What is 'Globus' that indicates the position of the spacecraft in the globe used in the space development of the former Soviet Union?

In the space development conducted in the former Soviet Union, an
Inside the Globus INK: a mechanical navigation computer for Soviet spaceflight
https://www.righto.com/2023/01/inside-globus-ink-mechanical-navigation.html
Globus is an inertial navigation system for displaying the position of the Soyuz without receiving information from the outside, and has multiple dials for astronauts to set the initial position and orbital period. Latitude, longitude, number of satellites, etc. are displayed. In addition, this device also had a mode to predict the landing position of the landing ship.
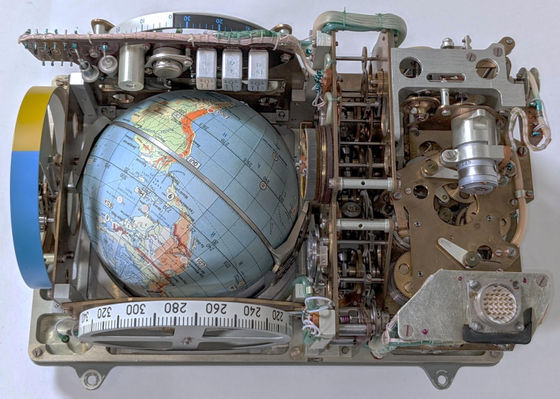
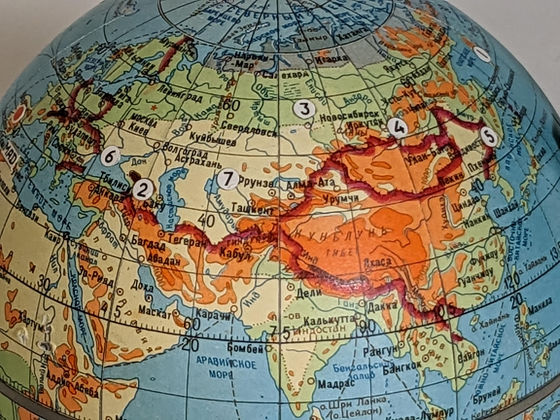
The globe placed in front of the Globus displayed terrain such as mountains, rivers, and lakes, and was used to select landing sites. In addition, the borders of the Soviet Union and the division of communist and non-communist countries were also displayed.
A metal ring was attached to the globe's equator and rotated around a horizontal axis. Since the
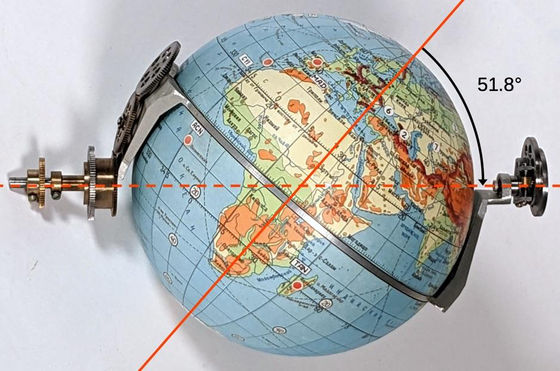
Globus was able to adjust the
In addition, Globus has a mechanism for displaying lander candidate sites with an accuracy of about 150 km by projecting the current Soyuz trajectory and calculating the landing position based on the angle specified during landing. bottom. When setting, set the angle of landing with a dial. Then Globus rotated the globe considering the landing site and the position of the earth, etc., and automatically stopped the rotation of the globe at the specified position.

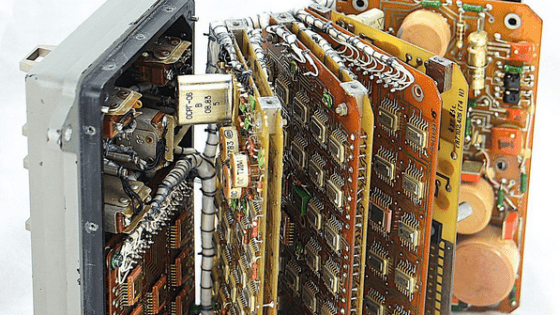
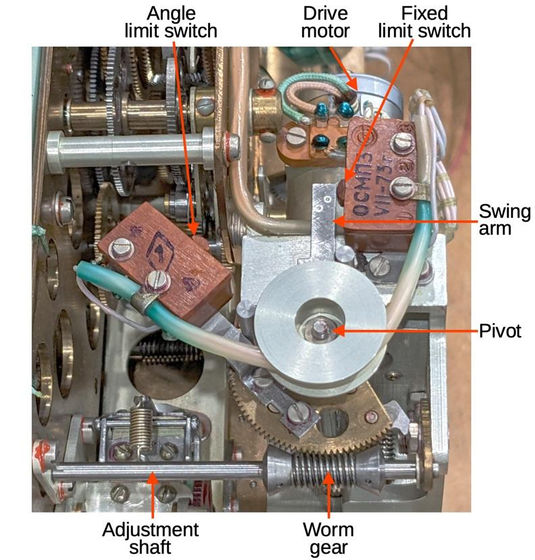
The Globus electronic board has four

In addition, Globus was driven by two

The Globus was built for the 1975

Globus has a long history, starting in the 1960s with the simple systems used in the

Globus was able to calculate the orbital position of the Soyuz through a complex system of gears, cams and differentials , allowing it to accurately display the spacecraft's position.
However, it requires manual settings and cannot be remotely operated from the outside, so it is said to have low accuracy and limited functionality. ``It's true that modern digital displays are full of features, but they lack the physical appeal of Globus's actual rotating globe,'' Shirriff said.
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1r_ut