How are used satellites discarded from space?

There are more than 500,000 pieces of artificial satellites and rockets called '
What Happens to Old Satellites When They Die?-YouTube
Rocket launches made during the 60 years from 1960 to 2020 were about 5,250. And there are about 42,000 artificial objects launched by rockets such as artificial satellites, of which only 23,000 or more, more than half of which were launched by the United States.

Most of the space debris that flies around the earth is small, such as screws or debris measuring at most 5 cm to 10 cm. However, collisions with small debris not only cause satellite failures, but can also generate large amounts of new space debris. In 2009, it was reported that

Despite the occurrence of such an accident, agreements to prevent satellite collisions and near misses were made by countries active in space development, such as China, Russia, and the United States, and private space companies, such as

However, in 2007, (PDF file) the

In these guidelines, three methods of processing satellites that have completed their role were indicated: ' reentry into the atmosphere ', ' guidance to the graveyard orbit ', and ' the process of removing directly from space '.

According to the ' reentry into the atmosphere ', it is said that approximately 80% of the main body of a satellite is burned out by high heat.
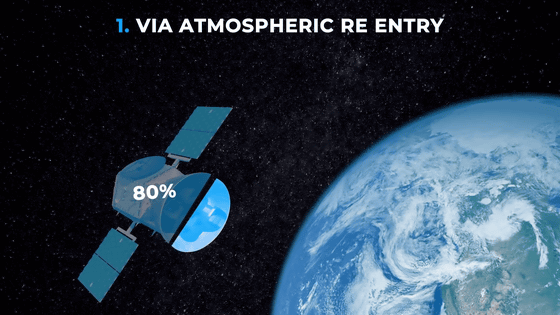
However, the remaining 20% will remain on Earth.

In January 1997, in the state of Oklahoma in the United States, a fragment of the American launch vehicle '

However, such disasters are very rare. It sounds very dangerous to hear that satellite fragments come down from the sky, but most of the satellites that have re-entered the atmosphere fall into the ocean, which accounts for more than 70% of the earth.

Of course, the point at which the satellite is dropped is almost fixed, and it is assumed that the damage caused by the fall will be the lowest, so it seems that the drop point is often set just in the middle of New Zealand and South America. Therefore, this area is sometimes called 'Spacecraft
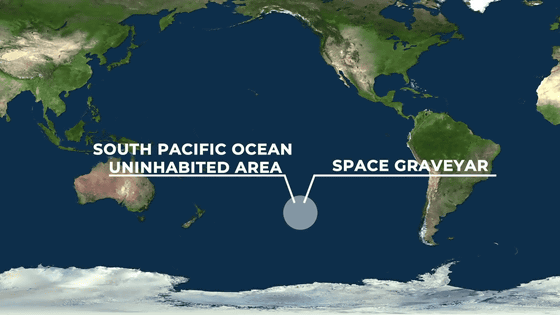
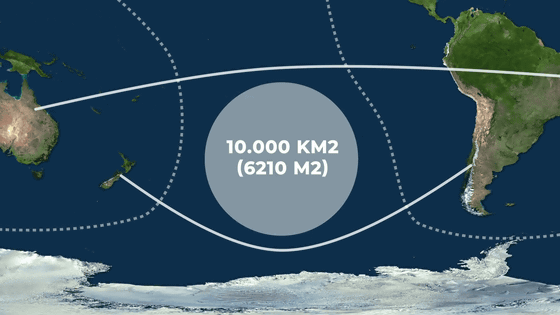
Spacecraft Cemetery measures approximately 10,000 km 2 . There are no routes or air routes in this area. If it is an artificial satellite that can be controlled from the ground, dropping it in this spacecraft cemetery can be disposed of with a low budget.
However, satellites are expensive to develop. If parts such as the engine and antenna can be collected, they can be reused just by repairing them, possibly reducing development costs. Therefore, in recent years, a project to develop artificial satellites for reuse while reducing the consumption of artificial satellites due to re-entry into the atmosphere has been promoted.

' Guiding to the graveyard orbit ' is to transfer the satellite to an orbit dedicated to the satellite that has completed its role. For example, when discarding a
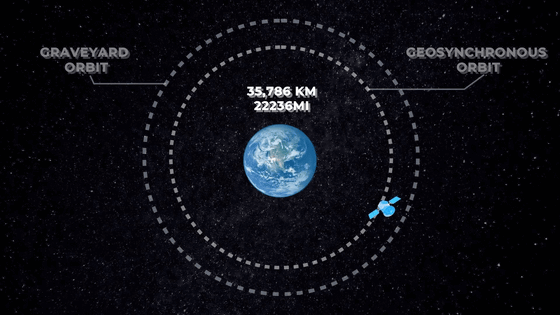
Therefore, the process of direct exclusion from space has been studied in recent years. For example, the

The mission was invented by Swiss startup

However, it is easy to imagine that SpaceX has already begun the

Related Posts:







