Benchmark results show that Microsoft's 'Copilot + PC' does not have as high AI processing performance as claimed
Microsoft has categorized PCs suitable for performing AI tasks, including the AI assistant 'Copilot,' as '
GitHub - usefulsensors/qc_npu_benchmark: Code sample showing how to run and benchmark models on Qualcomm's Window PCs
https://github.com/usefulsensors/qc_npu_benchmark
Microsoft defines Copilot+ PC as a Windows 11 device equipped with an NPU of 40 TOPS or more. In other words, even if it has a GPU with high AI processing performance, a PC without an NPU cannot be recognized as a Copilot+ PC.
An 'NPU' is a processor designed to speed up AI inference processing. Although GPUs can also execute AI tasks at high speed, they consume a lot of power because they have built-in units that handle not only AI processing but also various other calculations. In contrast, NPUs specialized for AI processing have a minimum number of calculation units, so they consume much less power even when performing the same AI processing.
Additionally, 'TOPS' is a unit used as an index to express the processing speed of an AI chip. Conventionally, the computing power of a computer was expressed as ' FLOPS ', which indicates how many floating-point operations can be performed per second. However, since AI tasks often involve integer operations rather than floating-point operations, 'TOPS', which indicates the number of integer operations per second, is used to express the processing speed of AI tasks.
The requirement for Copilot+ PC is 'NPU with 40 TOPS or more,' which means 'NPU that can perform more than 40 trillion integer operations per second.' Therefore, Useful Sensors actually used the test script to benchmark the Microsoft Surface Pro (11th generation).
Useful Sensors uses Python to run its test scripts, but the Python available in the Microsoft Store as of October 2, 2024 does not support Arm architecture processors. Therefore, it is not suitable for running packages that access Qualcomm's NPU installed in existing Copilot+ PCs. Instead, Useful Sensors explains that it used the official Python.org installer .
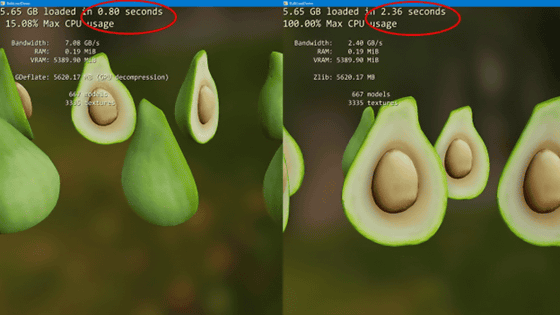
The benchmark is designed to resemble a real-world AI model, running six huge matrix multiplications similar to the slowest layers in Transformer models such as OpenAI's Whisper . The latency is measured as the real time it takes to run the model from start to finish, and the number of operations per second is calculated backwards from that latency.
Tests have shown that the Qualcomm Snapdragon X Elite (12 cores, clocked at 3.40 GHz) running on the Microsoft Surface Pro (11th generation) is not as capable of AI processing as claimed, with the benchmark showing a performance of 573 billion operations per second (0.573 TOPS), falling short of the 45 trillion operations per second (45 TOPS) claimed in the marketing materials.
Meanwhile, when the same benchmark test was run on an Nvidia Geforce RTX 4080 laptop, it reportedly achieved 2.16 trillion operations per second (TOPS).
'We have seen on other platforms, such as Android, that the underlying hardware works very effectively, so we hope to see software changes in the future, either at the application, framework, or driver level, that will improve these results,' Useful Sensors said.
Related Posts: