What was previously thought to be a black hole may look like a black hole but is actually a different entity

Imaging topological solitons: The microstructure behind the shadow
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevD.107.084042
Black Holes Might be Defects in Spacetime - Universe Today
https://www.universetoday.com/161291/black-holes-might-be-defects-in-spacetime/
Some black holes may actually be tangles in the fabric of space-time, new research suggests | Live Science
https://www.livescience.com/space/black-holes/some-black-holes-may-actually-be-tangles-in-the-fabric-of-space-time-new-research-suggests
In his theory of general relativity , Albert Einstein predicted the existence of black holes, which are formed when giant stars collapse. The existence of black holes was initially questioned, but based on recent observational results, many scientists have acknowledged the existence of black holes.
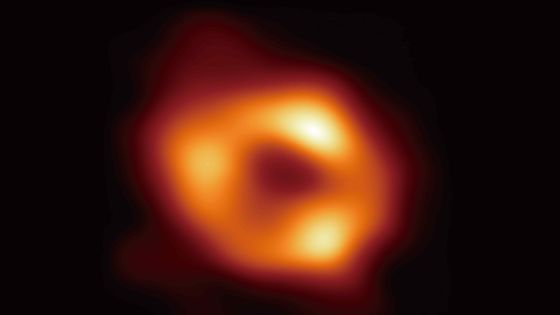
In 2019,a black hole was photographed for the first time in history, and in 2022, an image of a black hole in the same galaxy as Earth was released.
The first image of a black hole existing in the same galaxy as Earth is taken - GIGAZINE
However, there are still strong voices questioning the existence of black holes. The main problem is that although the theory of general relativity states that black holes have a gravitational singularity where their density and gravity are infinite, there is physically a singularity in space where the density is infinite. This is something that is considered impossible.
Based on this idea, ``Although there is no actual celestial object called a black hole, there is another celestial object that behaves like a black hole in observation.''
One of the theories that resolves the contradictions surrounding black holes and gravity theory is string theory, which posits that the particles that make up the universe are not zero-dimensional points, but are actually vibrating one-dimensional strings. Since these strings cannot vibrate in three-dimensional space, string theory predicts the existence of another dimension compacted on the quantum scale.
The research team claims that the existence of this extra dimension shrunk on an incredibly small scale causes a distortion of the space-time structure called a ``topological soliton'' (topological defect). Topological solitons are defects that stably exist in the space-time structure, and do not require matter or other forces to exist.

When the research team investigated the behavior of light passing near a topological soliton, they found that a topological soliton that distorts space-time affects light in much the same way as a black hole, with the light bending around the topological soliton and returning to the center. It turns out that the area looks like a dark shadow. Therefore, what was thought to be a 'black hole' observed so far may actually be a topological soliton.
However, since a topological soliton is not a singularity, there is no event horizon that light and electromagnetic waves cannot escape from, and it is thought that it will be possible to escape even if it approaches.
In addition, topological solitons are highly hypothetical entities based on string theory, and at the time of writing, no black holes have been found that are close enough to the Earth to be sufficiently researchable. However, if we can discover the observational differences between topological solitons and black holes, it may open the way to testing string theory itself.
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1h_ik







