Do older people who are at higher risk of new coronavirus infection have more infection countermeasures?

Since new coronavirus infection (COVID-19) is
Elderly people and responses to COVID-19 in 27 Countries
https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0235590
COVID-19 safety: Around the world, many of the elderly can't be bothered | Ars Technica
https://arstechnica.com/science/2020/07/global-survey-shows-the-elderly-arent-protecting-themselves-from-covid-19/

Jean-François Daoust , a sociologist at the University of Edinburgh in the United Kingdom, analyzes the survey data conducted by Imperial College London and the data analysis company YouGov. Daoust analyzes the data in a survey of 72,000 people in 72 countries around the world to see how well the subject was following the advice of public health professionals, and how age-dependent they were. It was.
Questionnaire questions include 'Do you want to be self-isolated if symptoms occur?' 'Do you follow if you are advised by a public health expert or government to self-isolate?' or 'Do you wear a mask?' Inquiries about specific countermeasures against infection, such as 'Do you want to welcome visitors?'
Elderly be COVID-19 is likely to severe have been found from the investigation so far , Ideally, you will be required to perform a sense of crisis is growing defense as the become older. However, when Mr. Daoust actually analyzed the survey, the number of people who wanted self-isolation when the symptoms appeared gradually increased from 20 years old to 60 years old, but at 75 years old the graph It is falling sharply.

Many young people also say, “When they receive advice from a specialist for self-isolation,” the number gradually increases until the age of 60, and then the graph has leveled off.
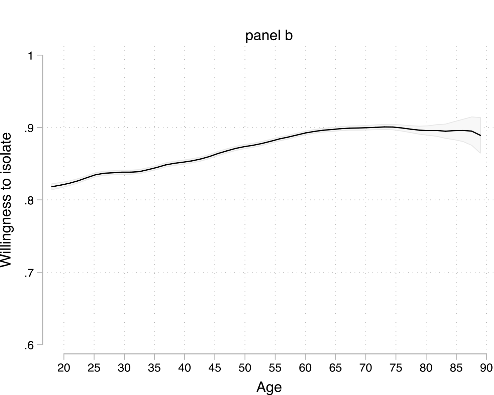
Whether or not they took actions to prevent infection, such as wearing a mask, did not make a big difference according to age.
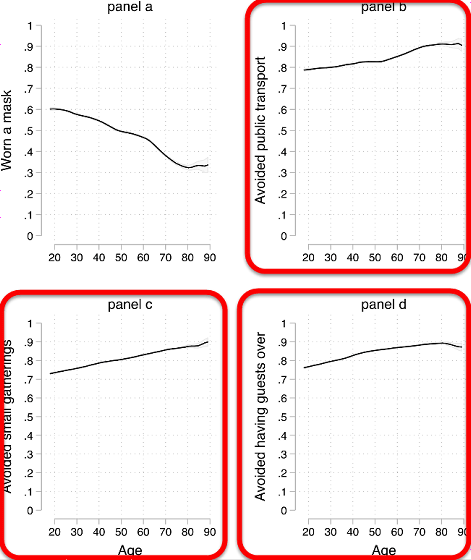
Looking at individual preventive measures, most people in their 20s take the preventive measure of 'wearing a mask', and the graph declines with age.

On the other hand, three of 'Avoid public transportation (upper right)', 'Avoid small gatherings (lower left)' and 'Avoid visitors (lower right)' are increasing in number as people age. Is shown.
Daoust admits that there are few data available for people over the age of 80, but points out that older people who were required to be self-isolated were less likely to follow their experts. In addition, it is concerned that older people are not willing to wear masks because it becomes important when social distance strategies are relaxed, and it is necessary to reconsider the government's approach to older people. He said.
Related Posts:
in Note, Posted by darkhorse_log