What is the Russian cyber attack system revealed in the cyber attack report?

by
Check Point Research , which collects and analyzes data on threats in cyberspace, and Intezer have jointly released a report analyzing APT attack actors that are allegedly related to the Russian government.
Mapping the connections inside Russia's APT Ecosystem-Check Point Research
https://research.checkpoint.com/russianaptecosystem/
Russian APT Map Reveals 22,000 Connections Between 2000 Malware Samples
https://thehackernews.com/2019/09/russia-hacking-groups-map.html
The APT attack is a technique for aiming at a specific target and conducting advanced and continuous attacks, and actors (attack groups) under the influence of Russia are threats all over the world. Turla , Sofacy , and APT29 (The Dukes) are known as APT attack actors that appear to be supported by the Russian government and military organizations. These actors are engaged in various operations involving Russia, using advanced tools, unique approaches, and solid infrastructure.
Various organizations such as the Russian Federation Security Agency (FSO) , the Russian Federation Security Agency (FSB) , the Russian Foreign Information Agency (SVR) , and the Russian Federation Army Staff General Information Office (GRU) use their own APT attack actors around the world. Is believed to be attacking other institutions and organizations.
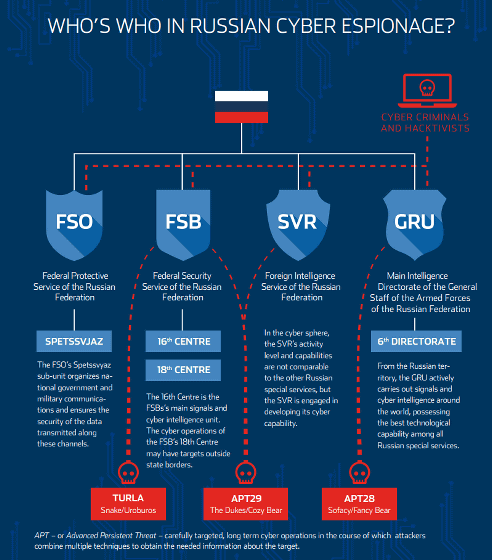
Researchers have pointed out that Russia has been engaged in a variety of cyber espionage and sabotage activities over the last 30 years. In addition, research so far has revealed a variety of information about each actor, but the details of the interaction between multiple actors supported by Russia It ’s not.
So researchers collected, classified and analyzed 2000 malware samples from Russian actors and found nearly 22,000 interconnections based on 3.85 million codes. A map of the researcher's mapping for each actor's interconnection can be found on the following page.
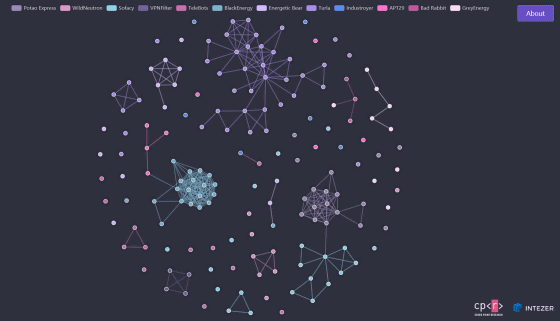
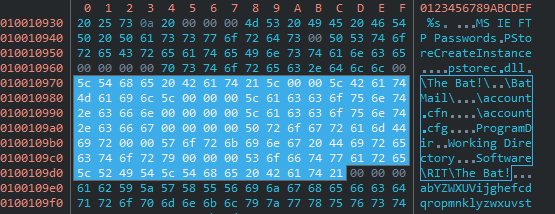
Analysis revealed that some malware and code shared among actors were found. For example, there was code to share in the software called BlackEnergy Password Stealer and the credential acquisition software distributed by the Russian-speaking underground forum about 10 years ago, called PinchDuke .
PinchDuke source code
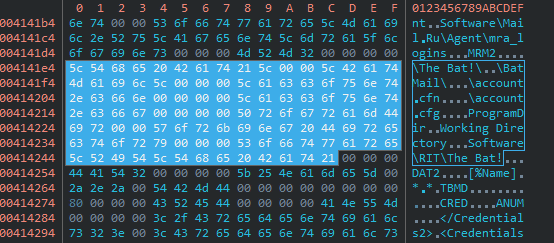
Source code of BlackEnergy Password Stealer
Also, between the actors BlackEnergy and Energetic Bear , the same self-deleting function was confirmed in the software developed by each. However, it seems that it was very rare for code to be shared between different actors, and this feature was not shared actively among actors, but was obtained from a public source. It is considered a thing.
BlackEnergy source code
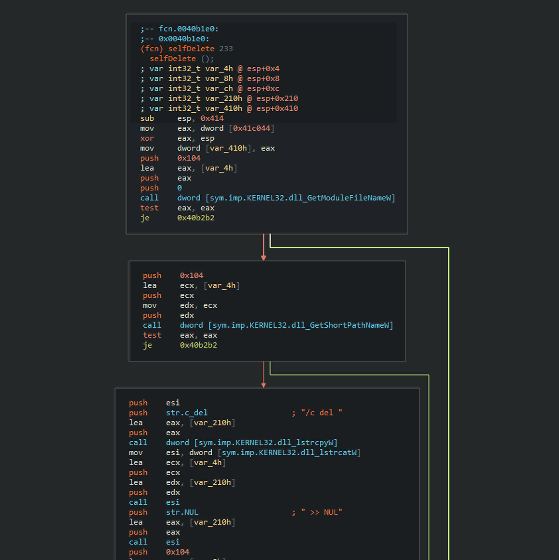
Energetic Bear source code
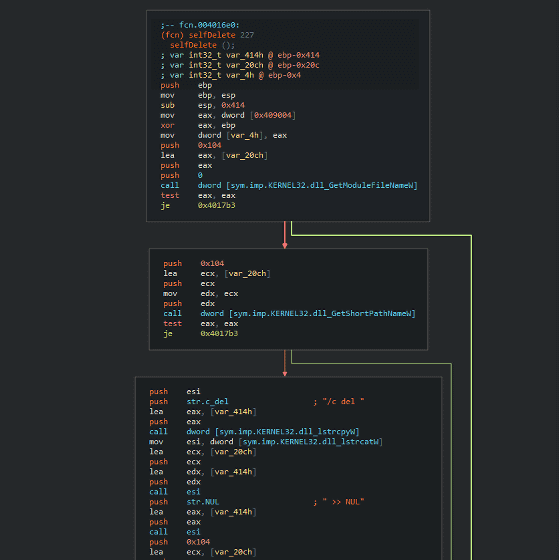
According to researchers, common codes are seen between different projects of the same actor, and code sharing is organized within the same actor, suggesting that they are aware of the mutual work situation etc. It has been done. This can reduce the man-hours in the actor.
On the other hand, researchers have also found that little code is shared between different actors. For researchers, this result seems unexpected, and the reason why there is no code sharing among actors is that `` Even if the malware has the same purpose, each actor develops it individually to ensure redundancy. '' In addition to the theory, there is also a theory that 'there is no mutual cooperation due to political disputes between organizations that support actors'.

by Soumil Kumar
In the United States, in preparation for the presidential election in 2020, we are strengthening caution against foreign cyber attacks and election obstruction. The efforts against cyber attacks involve the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) , the US Department of Homeland Security, and the United States Secretary of State of the United States , and it is reported that they are trying to prevent foreign influences for their own interests.
2020 campaigns get Trump administration help on cybersecurity, counterintelligence
https://www.nbcnews.com/politics/2020-election/2020-campaigns-get-trump-administration-help-cybersecurity-counterintelligence-n1057366
Related Posts: