Lithium-ion battery prices have fallen 97% in the last 30 years

In order to reduce global greenhouse gas emissions, there is an urgent need to shift to power generation using renewable energy such as solar power and wind power, but this also requires the maintenance of batteries to store the generated energy. is.
The price of batteries has declined by 97% in the last three decades --Our World in Data
https://ourworldindata.org/battery-price-decline
Since three-quarters of the world's greenhouse gas emissions come from the use of energy, it is important to move from fossil fuels to renewables to stem climate change. 'Power generation costs' are cited as a major barrier to this energy transition, but in recent years the costs of solar power generation and wind power generation have fallen sharply, and power generation costs are now lower than fossil fuels.
Why did the cost of generating renewable energy fall so rapidly? --GIGAZINE

But power generation costs are not the only consideration for energy source migration. One of the challenges facing renewable energy is that 'it is not always possible to generate electricity stably throughout the day because it uses natural energy.' In other words, solar power cannot generate electricity at night when the sun does not come out, and wind power cannot generate electricity on days when the wind is not blowing.
A simple solution to this problem is to 'store the generated energy in a battery and release it later when needed', which requires a huge battery and cost that can store a large amount of energy. .. Therefore, Our World in Data has investigated the price transition of lithium-ion batteries widely used in smartphones, electric vehicles, renewable energy power generation facilities, etc. over the past 30 years.
Below is a semi-logarithmic graph showing the price of a lithium-ion battery with a capacity of 1 kilowatt hour, with the vertical axis representing the logarithmic scale price and the horizontal axis representing the year. The battery price, which was 7523 dollars (about 1.02 million yen at that time) in 1991, became 181 dollars (about 19,800 yen) in 2018, and it turns out that it has dropped by nearly 97%. I will. The price decline has not stopped even in recent years, and it is said that it has halved in the four years from 2014 to 2018.
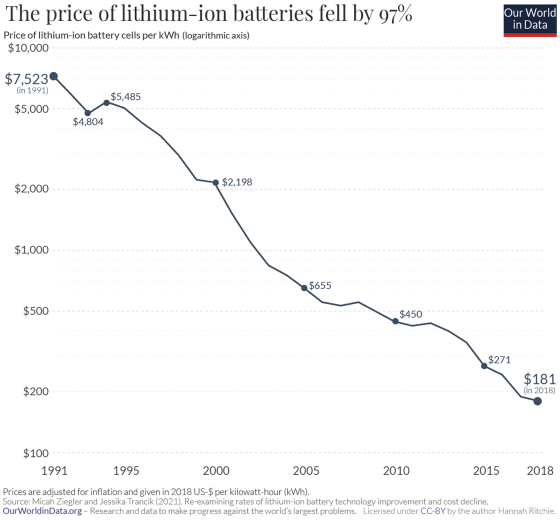
Considering the price of lithium-ion batteries in 1991 and 2018 for electric vehicle batteries, the 40kWh battery installed in the Nissan Leaf is about $ 7,300 (about 800,000 yen) as of 2018. As of 1991, it is about 300,000 dollars (about 40 million yen). In addition, the 75kWh battery installed in Tesla's Model S is about $ 13,600 (about 1.49 million yen) as of 2018, and about $ 564,000 (about 76.1 million yen) as of 1991, and the battery It's just a ridiculous price.
In this way, the decline in lithium-ion battery prices is extremely important in fields other than renewable energy power generation. Our World in Data points out that 'the size of the lithium-ion battery market' is related to the reason why lithium-ion battery prices have fallen sharply in the last 30 years.
In the logarithmic graph below, the vertical axis shows the price of a lithium-ion battery with a capacity of 1 kilowatt hour on a logarithmic scale, and the horizontal axis shows the cumulative installed capacity of a lithium-ion battery on a logarithmic scale. As of 1991, only 0.13 MWh of lithium-ion batteries were installed, which is less than the two 75kWh batteries installed in Tesla vehicles. However, after that, the cumulative installed capacity increased rapidly, and by 2016, 78,000 MWh lithium-ion batteries had been introduced.
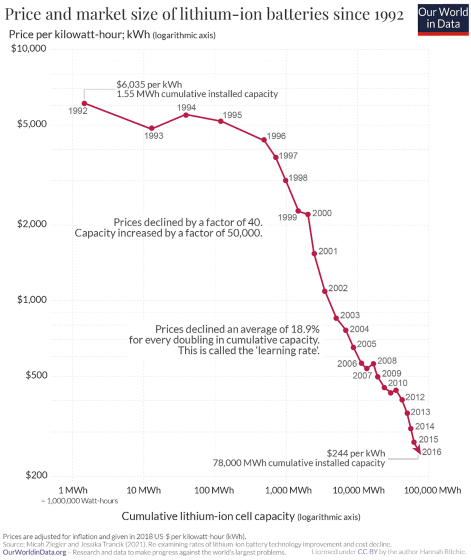
As the demand for lithium-ion batteries increases, so do the incentives and opportunities for manufacturers to innovate. As a result, technological innovations such as the ability to produce batteries of the same capacity at lower cost will occur, and the demand for lithium-ion batteries will increase, and the benefits of the next technological innovation will be created.
Technological innovations in lithium-ion batteries are not only reducing costs, but also making batteries of the same capacity smaller and lighter. As of 1991, the capacity of the lithium-ion battery per liter was 200 watt hours, but as of 2018, it seems to have improved to 700 watt hours. However, Lithium-ion batteries are still quite heavy, and Our World in Data pointed out that weight is an issue in fields such as electric airplanes where weight is greatly related to performance.

Related Posts:
in Note, Posted by log1h_ik






