If you live in a ``food swamp'' where there are only convenience stores and fast food stores nearby, the probability of dying from cancer increases by 77%

Whether or not food can be procured at familiar shops is an important point in considering the ease of living, and areas with the problem of almost no supermarkets where fresh food can be purchased are called ' food deserts'. is included. In addition to these problems, it has been confirmed that people who live in ' food swamps, ' which are lined with shops offering unhealthy meals, have a very high mortality rate from cancer, which is closely related to obesity. I was.
Association of Food Deserts and Food Swamps With Obesity-Related Cancer Mortality in the US | Lifestyle Behaviors | JAMA Oncology | JAMA Network
https://doi.org/10.1001%2Fjamaoncol.2023.0634
'Food Swamps': Scientists Explain The Health Risks of Living Inside Them : ScienceAlert
https://www.sciencealert.com/food-swamps-scientists-explain-the-health-risks-of-living-inside-them
Since the 1990s, when the term “food desert” was born, many studies have clarified the concrete picture of this problem. For example, in the case of the United States, wealthy districts have three times as many supermarkets as poor districts, and districts where many whites live have four times as many supermarkets as black-dominated districts. Also, many of the suburbs of Western Sydney, Australia, which are highly dependent on cars, do not have restaurants, and even if there are, 85% are occupied by fast food restaurants.

A research team led by Malcolm Seth Bevel et al. conducted a survey of 3,038 counties, representing 96.7% of the 3,142 counties nationwide.
The research team defines ``poor grocery store access'' as the lack of a supermarket where you can buy healthy food within a radius of 1 mile (about 1.6 km) in urban areas and a radius of 10 miles (about 16 km) in rural areas. , calculated the 'food desert score' from the poor accessibility and low income of the region. In addition, the ratio of fast food restaurants and convenience stores to supermarkets was used to calculate the 'Food Swamp Score' for the area. Then, based on medical data from 2010 to 2020, we calculated the mortality rate of 13 types of cancer mainly caused by obesity, so-called 'obesity-related cancer', and compared it with the 'food desert / swamp score'. Did.
The study found that people who lived in 'food swamps' were 77% more likely to die from obesity-related cancers than those who lived in areas with healthy food choices. Below is a table detailing the results. People in areas with high food desert scores are 1.59 times more likely to die of obesity-related cancer than in areas with low scores (red box above), and in areas with high food swamp scores, they are 1.77 times more likely than in areas with low scores ( red frame below).
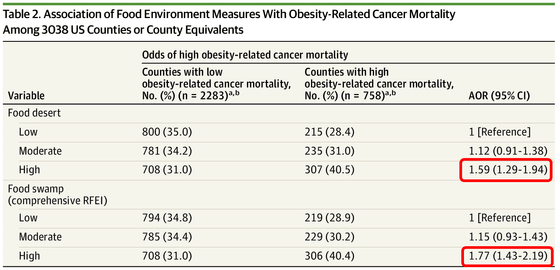
Areas with higher mortality from obesity-related cancers tended to have higher proportions of black residents and older people, but even after adjusting for the effects of these factors, food swamp residents had a 30% higher mortality rate. It turned out to be high. The results of this study are positioned to overturn the conventional stereotype that 'diet is one of the factors that can be changed by the individual's efforts, and it is possible to reduce the risk of cancer by making smart choices.' increase.
In

In addition, Mr. Bevel et al., ``In order to make access to food equitable, it is not just about increasing the number of healthy grocery stores, but also creating walkable areas so that people without cars can go shopping. is important,” he pointed out.
Related Posts:







