused it. ' The mural was painted at the end of the
It is said that large animals such as mastodon have become extinct due to the effects of climate variability and human hunting, and the appearance of animals drawn on the mural is a valuable clue to tell the situation at that time. 'Paintings make the lives of indigenous communities look vibrant and inspiring. For us today, it's amazing that they lived and hunted around herbivores as big as small cars,' Robinson said. He said.
In the painting, not only the figure of a human hunting an animal, but also the figure of a person wearing a mask with a bird-like beak, the appearance of raising his hand around a large animal and worshiping it, etc. And the interaction of animals is also depicted. A part of the mural is drawn higher than the human height, and the research team used the 'wooden tower like a bungee jumping platform' seen in the mural to paint on the high part of the rock wall. I guess I drew it.

by Marie-Claire Thomas / Wild Blue Media
It seems that there was also a picture of a plant that induces hallucinations in the mural painting, and it seems that there is evidence that the indigenous people performed various rituals. José Irialte, an archaeologist at the University of Exeter, claims that the people of the Amazon believe that non-human flora and fauna also have souls and communicate through rituals and shamanism as seen in mural paintings.
'These murals are magnificent evidence of how people adapted to the land and hunted, cultivated and fished. Art is a powerful part of culture and people are socially connected,' said Irialte. It seems that it was the way. '

by Marie-Claire Thomas / Wild Blue Media
Local media in Colombia pointed out that the murals claimed to have been newly discovered by the University of Exeter have been known for decades. He argues that the headline 'New Discovery' is a hype in foreign media.
El polémico “descubrimiento” de pinturas rupestres en Guaviare | EL ESPECTADOR
https://www.elespectador.com/noticias/medio-ambiente/el-polemico-descubrimiento-de-pinturas-rupestres-en-guaviare/

Related Posts: