5 'Medical Discoveries Found by Accident', such as the New Corona Vaccine, which was highly effective due to administration errors
The new coronavirus vaccine 'ChAdOx 1 nCoV-2019' developed by Oxford University in the United Kingdom and AstraZeneca, a major pharmaceutical company, gave a slightly conservative result of 'effective rate 62%' in clinical trials, but another trial Then, we also obtained very promising data with an effective rate of 90%. Adam Taylor, director of the Center for Clinical Anatomy and Learning at Lancaster University, has compiled five anecdotes that led to the discovery of human history from the name of the injury and the accident, including the 'accident' that led to this promising result.
Five serendipitous medical discoveries – starting with the Oxford vaccine dose
◆ 1: New coronavirus vaccine with improved effect due to administration error
Phase III clinical trials of the new coronavirus vaccine 'ChAdOx 1 nCoV-2019' developed by Oxford University and others were conducted in the United Kingdom, Brazil, and South Africa. The study was conducted according to two dosing regimens, with an 'effective rate of 62%' in the group receiving the prescribed dose twice, and another group receiving the first half of the prescribed dose and the second full dose. Then, the result was 'effective rate 90%'. In response, Oxford University announced that 'the vaccine efficacy rate averaged 70%.'
Report that the new corona vaccine developed by Oxford University and AstraZeneca showed high efficacy --GIGAZINE

In response to this news, many scientists and medical professionals wondered, 'Why did you divide the administration method into two types?', But in fact, half of the prescribed amount was ' just a mistake '. That thing. In addition, the group in which the first dose was half of the prescribed dose was not only more effective but also had fewer side effects than the group in which the full dose was administered both times.
◆ 2: Penicillin
The antibiotic penicillin , one of the 'great discoveries of the 20th century,' is actually a coincidence. When Alexander Fleming , a British bacteriologist, discovered penicillin in 1928, he began a trip to culture Staphylococcus aureus .
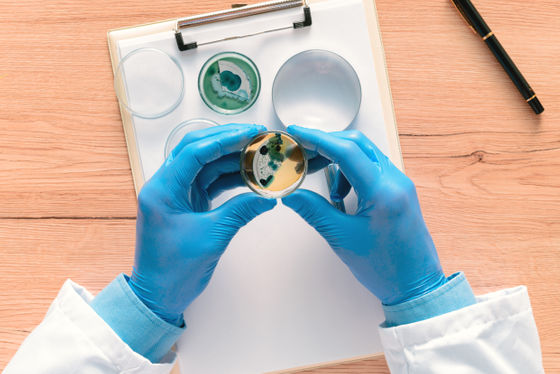
Fleming, who returned to the laboratory after the holidays, found that penicillium was growing on one of the petri dishes for culturing the fungus, and that the fungus was not growing at all around it. The antibiotic obtained by culturing the mold was named 'penicillin' from the scientific name of Penicillium.
In addition to penicillin, Fleming has discovered a bactericidal enzyme, lysozyme , contained in saliva, triggered by accidental sneezing on a petri dish coated with bacteria.
◆ 3: Discovery of the causative agent of the disease for the first time in human history
Penicillin was discovered by chance in an experiment to culture bacteria, but the 'method of culturing bacteria' was also born from the accidental discovery. Prior to the German doctor Robert Koch establishing a method for purely culturing bacteria, researchers used liquids such as gravy to cultivate the bacteria. However, with this method, various bacteria are mixed with muddy and propagate, so it was difficult to culture only specific bacteria and use them as research materials.
Meanwhile, Koch saw mold growing on the cut end of the potato in 1872, and thought, 'If you use a solid medium, fungal colonies can be formed, so separation is easy.' Therefore, Koch identified the pathogen of charcoal disease in an experiment in which the culture medium was solidified with gelatin to prepare a medium, and the isolated bacteria were administered to animals. The pathogen is charcoal bacterium, which is the first bacterium that human beings proved to be associated with the disease.
After that, Koch discovered tubercle bacilli and Vibrio cholerae one after another, and is called 'the founder of modern bacteriology' together with Louis Pasteur .
◆ 4: Discovery of X-rays
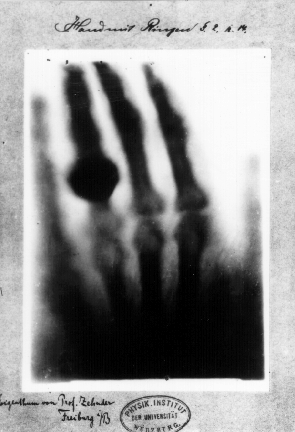
X-ray photography using X-rays is also called 'radiography' after the discoverer Wilhelm Röntgen . At one point, Roentgen, who was studying cathode rays, noticed that a mysterious ray of light penetrating cardboard was emitted from the device, and named it 'X-ray' because the origin of the ray was unknown. This later became the basis for X-ray photography, which allows the inside of the human body and the contents of baggage to be seen through from the outside.
Below is the left hand of his wife Anna Versa Ludwig, photographed by Roentgen using X-rays. You can see the joints of the finger bones and the ring on the ring finger.
◆ 5: Discovery of bacteria that cause gastric ulcer
In the past, gastric ulcers were thought to be caused by harsh food and drink and stress. However, according to Taylor, these factors can exacerbate gastric ulcer but do not cause it. Australian microbiologists Barry Marshall and Robin Warren discovered the Helicobacter pylori that causes such gastric ulcers.
In 1982, Marshall and his colleagues, who were studying the stomach contents of patients with various gastrointestinal disorders, left the device that was culturing the stomach contents in the laboratory because of Easter during the experiment. did. At this time, accidentally leaving the experimental equipment for a longer period than the normal culture period led to the identification of Helicobacter pylori, which grows slower than normal bacteria.
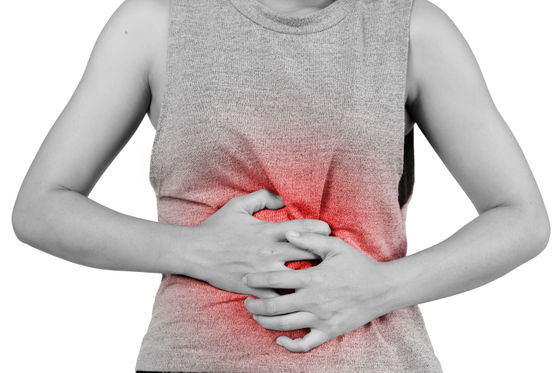
Marshall and his colleagues discovered Helicobacter pylori, the causative agent of gastric ulcer, but in the medical community at the time, the general idea was that microorganisms could not grow in a stomach filled with strong acid. Was not recognized. Moreover, since Helicobacter pylori affects only primates, it was not possible to prove a causal relationship by experiments with mice.
Therefore, Mr. Marshall swallowed Helicobacter pylori, which was taken out from a patient with gastric ulcer and cultured, and conducted a human experiment on his own body. As a result, Marshall successfully developed a gastric ulcer and was able to prove that the cause of the gastric ulcer was Helicobacter pylori. Marshall and Warren were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2005 for their work that does not even care for their own body.
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1l_ks