It turns out that there are several saltwater lakes beneath Mars, increasing the chances of discovering life

by
At the bottom of the Antarctica ice Lake Vostok , such as, in the cold regions of the Earth subglacial lake , but there is, it announced the paper of the same lake there is a possibility that there are a plurality in the basement of Mars It was. It is hoped that this discovery will further increase the chances of finding life and its traces on Mars.
Multiple subglacial water bodies below the south pole of Mars unveiled by new MARSIS data | Nature Astronomy
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41550-020-1200-6
Water on Mars: discovery of three buried lakes intrigues scientists
https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-020-02751-1
Salty lake, ponds may be gurgling beneath Mars' South Pole
https://phys.org/news/2020-09-salty-lake-ponds-gurgling-beneath.html
Liquid water on Mars? New research indicates buried'lakes'
https://www.nbcnews.com/science/space/liquid-water-mars-new-research-indicates-buried-lakes-n1241234
In July 2018, a research team led by Roberto Orosei of the Italian National Institute of Astrophysics announced that a lake with liquid water was found under the ice in the South Pole of Mars. This discovery came from the Mars probe Mars Express , which is said to contain more than 10 billion liters of liquid water in the single subglacial lake found at that time.
Evidence of 'lake made of liquid water' found on Mars-GIGAZINE

The subglacial lake in Mars' Antarctic found in 2018 was identified by only 29 observations between 2012 and 2015, supporting the findings by Orosei and colleagues. Further observations will be carried out. Based on the data set obtained from a total of 134 observations from 2012 to 2019, we conducted a wider search than the previous time.
As a result, it was newly found that there are three subglacial lakes with a diameter of several kilometers around the previously found subglacial lake with a diameter of about 30 kilometers. Regarding the effectiveness of this discovery, co-author of the paper, Professor Elena Petinelli, a geophysicist at Roma Tre University, said, 'We are much more confident this time than before. We have more observations. Not only did we do it, but we processed the data in a completely different way than before. '
The following is a radar map of the South Pole of Mars based on the data sent from the Mars probe, and the part where there is water is shown in blue.
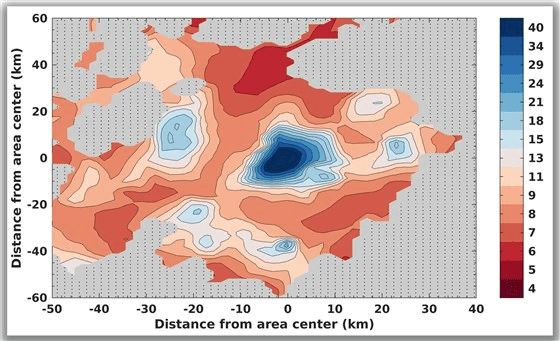
Mars is cooler than Earth, with a surface temperature of minus 113 degrees Celsius at the South Pole. Underground temperatures are said to be higher than the surface, but scientists speculate that the subglacial lakes found this time are quite salinity, as fresh water cannot still exist as a liquid. ..
As with the Earth's oceans, salt water can nurture life, but the problem is its concentration. John Presk, an environmental scientist at Montana State University, said, 'Life can be sustained if the salt concentration is about five times that of the Earth's sea, but if it is about 20 times the concentration of seawater, life no longer exists. You can't do that. '
Other scientists suspect the existence of subglacial lakes because the temperature of the South Pole on Mars is so low. 'I don't think there's a flow of heat under the ice cap that can keep liquid salt water underneath,' said Jack Holt, a planetary scientist at the University of Arizona, a member of NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. So I don't think there is a subglacial lake. If so, it's a moist deposit, and the lake is a misleading expression. '
Still, Petinelli said, 'Mars may have had a lot of water in the past, and if it did, life could have been born,' said Mars. He expressed his hope that signs of life would be found in the subglacial lake, which is considered to be a remnant of the era. In addition, the research team wrote in a paper that 'the future mission of Mars should target the area where the subglacial lake was found this time', and the need for direct investigation not only from satellites but also by exploration rover etc. I am suing.
Currently, the spacecraft ' Tianwen-1 ' launched by China on July 23, 2020 is heading for Mars, and the Mars exploration mission by satellite and rover is scheduled to start in February 2021.
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1l_ks