Intense exercise may suppress your appetite

Some people may be worried that exercising for weight loss will increase their appetite and make them gain weight, even though they think it is better to exercise. A new study has found that intense exercise can suppress appetite, but it has also been pointed out that the effect may differ between men and women.
Impact of Exercise Intensity and Sex on Endogenous Ghrelin Levels and Appetite in Healthy Humans | Journal of the Endocrine Society | Oxford Academic
Study finds intense exercise may suppress appetite in healthy humans | Endocrine Society
https://www.endocrine.org/news-and-advocacy/news-room/2024/study-finds-intense-exercise-may-suppress-appetite-in-healthy-humans
Vigorous Workouts May Be The Key to Suppressing Appetite, Study Says : ScienceAlert
https://www.sciencealert.com/vigorous-workouts-may-be-the-key-to-suppressing-appetite-study-says
Ghrelin , a hormone produced by the stomach, is involved in regulating appetite and acts on the hypothalamus to create a feeling of hunger. It is known that blood levels of ghrelin increase with fasting and decrease with eating, but the relationship between exercise intensity and ghrelin was not well understood.
The researchers recruited 14 participants, eight men and six women, to fast overnight before engaging in exercise of various intensities, as measured by the level of lactate in the blood. They also analyzed blood samples and completed a questionnaire about their appetite.

The study found that women had higher baseline ghrelin levels than men, and that women in particular showed a decline in ghrelin levels after intense exercise. 'We found that high-intensity exercise suppressed ghrelin levels more than moderate-intensity exercise,' said Kara Anderson, lead author of the study and an endocrinologist at the University of Virginia.
The graph below shows the blood ghrelin concentrations of subjects who did not exercise (left), subjects who did moderate exercise (middle), and subjects who did intense exercise (right). The solid line represents women, and the dotted line represents men. Subjects who did moderate exercise had slightly higher blood ghrelin concentrations than subjects who did not exercise, but subjects who did intense exercise had significantly lower ghrelin concentrations. The decrease in ghrelin concentrations due to intense exercise was particularly noticeable in female subjects.
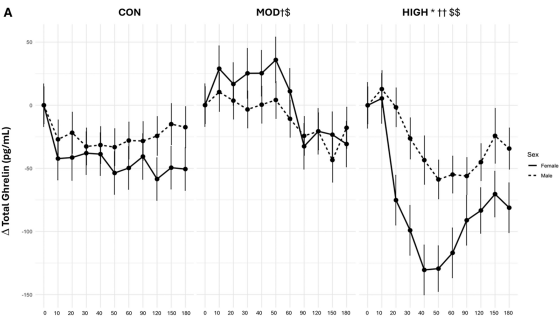
'In our experimental protocol, we used blood lactate to determine the intensity of exercise. Therefore, these findings suggest that exercise above a lactate threshold may be necessary to suppress ghrelin,' the team wrote in their paper.
'Exercise should be thought of like a drug, with dosage tailored to individual goals,' said Anderson. 'Our study suggests that high-intensity exercise may be important in suppressing appetite, which is particularly useful as part of a weight-loss program.'
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1h_ik







