It turns out that 58% of infectious diseases are intensifying due to worsening climate change

The pandemic of the new coronavirus infection showed no signs of convergence, and the WHO newly
Over half of known human pathogenic diseases can be aggravated by climate change | Nature Climate Change
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-022-01426-1
58% of human infectious diseases can be worsened by climate change – we scoured 77,000 studies to map the pathways
https://theconversation.com/58-of-human-infectious-diseases-can-be-worsened-by-climate-change-we-scoured-77-000-studies-to-map-the-pathways-188256

As
Therefore, a research team led by Camilo Mora of the University of Hawaii at Manoa identified 10 weather disasters associated with increased greenhouse gas emissions: atmospheric warming, ocean warming, heat waves, droughts, and wildfires.・We focused on heavy rains, floods, storms, rising sea levels, and changes in land cover (deforestation), and conducted research to investigate the literature that discusses these disasters.
In total, more than 77,000 papers were found as a result of the search by the research team. Analysis of these research data revealed that climate change affects 1006 infection routes. As a result, it was found that 218, or 58%, of the 375 infectious diseases were exacerbated by weather disasters.
Infectious diseases exacerbated by climate change were mainly transmitted by mosquitoes, bats, and rats. As for the types of meteorological disasters that affect infectious diseases, atmospheric warming is the most common with 160 types of infectious diseases, including heavy rains of 122 types, floods of 121 types, and droughts of 121 types. 81 types followed.
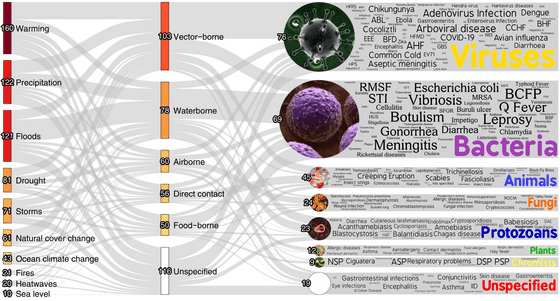
by Camilo Mora, CC BY-ND
The research team believes that there are four mechanisms by which climate change exacerbates infectious diseases.
◆ 1: Disasters related to climate change bring pathogens closer to humans
This occurs when disasters shift the habitat of dangerous infectious disease vectors. As a specific example, it has been pointed out that global warming and changes in precipitation patterns may alter the distribution of mosquitoes, which are known to carry many pathogens such as malaria and dengue fever.
◆ 2: Disasters related to climate change bring humans closer to pathogens
Humans are forced to move and change their behavior patterns in the same way that living things move due to disasters. For example, when heat waves occur, people spend more time near water, so it is thought that water-
In August 2022, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention picked up a case in 2021 in which people who entered a fountain in a wildlife park in Kansas developed acute gastrointestinal illness one after another, saying that drinking water such as fountains I warned you not to.
``Don't put the fountain water in your mouth,'' warns the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention-GIGAZINE

3: Climate change-related disasters strengthen pathogens
Disasters caused by climate change may increase the chances of contact with organisms that carry pathogens, or increase the ``ability of pathogens to infect humans and cause severe disease''.
For example, the water of heavy rains and floods becomes a breeding ground for mosquitoes, which increases the number of mosquito-borne infectious diseases, and the increase in temperature makes the virus more heat-resistant and adapts to human fever. There is also a case.
Candida auris , a type of fungus that was discovered in Japan in 2005, until then mostly infected people with weakened immune systems, but in recent years it has suddenly acquired resistance to treatment. It has been reported that it did, and according to the research team, this is also related to the rise in temperature. It has also been found that fungi in hot urban areas are more heat tolerant than fungi in relatively cool rural areas.
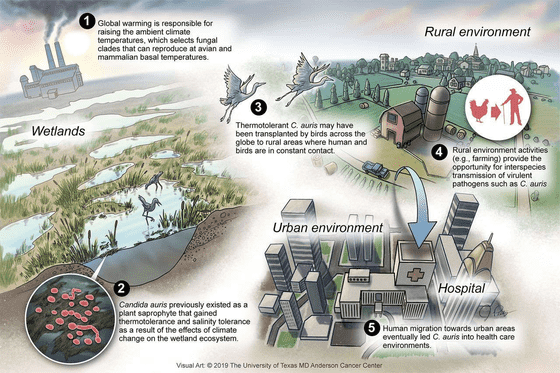
by Arturo Casadevall, Dimitrios P. Kontoyiannis, Vincent Robert
◆ 4: Disasters related to climate change weaken human resistance to pathogens
While disasters strengthen pathogens, they reduce humans' ability to fight off infectious diseases. For example, if there is a shortage of food and supplies due to a disaster caused by climate change, malnutrition may weaken physical strength, and stress may weaken the human body's immune system.
In addition, there are cases in which contact with pathogens and sick people increases and sanitary conditions deteriorate due to being forced to evacuate due to the occurrence of a disaster.
In this way, climate change poses a major threat to people's health and lives. I think we have to put the brakes on,' and once again appealed for the need for climate change countermeasures.
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1l_ks







