Details of the target '25 × 20' that AMD has achieved 25 times the energy efficiency of the processor, TSMC's 7 nm process contributes greatly
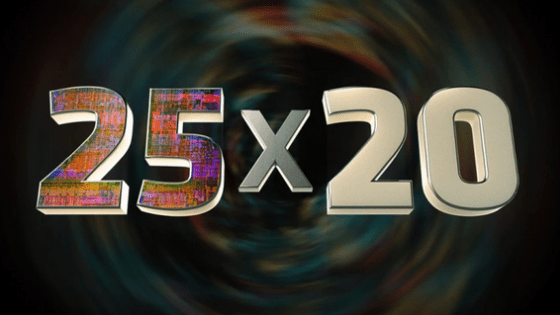
AMD's 2014 goal of ' 25x20 energy efficiency of mobile processors by 2020' has been achieved. The Ryzen Mobile 4000 , codenamed “Renoir” released in 2020, is 31.77 times more energy efficient than the 2014 Kaveri generation.
AMD Exceeds Six-Year Goal to Deliver Unprecedented 25 Times Improvement in Mobile Processor Energy Efficiency | AMD
https://www.amd.com/en/press-releases/2020-06-25-amd-exceeds-six-year-goal-to-deliver-unprecedented-25-times-improvement
AMD Succeeds in its 25x20 Goal: Renoir Crosses the Line in 2020
https://www.anandtech.com/show/15881/amd-succeeds-in-its-25x20-goal-renoir-zen2-vega-crosses-the-line-in-2020
'25 x 20' is the goal set by AMD in 2014 to '25 times increase the energy efficiency of mobile processors by 2020.' With the advent of the Renoir generation of the Ryzen 7 4800H in 2020, the 25x20 goal was achieved. Ian Cutress , a reporter at tech media AnandTech , has analyzed AMD's 25x20 trajectory in detail and summarized it in a graph.
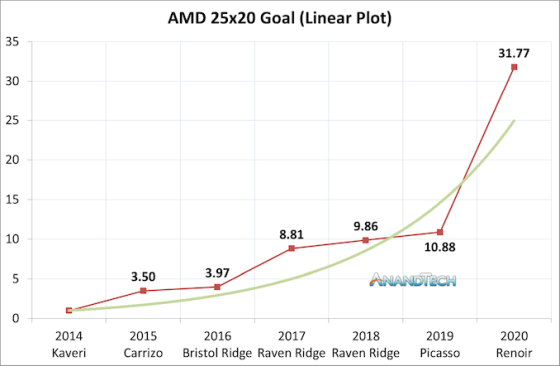
If you look at the graph, you can see that the performance has improved significantly from the Kaveri generation to the Carrizo generation, the Bristol Ridge generation to the Raven Ridge generation, and the Picasso generation to the Renoir generation.
The change between the Kaveri generation and the Carrizo generation is the implementation of a new power monitoring feature on the chip that allows the system to better distribute power, said Cutress. Raven Ridge combines Zen generation processors with Vega generation integrated graphics to significantly improve performance.
In Renoir generation from Picasso generations, GlobalFoundries from Zen + architecture employing a 12nm process TSMC proceeds to Zen2 architecture according to 7nm process. Achieved the greatest performance improvement from 2014 to 2020.
The energy efficiency of 25×20 is calculated by calculation performance and power consumption, and the specific calculation method is as follows.
・Base : Kaveri generation value
- 'C', which represents computational performance : The CPU multi-thread performance measured with Cinebench R15 and the GPU performance based on the overall score of 3DMark11 are averaged at a ratio of 50:50.
・'E' for power consumption : 'Typical energy consumption of notebook PCs' based on the requirements of the International Energy Star Program
・'X', which represents the overall energy efficiency : C divided by E
The concrete formula to calculate 'C' which shows the calculation performance is as follows. The Cinebench R15 and 3D Mark 11 measurements in the new generation are each divided by the Kaveri generation measurements to calculate the average.
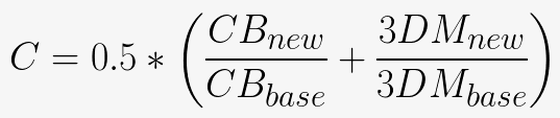
The calculation formula of power consumption 'E' is very complicated, and the power consumption is calculated by dividing the state of the notebook PC into several stages such as during sleep and idle.
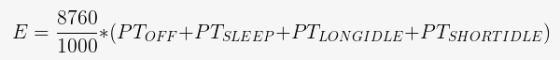
Cutress points out that the value of E is the power consumption of the entire notebook PC and is also affected by other parts that make up the notebook PC. AMD uses an internal reference platform to measure the value of E, and usually the first notebook PC with the platform to be measured will be the reference.
The final energy efficiency is C divided by E, so the higher the performance represented by C and the lower the power consumption represented by E, the higher the energy efficiency value. ..
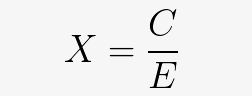
The platforms AMD used to evaluate the 25x20 project are: Note that some of these platforms do not work with standard TDP.
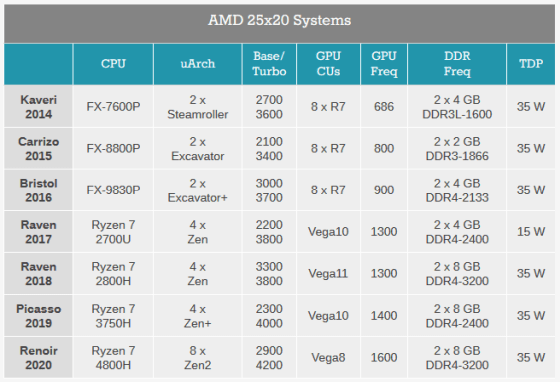
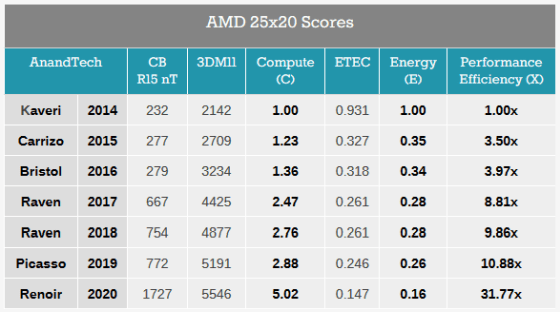
Performance, power consumption and energy efficiency are shown in the table like this. Performance has increased 5.02 times since 2014, power consumption has increased 0.16 times since 2014, and final energy efficiency has increased 31.77 times.
The project, which started in 2014, is said to have been advanced by technological development such as high integration and efficiency of CPU and GPU, real-time power management and optimization at the silicon level. AMD says that if it replaces a notebook computer equipped with 50,000 AMD processors with a 2014 model from a 2020 model, it can expect a carbon reduction of 971 tons. The amount of carbon dioxide reduction is said to be equivalent to the 'effect of growth of 16,000 trees for 10 years'.
'Without TSMC's 7nm process, it would have been impossible to achieve our goals,' said AMD N fellow researcher Sam Naffziger. 'I'm looking forward to the next five years,' he said.
Related Posts:
in Hardware, Posted by darkhorse_log