How does fluoride prevent tooth decay?
Many toothpastes contain fluoride as an active ingredient in preventing tooth decay, and in some countries and regions, fluoride is added to tap water to prevent tooth decay. Live Science, a science news site, interviewed experts about the causes of tooth decay and the mechanism by which fluoride prevents it.
How does fluoride prevent cavities? | Live Science
Around the world, efforts are being made to add fluoride to tap water, milk, and table salt, and to have schools provide children with fluoride mouthwash. These efforts were prompted by the discovery that children living in certain areas had extremely low rates of tooth decay.
'Epidemiological data showed that the area's tap water contained natural fluoride at a concentration of about 1 ppm (parts per million), which was effective in preventing tooth decay,' said Lucy O'Malley, an applied health scientist at the University of Manchester in the UK.

Human teeth are made up of a hard, shiny surface called enamel, a layer of dentin that makes up the majority of the tooth, a layer of soft tissue called pulp inside the tooth, and a thin layer of cementum that attaches the tooth root to the jaw.
Of all the components of teeth, the most important is enamel, the hardest substance in the human body. The main component of enamel is
However, when you consume sweet snacks or drinks, the bacteria in your mouth break down the sugar and release acids, which cause ' demineralization ' that deteriorates enamel.
When demineralization occurs, the acid dissolves the phosphate and hydroxide ions from the enamel, weakening its overall strength. If the holes in the enamel surface reach the dentin, bacteria can penetrate the inside of the tooth, accelerating the decay process . This breakdown of tooth structure is called tooth decay.
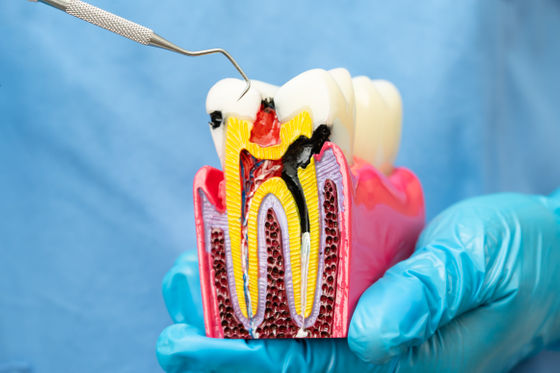
The aforementioned fluoride prevents this process, and it has two main protective effects.
Alexander Morris, professor of dental hygiene at the University of Birmingham, explains: 'When fluoride is incorporated into tooth enamel, it makes it more resistant to the acids produced by bacteria, making it less likely to develop cavities in the first place. Fluoride can also help repair early decay by making enamel more resistant during the repair process.'
Tooth repair is a phenomenon called '
Because fluoride ions are much smaller than hydroxide ions, they can fit more tightly between the phosphate particles, forming fluorapatite , a crystal structure that is more compact and stronger than the parent hydroxyapatite.
The benefits of fluoride for dental health have been well proven and it has been used as an additive in toothpaste for half a century, since the 1970s.
'Since the widespread use of fluoride, the incidence of tooth decay has dropped dramatically,' O'Malley said.
However, there are voices of opposition to ' tap water fluoridation ,' which involves adding fluoride to tap water, due to concerns about its effects on health. Note that fluoride is not added to tap water in Japan.
There is a debate going on about regulating 'tap water fluoridation,' which adjusts the fluoride concentration in tap water to prevent tooth decay, as it has a negative effect on brain development - GIGAZINE

Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1l_ks