NASA's artificial satellite 'RHESSI' will soon fall to the earth, the possibility that some parts will not burn out and fall on the earth is 'about 1/2467' NASA

The artificial satellite ``
NASA Retired Solar Energy Imager Spacecraft to Reenter Atmosphere | NASA
https://www.nasa.gov/feature/nasa-retired-solar-energy-imager-spacecraft-to-reenter-atmosphere
Out-of-control defunct NASA satellite will smash into Earth today | Live Science
Dead NASA satellite will crash to Earth this week | Space
RHESSI is a 660-pound (approximately 300 kg) artificial satellite launched by
During its mission, RHESSI made over 100,000 x-ray observations, helping to study the high-energy particles in solar flares. However, RHESSI ended its 16-year operation in 2018 due to aging equipment.
RHESSI, which has completed its role, is expected to re-enter the Earth's atmosphere at 9:50 am on April 20, 2023 Japan time, with an error of 16 hours. NASA said, ``We expect that most of RHESSI that entered the atmosphere will burn up, but some components may not burn up after re-entry and fall back to Earth.'' However, NASA estimates that ``the probability of harm to humans on Earth is low, about 1 in 2467.''
Astronomer Jonathan McDowell predicts, ``RHESSI is a satellite of only 300 kg, so there should be no significant risk from materials that have fallen to Earth.''
To reiterate, this is only a 300 kg satellite and I don't expect significant risk from materials impacting the ground.
— Jonathan McDowell (@planet4589) April 19, 2023
``Unless you observe the fireball when someone re-enters and splits, you can't know when and where RHESSI re-entered the atmosphere,'' McDowell said.
Reentry window for RHESSI has now opened. It will reenter in the next 2 hours. However we may not know when and where it reentered for seveal hours after that, unless someone sees the reentry breakup fireball
— Jonathan McDowell (@planet4589) April 19, 2023
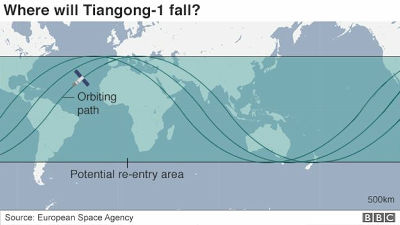
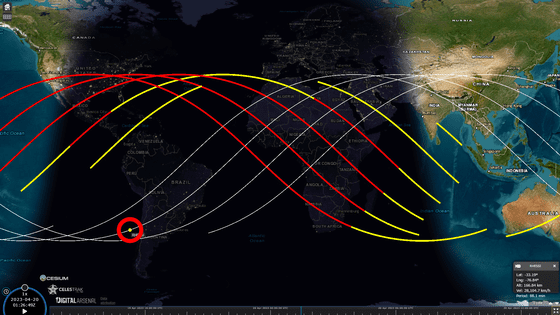
According to the website that predicts the current position of RHESSI, at the time of writing the article, RHESSI was located in the sea west of South America at an altitude of about 166 km.
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1r_ut