How much difference is there in 'latency' between HDD, SATA SSD, NVMe SSD, and Optane SSD?
A journey to io_uring, AIO and modern storage devices
https://clickhoμse.tech/blog/en/2021/reading-from-external-memory/
When an auxiliary storage device exchanges data with a host, it does so in units called 'blocks,' which are groups of data, rather than in bytes. The size that is treated as one block varies from manufacturer to manufacturer, and in some cases, some manufacturers have neglected to update the block size they have been using for many years, and as a result, they continue to set blocks that are inappropriate for the latest equipment.
This time, Savchenko attempted to calculate the 'optimal block size' for HDDs, SSDs, etc. Savchenko had each auxiliary storage device randomly read blocks of 4KB to 16MB, and measured the access time delay (latency) at that time: MAX (maximum), P99.9 (99.9th percentile), P99 (99th percentile), AVG (average), and MIN (minimum).
The results for HDD are as follows. The horizontal axis is block size, the vertical axis is latency in seconds, and the graph itself is a log-log graph .
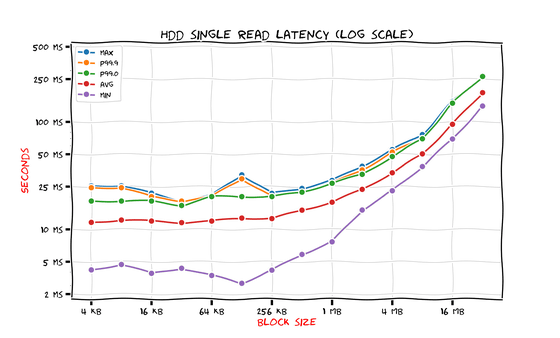
A feature of HDDs is that 'latency is almost the same for block sizes of 256KB or less.' Savchenko explained that this is because 'seek time is much longer than data transfer time.' He said that this is because the '
Next, the results for SATA SSD are as follows.
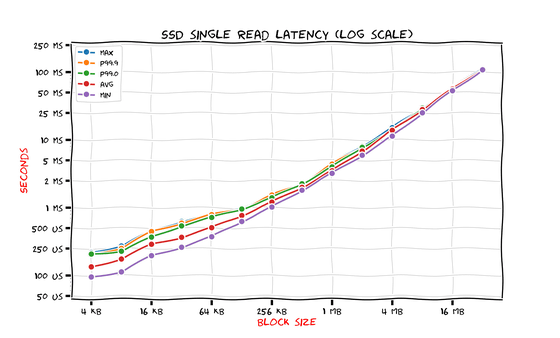
Latency has reached the microsecond level, which HDDs could not achieve, with a minimum latency of just 140μs at 4KB. Another feature is that the block size and latency are almost consistently proportional. Savchenko cited the results of the HDD mentioned above and commented, 'SATA SSDs are 10 times faster than HDDs at block sizes of 256KB, but only twice as fast when the block size is large enough (4MB or more).'
Next are the results for NVMe SSDs.
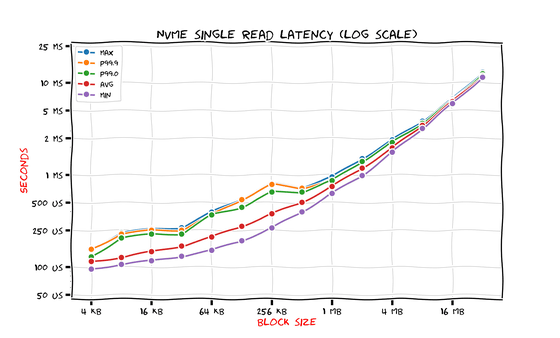
This result goes beyond the SATA SSD, which showed a significant improvement over HDDs. When comparing SATA SSDs and NVMe SSDs at a 4KB block size, Savchenko noted that while the average latency was roughly the same, the NVMe SSD's 99th percentile was twice as fast, and that at a 1MB block size, the NVMe SSD's results were both below 1ms, while the SATA SSD's results were both above 3ms. However, he commented that 'it's not as big a leap from HDD to SATA SSD.'
Lastly, the Optane SSD.
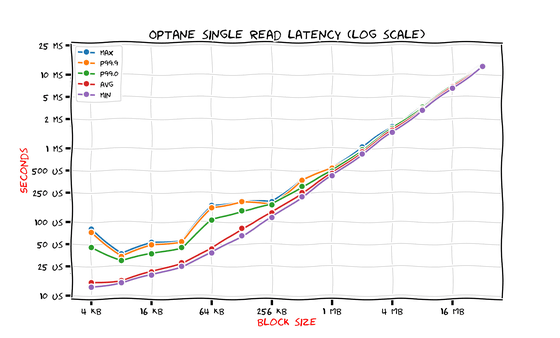
The minimum latency at 4KB is only 12μs, which is an astonishing result that is about 10 times faster than NVMe SSD and 1000 times faster than HDD. However, the maximum latency and 99th percentile latency are significantly worse than the minimum latency and average latency, and 'the unevenness is quite large,' Savchenko noted.
In addition, for Optane SSDs, we also measured the latency in polling mode, with the assumption that 'if the latency is very small, polling mode is effective.' The results are as follows.
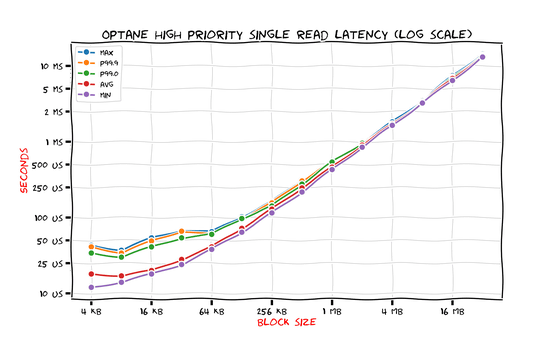
'At 256KB block size, we've cut the maximum latency in half,' Savchenko said.
The graph below shows the results for HDD, SATA SSD, NVMe SSD, and Optane SSD at a glance. The four bar graphs for each block size are, from left to right, Optane SSD, NVMe SSD, SATA SSD, and HDD. The longer the graph, the higher the latency. Note that block sizes above 4MB are omitted as they are easier to predict.
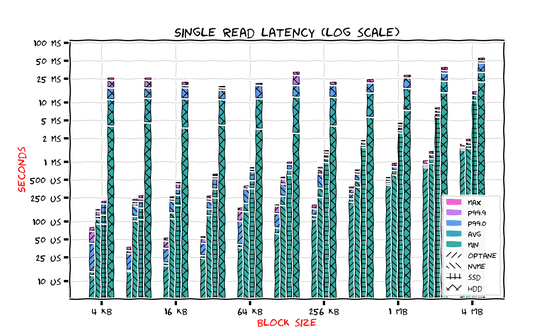
Regardless of the standard and block size, it is clear that 'SSDs are superior to HDDs in terms of latency.' The optimal block size for random reads was '256KB for HDDs, 4KB for SATA SSDs and NVMe SSDs, and 8KB for Optane SSDs.'
Related Posts:
in Free Member, Hardware, Posted by darkhorse_log







