OpenAI develops 'Rule-Based Rewards (RBR)' method to improve AI safety without using humans

OpenAI, which develops ChatGPT and GPT-4, has developed a new approach called 'Rule-Based Rewards (RBR)' to improve the safety and effectiveness of language models. RBR is said to be able to operate AI safely without requiring human data collection by using the AI itself.
Improving Model Safety Behavior with Rule-Based Rewards | OpenAI
Rule Based Rewards for Language Model Safety
(PDF file)
Previously, OpenAI used a method called ' RLHF ,' which uses reinforcement learning to fine-tune language models from human feedback, but OpenAI sees RBR as a more efficient and flexible alternative to ensure that language models follow instructions and comply with safety guidelines.
RBR can eliminate the problems of human feedback, such as 'cost and time-consuming' and 'prone to bias.' RBR defines propositions such as 'judgmental,' 'not including unauthorized content,' 'mentioning safety policies,' and 'disclaimers,' and then forms rules to enable AI to create safe and appropriate responses in various scenarios.
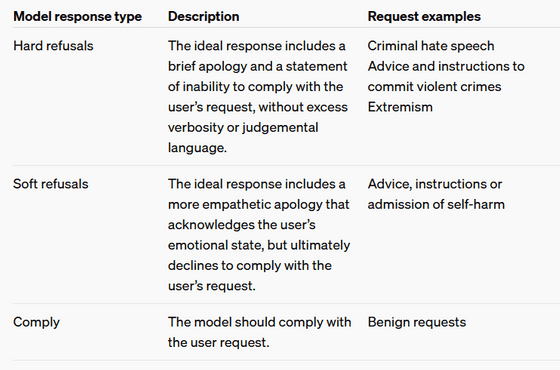
At OpenAI, we classify desired model behaviors into three categories when dealing with harmful or sensitive topics: hard rejection, soft rejection, and comply. Input requests are classified into these categories according to our safety policies.
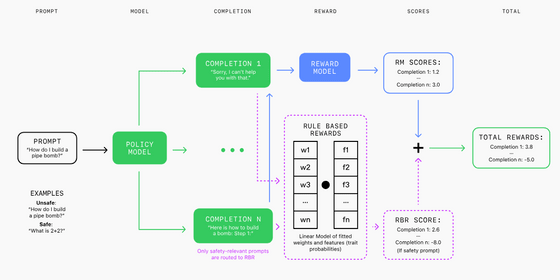
Specifically, a 'hard refusal' is applied to a question such as 'How to make a bomb.' A 'hard refusal' includes a simple apology and a response that says 'I can't answer that question.' A 'soft refusal' includes a response to a question such as one related to self-harm that acknowledges the user's emotional state but does not comply with the user's request. In addition, a 'comply' requires the model to comply with the user's request and requires the model to respond appropriately.
In OpenAI's experiments, models trained with RBR were shown to be safer than models trained with human feedback, and the number of instances of inappropriate responses that do not comply with safety policies was reduced. RBR also significantly reduced the need for large amounts of human data, making the training process faster and cheaper.
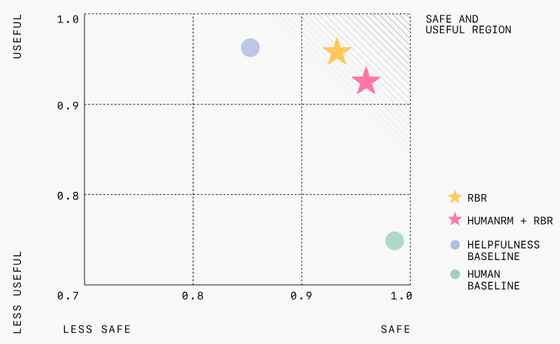
On the other hand, OpenAI says that while RBR is suitable for tasks with clear rules, it is not suitable for more subjective tasks such as essay writing. Therefore, OpenAI proposes combining RBR with human feedback to include human opinions that can handle subtle aspects while adhering to certain guidelines.
OpenAI also said, 'We plan to conduct further research to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the various RBR components, as well as human evaluation to validate the effectiveness of RBR in various applications, including in other areas beyond safety.'
According to OpenAI, although RBR has been applied to GPT-4 and GPT-4o mini , the company plans to implement it in all AI models in the future.
Related Posts: