Possibility of revolution in industrial chemistry, 'Platinum liquid at room temperature' is developed

Dr Md. Arifur Rahim, UNSW Sydney
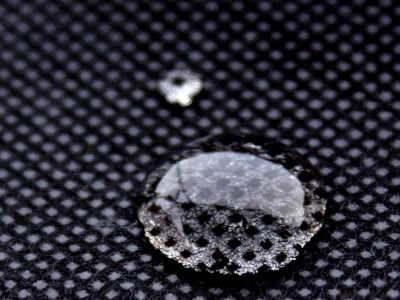
Researchers in Australia have revealed that they have found a way to process platinum, which has an extremely high melting point of over 1700 degrees Celsius, so that it can be melted at room temperature. It has been shown that platinum, which has excellent catalytic performance but is costly, can be used much more efficiently than existing methods.
Low-temperature liquid platinum catalyst | Nature Chemistry
Liquid platinum at room temperature: The'cool' catalyst for a sustainable revolution in industrial chemistry
https://phys.org/news/2022-06-liquid-platinum-room-temperature-cool.html
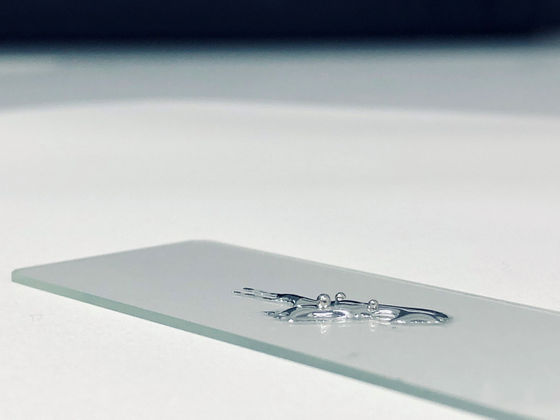
Researchers at the University of New South Wales and the Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology have devised a method of melting gallium with a melting point of 29.76 degrees and combining it with platinum to melt platinum at room temperature. Even in this method, platinum functions as a catalyst, and the efficient ratio of platinum to gallium 1 is less than 0.0001.
Platinum is a very good catalyst, but when using solid platinum for industrial purposes, a carbon-based catalyst system requires around 10% platinum. The value of platinum itself is high, and the energy cost required for operation also overlaps, so the reality is that it is not widely adopted on an industrial scale. However, the liquid-based catalyst system devised by the researchers is more than 1000 times more efficient than that of the solid-based one, which has the potential to revolutionize the chemical industry.

Dr Md. Arifur Rahim, UNSW Sydney
According to researchers, high-temperature treatment is required only in the initial stage of combining platinum and gallium to construct a catalyst, but it is still about 1 to 2 hours at a temperature of around 300 degrees Celsius, which is an industrial scale. It is far from the continuous high temperature treatment often required in chemical engineering.
Furthermore, because it is liquid-based, it will be more reliable than solid-based catalysts that will eventually clog and stop functioning. Researchers say it works for a long time because it constantly circulates like a fountain-incorporated aquarium.
Combining platinum with liquid gallium is expected to have many possibilities in the chemical industry, such as reducing carbon dioxide and synthesizing ammonia in fertilizer production.
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1p_kr