A Raspberry PI machine that automatically detects mosquitoes and destroys them with a laser is born

by
Mosquitoes are sanitary pests that transmit diseases such as malaria , dengue fever , and Zika fever , and are responsible for the deaths of more than 700,000 people worldwide each year, twice the number of deaths from homicides. A Raspberry PI machine was developed that detects such mosquitoes using machine vision and machine learning and burns them to death with laser irradiation.
Raspberry PI for Kill Mosquitoes by Laser[v1] | Preprints
https://www.preprints.org/manuscript/202101.0412/v1
Ildar Rakhmatulin of Russia's South Ural State University created a machine that automatically detects and burns mosquitoes. He said that in order to overcome the situation where mosquitoes cause many deaths around the world every year, a groundbreaking invention is needed. We have developed a prototype machine for.
This machine is based on the Raspberry Pi 3 MODEL B and is equipped with a dedicated camera module equipped with Sony's IMX219 image sensor, a galvanometer, and a 1W high-power laser.
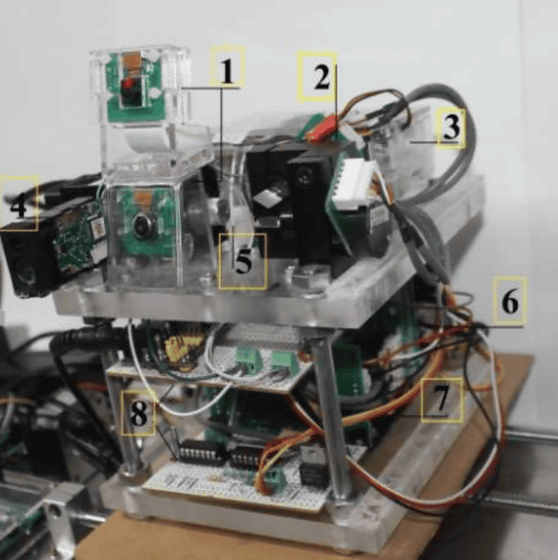
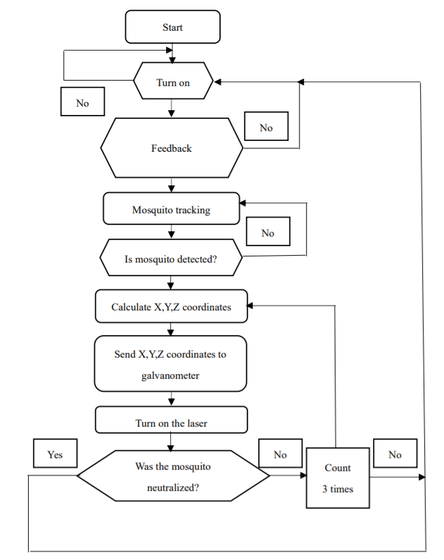
The process from detecting mosquitoes to destroying them with a laser is to first analyze image information acquired by a camera using machine learning to detect mosquitoes, and then use TrackerCSRT, TrackerKCF, TrackerBoosting, TrackerMIL, TrackerTLD, TrackerMedianFlow, TrackerMOSS, etc. Tracking system API that keeps track of moving objects. The system uses deep learning to predict the trajectory of a mosquito in flight, which changes every moment, and irradiates it with a laser.
Convolution 2D and MaxPooling 2D
There is also a problem with detection accuracy, and cases have been confirmed where the mosquito fails to be captured, as shown in (d) below, when the mosquito suddenly changes course.
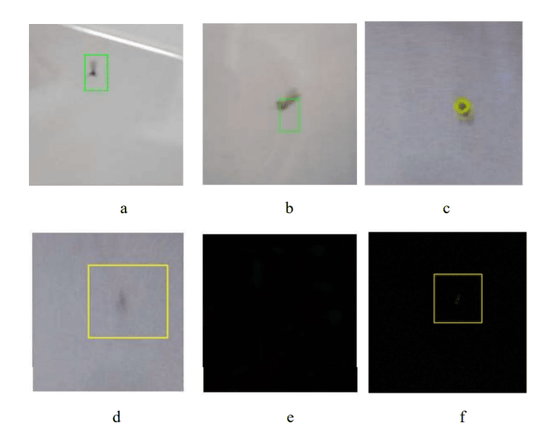

The prototype machine created this time is actually being tested on mosquitoes caught in a transparent case. In this test run, the laser successfully neutralized mosquitoes 15% of the time, and the probability of the mosquito dying when the laser landed was over 50%.

This machine uses a method that ``identifies mosquitoes using image information from a camera.'' Mr. Rakhmatulin also considered ``sonic wave sensing using sonar'' and ``thermal sensing using infrared sensors'', but the problem with sound wave sensing is that it is mixed with noise in an open space and reduces accuracy, and that it is difficult to detect when there are multiple mosquitoes. However, there is a problem with thermal detection in that the mosquito's body temperature is greatly affected by the environmental temperature, so this time it says that it adopted a method called image recognition.
According to Rakhmatulin, the method of exterminating mosquitoes with laser irradiation 'can be used even outdoors in strong winds,' 'can achieve a range that covers a wide area,' and 'can be used on the move by being mounted on an unmanned drone or directly on the human body.' Rakhmatulin says it has the advantage of being a promising solution for mosquitoes that are spreading diseases around the world.
Related Posts: