Studies show that blood androgen levels are associated with aggravation of coronavirus infections

The new coronavirus infection (COVID-19) is said to be at high risk of aggravation in the elderly and those with underlying diseases (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic kidney disease, diabetes, hypertension, cerebrocardiovascular disease, obesity, etc.) Survey results have been obtained, and similar results have been confirmed in follow-up surveys by research institutes in each country. Regarding the risk of COVID-19 becoming more severe, a new research result has been announced that 'the concentration of male hormones in the blood is related'.
Association of Circulating Sex Hormones With Inflammation and Disease Severity in Patients With COVID-19 | Infectious Diseases | JAMA Network Open | JAMA Network
Low testosterone in men linked to more severe COVID-19 | Live Science
https://www.livescience.com/low-testosterone-men-linked-increased-risk-severe-covid.html
For men, low testosterone means high risk of severe COVID-19 – Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis
https://medicine.wustl.edu/news/for-men-low-testosterone-means-high-risk-of-severe-covid-19/
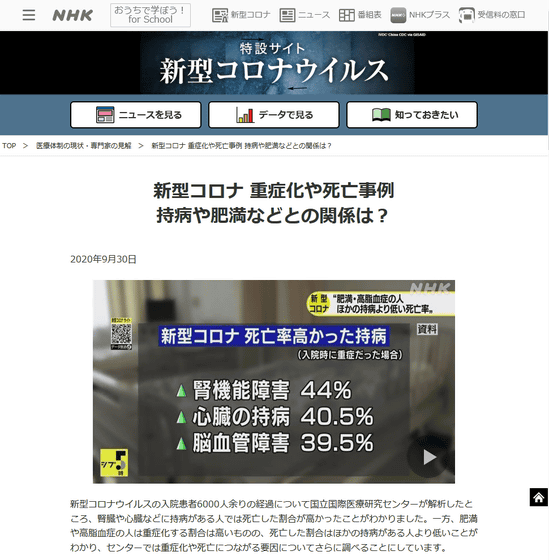
The case fatality rate of COVID-19 is calculated to be about 2%, but it has been confirmed that the case fatality rate varies greatly depending on the age of the infected person and the presence or absence of the underlying disease. According to the February 2020 announcement by the China Infectious Disease Prevention and Control Center, the case fatality rate of elderly people aged 80 and over jumps to 14.8%, the case fatality rate of men is higher than that of women, and hypertension and diabetes.・ It has been shown that the case fatality rate depends on the presence or absence of cancer, and similar results have been obtained in studies in Japan regarding chronic diseases.
Cases of aggravation and death of the new corona What is the relationship with chronic diseases and obesity? | NHK
https://www3.nhk.or.jp/news/special/coronavirus/medical/detail/detail_39.html
A research team at Washington University in St. Louis has newly announced that 'the amount of testosterone' is related to the risk of COVID-19 aggravation. Testosterone is a type of hormone that represents androgen (male hormone) , and is known to be involved in masculine personality such as sexual function, muscle mass, skeletal development, struggle instinct and desire for loneliness.
The research team collected blood samples from a total of 152 subjects, 90 males and 62 females, who were diagnosed as COVID-19 positive at the Burns-Jewish Hospital in St. Louis. For 143 of these 152 patients who were hospitalized, if they continued to be hospitalized on the 3rd, 7th, 14th, and 28th days of hospitalization, additional blood samples were collected and the testosterone concentration in each sample was measured. I measured it.
As a result, there was no association between the severity of COVID-19 and testosterone in women, but in men, '52 ng / dL in patients with high blood testosterone levels, severe. There was an association between testosterone levels and severity, with 151 ng / dL in low-grade patients. It has been confirmed that this association between testosterone concentration and severity is significant even after considering factors that may affect COVID-19, such as age, BMI, presence or absence of underlying disease, smoking status, and race.
It was also found that the blood testosterone concentration during continued hospitalization had decreased to 19 ng / dL on the third day of hospitalization in severely ill male patients. From this, the research team explained that changes in blood testosterone levels could be a clue to the patient's future condition. A similar survey was conducted on IGF-1, which is known as growth hormone, but it was not found to be related to the severity of COVID-19 regardless of gender.
In this study, the research team confirmed that men with low blood testosterone levels have activated a gene that increases testosterone consumption in the body, but the activation status of this gene is COVID-19. It is unclear how it acts on severity, and whether severe COVID-19 reduces blood testosterone levels, or lower blood testosterone levels raises the severity of COVID-19. We conclude that the causal relationship between the two is also unknown.
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by darkhorse_log