Vulnerability 'BootHole' that can avoid secure boot is found in boot loader 'GRUB2' widely used in Linux

A vulnerability has been reported in the boot loader ' GRUB2 ', which is commonly used in Linux, which can prevent '
There's a Hole in the Boot-Eclypsium
https://eclypsium.com/2020/07/29/theres-a-hole-in-the-boot/
ADV200011 | Microsoft Guidance for Addressing Security Feature Bypass in GRUB
https://portal.msrc.microsoft.com/en-US/security-guidance/advisory/ADV200011
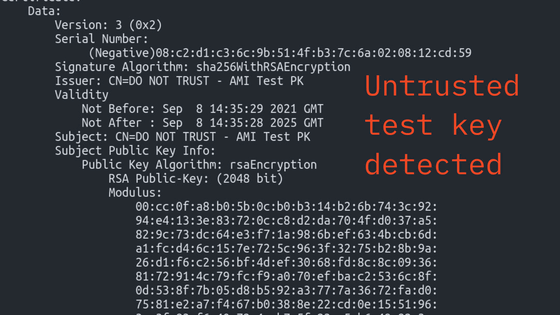
Debian-GRUB2 UEFI SecureBoot vulnerability -'BootHole'
The firmware ' UEFI ' installed in the PC has a mechanism called 'Secure Boot'. Secure Boot verifies the signature of the program that is executed before the OS starts, and protects the device by executing only the program that has a valid signature. However, the 'Boot Hole' reported by security firm Eclypsium has shown that it is possible to bypass secure boot and execute malicious programs.
BootHole is a vulnerability related to 'GRUB2' which is mainly used as a Linux boot loader. GRUB2 parses the configuration file 'grub.cfg' in the EFI partition and replaces it with a domain-specific language that can be executed when using UEFI, but there is a problem with this parsing and it is not possible to properly handle large parameters. I heard that. As a result, it was possible for an attacker to deliberately cause a buffer overflow, rewrite a memory area that was originally not rewritable, and execute malicious code.

Executing malicious code before booting the OS using BootHole to control the OS loading method, directly patch the OS, or boot another OS from the boot loader. It will be possible. This would allow an attacker virtually unlimited control over the target device. In addition to Linux, BootHole is reported to affect servers, desktops, IoT devices, etc. that perform secure boot using signature of programs by Microsoft UEFI CA.
To address the vulnerability, in addition to updating GRUB2 itself, you also need to update the UEFI firmware on the device to prevent the vulnerable version of the boot loader from running. However, if you update the firmware to a version that has already been fixed without updating the boot loader, there is a problem that the boot loader cannot be started, and it will take a very long time for the measures to be widely deployed. There is a nature.
Rewriting grub.cfg is required to use BootHole, so it is important to take system level measures such as keeping the OS up to date. Major vendors such as Microsoft , Debian , and RedHat have already announced BootHole support, and Eclypsium urges users and administrators to look closely at reports from hardware vendors and open source projects.
Related Posts:
in Security, Posted by darkhorse_log