Research results that New York is sinking 1 to 2 mm per year due to the weight of increasing skyscrapers are released

Many skyscrapers, including
The Weight of New York City: Possible Contributions to Subsidence From Anthropogenic Sources - Parsons - 2023 - Earth's Future - Wiley Online Library
https://doi.org/10.1029/2022EF003465
New York City May Be Sinking Under the Weight of Its Skyscrapers | Architectural Digest

New York City Could Be Sinking Under The Weight of Its Skyscrapers : ScienceAlert
Parsons and colleagues estimated the cumulative mass of over a million buildings in New York, excluding roads, sidewalks, bridges, railroads, and other paved areas. As a result of calculations, the cumulative mass of New York City was estimated at approximately 1.68 trillion pounds (approximately 764 million tons).
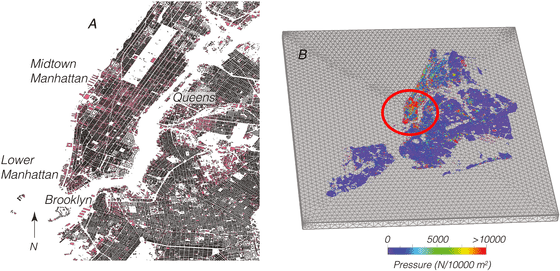
The research team then divided Mr. New York into 100 x 100 meter squares and calculated the downward pressure exerted by the mass of the building on deposits such as clay, sand and silt that make up most of the ground. Below is a diagram showing the pressure on the ground in New York. In Figure B, part of the central Manhattan ward is shown in red, and you can see that there is a strong pressure on the ground.
As a result of calculations by the research team, it was found that the subsidence rate related to
At first glance, a subsidence rate of 1 to 2 mm per year doesn't seem like much, but Parsons warns that the rate is 'more than enough to cause serious problems along the coast of New York in the future.' I'm here. According to Parsons et al., much of Lower Manhattan is located below 1 to 2 meters above sea level and is potentially at high risk of flooding. In addition, climate change and rising sea levels due to global warming and increasing hurricane intensity are increasing the risk of further flooding in areas such as coastal areas, including Lower Manhattan.
So far, the Lower Manhattan area has suffered damage such as flooding and power outages due to Hurricane Sandy in 2012 and Ida in 2021.
Mr. Parsons said, ``When the foundation of a building is repeatedly exposed to seawater, etc. due to repeated flooding, not only does the reinforcing steel that builds the building corrode, but the concrete becomes brittle, the strength of the building decreases, and eventually it collapses. There is a possibility,” he pointed out. Parsons also argued that New York developers still haven't fully taken the risk of land subsidence, saying, 'Even though New York has the third-highest risk of coastal flooding in the world, after Hurricane Sandy, About 90% of the approximately 67,000 structures built have not been built according to standards for flood risk.'

Mr. Parsons added, 'New York is a symbolic coastal city where land subsidence has been observed to progress, and the global challenge of countering the risk of flooding associated with the increasing land subsidence around the world is being addressed in New York. I also have it,' he said. Science news media ScienceAlert said, ``Many skyscrapers have already been built in New York, where land subsidence is progressing. By taking measures such as these to curb climate change, it is possible to reduce future risks such as rising sea levels and giant hurricanes.'
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1r_ut







