Pointed out that technology `` SMT '' that executes multiple threads with one CPU is becoming unreasonable
Modern CPUs use many advanced technologies to improve performance, such as '
Does SMT still make sense?
https://www.codeblueprint.co.uk/2019/11/05/does-smt-make-sense.html
Most modern CPUs use SMT and can process tasks in parallel. The SMT implemented by Intel is called 'hyperthreading' and has been installed on CPUs such as Pentium 4 and Xeon for servers that have not been required to increase clock frequency since 2002 with the aim of improving performance. Almost all current Intel CPUs have one of the SMTs called ' Hyper Threading Technology '.
AMD says that it makes full use of SMT. The image below shows the SMT operation of AMD's 'Zen' CPU architecture. It is difficult to determine at a glance which areas are independent and which areas are shared.
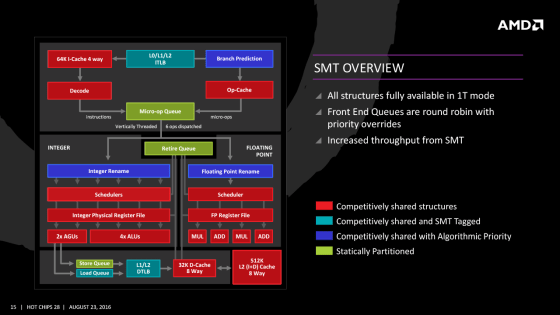
As an advantage of SMT, SMT is a common technology for
Another advantage of using SMT is that it is more efficient in terms of die size and power consumption than increasing CPU resources by physically doubling cores. According to Intel, using SMT's multi-threading technology, a 5% increase in die size could theoretically yield a 30% performance increase.
However, Intel's high-end CPU Intel Core i9-9980XE has 18 physical cores, and AMD will have 64 cores in the Ryzen third generation CPU `` AMD Ryzen Threadripper 3990X '' scheduled to be sold in 2020 The number of cores has increased in recent years, and it is said that high performance can be obtained without using SMT.

by
In addition, it is said that the difficulty in determining whether SMT is turned on on the OS side also leads to lowering the usefulness of SMT. When allocating physical cores to virtual machines, it is tempting to double the number of cores to double the performance, but when SMT is on, competition for resources occurs in the CPU, It is difficult to predict actual performance.
However, the biggest disadvantage of SMT is that it is a vulnerability related to SMT. Vulnerabilities such as ' Foreshadow ' and ' MDS ' of Intel CPUs found in 2018 are also related to SMT.

by Markus Spiske
It has been concluded that SMT should be turned off if security is a concern, given the implications of chip-level vulnerabilities.
Related Posts:
in Hardware, Posted by darkhorse_log