A major step toward lowering the cost of fuel cells, a new catalyst that can produce the same level of power generation efficiency at a price of 1/650 of the platinum catalyst
Generate electricity using hydrogen or methanol as a fuelFuel cellIs expected to be applied to various applications in the future from mobile phones to automobiles. However, in many fuel cells currently in practical use, in order to obtain high power generation efficiency, it is a very expensive and rare metal as an electrode catalystplatinum(Platinum) must be used, which has become a major barrier to practical application and dissemination. A quarter of the price of a fuel cell is said to be called platinum cost.
Meanwhile,Case · Western · Reserve UniversityOf chemists are hoping that it will be a major step toward lowering the cost of fuel cells by developing new catalysts that can achieve the same level of power generation efficiency at a price of 1/650 of platinum.
Details are as below.Cheap catalyst made easy
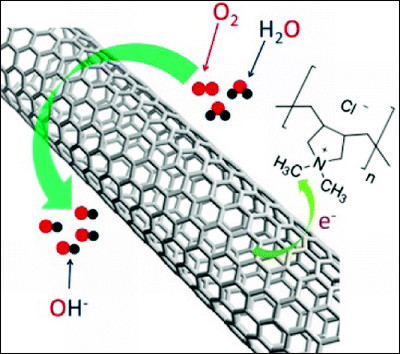
Professor Liming Dai, a chemical engineer at Case Western Reserve University,PDDA(Polychlorinated diallyldimethylammonium chloride) by coating with a polymer with strong electron withdrawing propertycarbon nanotubeDiscovered that it can achieve power generation efficiency comparable to that of platinum as a catalyst for the reduction reaction at the electrode of a fuel cell and can even be said to be superior to platinum in other factors (such as sustainability of catalysis). Thesis isJournal of the American Chemical Society(American Chemical Journal).
Professor Dai and colleagues analyzed carbon nanotubes coated with this polymerAlkaline electrolyte fuel cellCathode (the electrode where the reduction reaction occurs: the air electrode of the fuel cell), we confirmed that the same efficiency of power generation as the platinum catalyst can be obtained with the same fuel cell. Prof. Dai and others are thinking that it is possible to further increase power generation efficiency by optimizing various factors in the future.
When electrons in carbon are attracted to the surface by electron withdrawing polymer and positively charged, the reduction reaction of water and oxygen occurring at the cathode of the alkaline electrolyte fuel cell (2H2O + O2→ 4 OH-) As a catalyst.
Also, unlike platinum, this carbon-based new catalyst does not react immediately to carbon monoxide in fuel and loses its activity immediately. In a fuel cell using methanol fuel,Ion exchange membraneInfluence also on the "crossover phenomenon" that methanol permeated from the anode (pole at which oxidation reaction occurs: fuel pole of fuel cell) from the anode side to cathode side and also react at platinum catalyst on the cathode side to reduce power generation efficiency There is an advantage that it is not done. In other wordsIt is more stable than the platinum catalyst and it can keep high power generation efficiency for a long timeIt is.
Platinum with a limited amount of resources is now trading at around $ 65,000 per kg (about 5.26 million yen), whereas it can be made just by immersing carbon nanotubes in PDDA aqueous solution for several hours The catalyst can be manufactured at a cost of 1 kg 100 dollars (about 8100 yen), and it is expected not only for fuel cells but also for versatile use as an efficient nonmetallic catalyst for various reduction reactions in the future.

Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by darkhorse_log