A supermassive black hole with a mass of more than 30 billion suns is discovered from the center of the galaxy 2.7 billion light years away

A research team at Durham University in the UK has announced that it has discovered what is believed to be the largest known black hole to date. This black hole has a mass of more than 30 billion suns and is said to exist in the center of the galaxy 2.7 billion light years away from the earth.
Abell 1201: detection of an ultramassive black hole in a strong gravitational lens | Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society | Oxford Academic
Light-bending gravity reveals one of the bigg | EurekAlert!
https://www.eurekalert.org/news-releases/983991
The largest black hole ever discovered can fit 30 billion suns | Space
https://www.space.com/largest-known-black-hole-discovered-through-gravitational-lensing
According to the research team, the black hole in question is located at the center of a galaxy cluster called 'Abell 1201' about 2.7 billion light years away from the earth, and the mass is about 32.7 billion times that of the sun. Since the mass of a typical supermassive black hole is said to be several million to several billion times that of the sun, we can see how huge the black hole discovered this time is.
Because of their tremendous mass, black holes have a gravitational singularity at their center where not even light can escape. Most black holes are active and emit energy in the form of light, X-rays, and other radiation. very difficult to do.
The image of the black hole, which was captured for the first time in the history of astronomical observation in 2019, was successfully captured by using electromagnetic waves emitted by ultra-high temperature plasma gas.
Succeeded in the first ever ``imaging of a black hole'', existing in the galaxy M87 55 million light years from the earth with a mass 6.5 billion times that of the sun - GIGAZINE

One way to find such invisible black holes is to look for a phenomenon called gravitational lensing . If a celestial body with a huge mass like a black hole exists, the surrounding space-time itself will be distorted, so the light may be distorted or stretched as if it were passed through a lens. By observing this distortion of light, we can confirm the existence of a black hole.
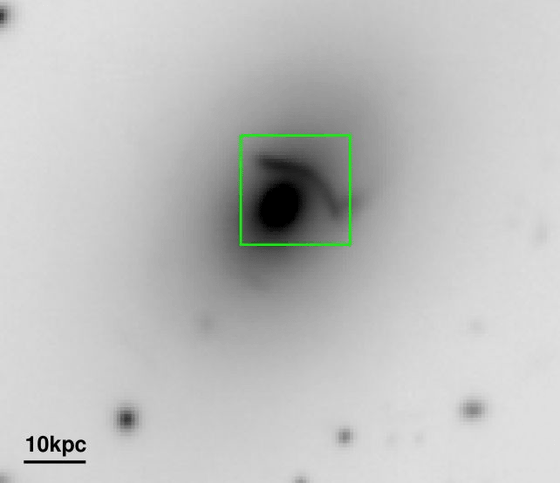
The star cluster galaxy (BCG) at the center of Abell 1201 was previously known to act as a strong gravitational lens. The following picture is a picture of Abell 1201 actually captured, and in the upper right of the black circle (BCG) in the center, the figure of the galaxy cluster on the other side of the BCG is distorted into a bow. For this reason, Abell 1201's BCG was thought to contain a very large black hole, but until now the details had not been clarified.

Therefore, a research team led by James Nightingale, a physicist at Durham University, analyzed photographs of Abell 1201 taken by the Hubble Space Telescope so far, and performed hundreds of thousands of computer simulations of light passing through the universe. Also, from the properties of gravitational lensing, we found that a supermassive black hole with a mass about 32.7 billion times that of the Sun exists at the center of Abell 1201.
The diameter of the event horizon of this supermassive black hole at the center of Abell 1201 is more than 1290 AU. Considering that the distance from the Sun to Pluto is about 40 astronomical units, it's easy to see just how big this black hole is.
“Testing for gravitational lensing will allow us to study inactive black holes,” Nightingale said. We can clarify how it has evolved, ”he commented.
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1i_yk







