Why did Earon Mask's brain implant company 'Neuralink' take a long time to receive approval for human clinical trials?

The brain implant company ``
The FDA finally approved Elon Musk's Neuralink chip for human trials.
https://theconversation.com/the-fda-finally-approved-elon-musks-neuralink-chip-for-human-trials-have-all-the-concerns-been-addressed-206610
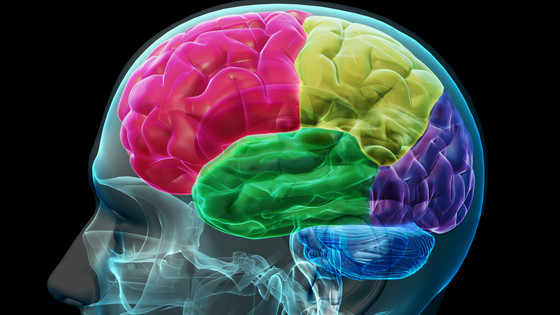
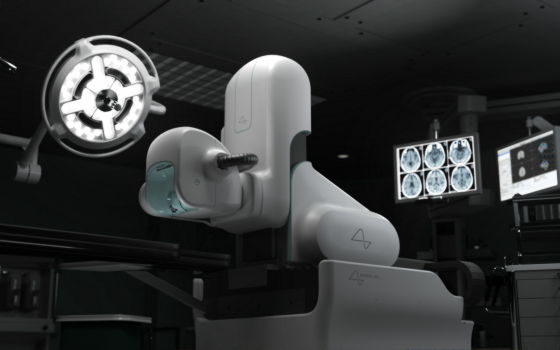
Neuralink is a company that develops a brain-computer interface (BCI) that connects the brain and a computer, claiming that a small implant embedded in the brain and connected to the nerve enables communication between the brain and an external computer via Bluetooth. doing. The brain implant to be developed is a coin-sized unit called `` Link '', which is embedded in the hole in the skull by a precision surgery robot, and connects 1000 `` ultra-fine wires '' connected to Link to cranial nerves. Each wire is about a quarter the diameter of a human hair.
Neuralink has already conducted experiments with monkeys, and it has also been demonstrated that monkeys can play games with just thinking using chips embedded in their brains.
A video of a monkey with a chip embedded in the brain playing a game with only ``thinking'' will be released-GIGAZINE

Neuralink claims that if BCI using brain implants operates safely, it will be possible to accurately control prosthetic limbs, and people who have lost limbs due to accidents or illness can recover their motor skills. In addition to being useful for treating diseases such as Parkinson's disease, epilepsy, and spinal cord injury, it has shown some promise in treating obesity, autism, depression, schizophrenia, and tinnitus. Companies other than Neuralink are also paying attention to the possibility of brain implants, such as devices that wirelessly connect the brain and spinal cord to allow paralyzed men to walk again , and people with disabilities to use cursors and devices with brain waves. cases have also been reported.
As ofFebruary 2021 , Musk was aiming for Neuralink to work with the FDA to conduct human clinical trials in 2021, but no clinical trials were approved in 2021. . In March 2022 , we applied to the FDA again, but after that it was difficult to receive FDA approval, and on May 25, 2023, the FDA finally gave Neuralink approval for human clinical trials. ``Given how strongly Neuralink has been seeking permission for human clinical trials, we can assume that clinical trials will begin soon,'' Taffrey said.
Clinical trial application by Elon Musk's brain implant company 'Neuralink' is finally approved by the FDA-GIGAZINE
The FDA reportedly had a long 'list of problems to solve' in granting Neuralink approval for human clinical trials, forcing Neuralink to undergo lengthy and exhaustive testing and data collection. About. The 'FDA's concerns' pointed out by Mr. Taffrey are as follows.
◆ Surgery safety
The important point in performing surgery on humans to embed a small implant and connect it to the cranial nerve is whether the surgery can be performed safely. Neuralink has developed a precision surgical robot called ' R1 ' that can reliably and safely place or implant implants while reducing the risk of damaging surrounding brain tissue, causing infection or inflammation, or bleeding. Claims it can be removed.
◆ Harmful side effects
The implanted BCI must work as intended and must not unintentionally adversely affect brain function or cause side effects such as seizures, headaches, mood changes, or cognitive impairment.
◆ Safe power supply
Lithium-ion batteries, which are often used in small devices, can damage the subject's brain by heating, and the risk of explosion due to deterioration or failure is not zero. Therefore, in the battery used for Neuralink's brain implant, in addition to basic items such as life, performance, and durability, biocompatibility and whether it can be replaced safely were also evaluated.
◆Movement of wire
Brain implants connect thin wires to cranial nerves, but natural movement, inflammation, and scar tissue formation can cause the implants and wires to migrate, placing the wires in the wrong place and causing damage to the brain tissue. Damage may occur. Through extensive animal testing, Neuralink has provided evidence that the wire does not move significantly over time or adversely affect the brain. Neuralink also had to show that there was a way to track and adjust the position of the wire depending on the situation, said Taffrey.
◆ Removal of brain implants
The FDA was also concerned about how easily the brain implant could be removed from the brain if it was no longer needed.
◆ Data privacy and security
Neuralink was also required to put in place strong safeguards to prevent the data collected by brain implants from being hacked or misused. “Neuralink needed to ensure the FDA could avoid the nightmare scenario of Link users being interfered with by hackers and protect the privacy of EEG data generated by the device,” Taffrey said. says.
Looking ahead, Taffrey noted that while critics recognize Neuralink's potential, they shouldn't cut corners to solve multiple problems. In addition, Mr. Musk envisions the idea of increasing intelligence by connecting AI and humans with brain implants, and telepathic communication via implants, but those who do not believe these claims until they actually see them is going to be good. “The Neuralink situation has clear parallels to current AI advances and the growing need for regulation. It should not be released to the public until then.'
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1h_ik