Statistical information of technology 'Borg' supporting services such as Google's Gmail and cloud is released

Google operates various services such as Gmail, search engines, and
(PDF) Borg: the Next Generation
https://www.eurosys2020.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/slides/49_muhammad_tirmazi_slides.pdf
GitHub-google / cluster-data: Borg cluster traces from Google
https://github.com/google/cluster-data
Large-scale cluster management at Google with Borg – Google Research
https://research.google/pubs/pub43438/
Borg is a cluster manager developed by Google, which is the base system for distributing the processing of programs to multiple machines. Kubernetes, an orchestration tool that was also developed by Google and is gaining popularity in the field of infrastructure, is said to have had a major impact.
Borg defines a collection of machines as a Cell and treats it as a single unit.
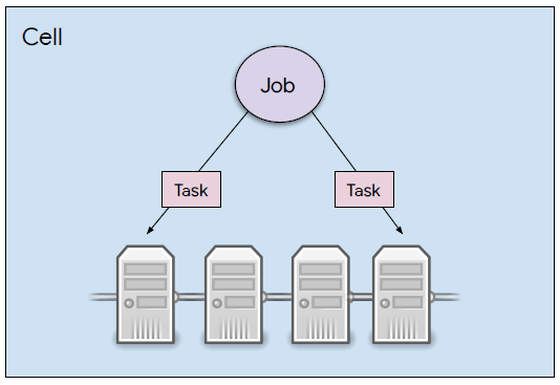
The user inputs processing to Borg in the form called Job. Job describes information such as the owner of the program, and is composed of multiple programs called Tasks. Job has priority, and 'production', 'mid', 'best-effort batch' and 'free' are set in order of priority. In addition, Task is not executed on the virtualized container like Kubernetes, but is executed directly on the hardware.
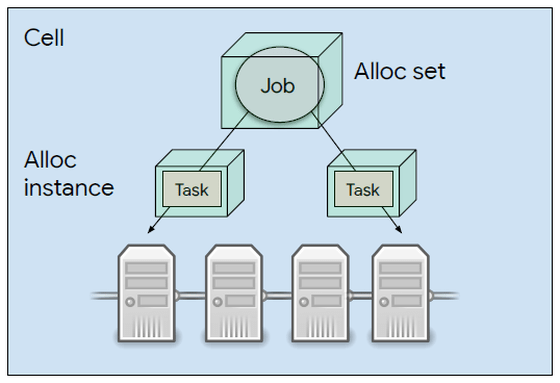
In order to distribute tasks to multiple machines, Borg has adopted the structure of 'pre-allocating resources across multiple machines and considering it as one resource'. This allocated resource is called alloc, and Job and Task are executed in alloc. As a result, processing is distributed among multiple machines.
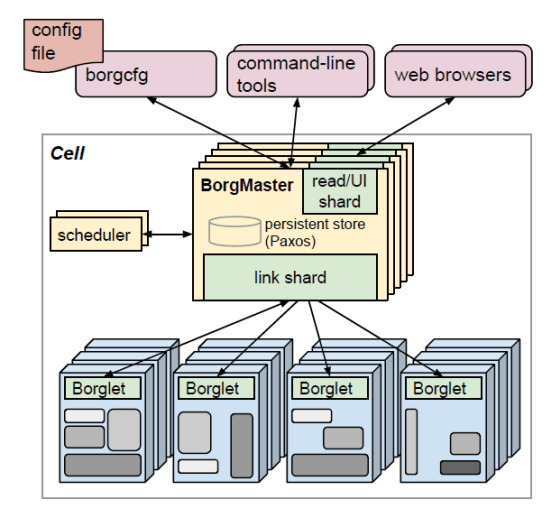
The whole picture of Borg looks like this. The user submits processing to the Cell via a browser or command line, and a management program called Borgmaster manages Jobs, Tasks, and alloc. A monitoring agent called Borglet is placed on the machine in the Cell, and starts, stops, and restarts Tasks assigned by the Borgmaster.
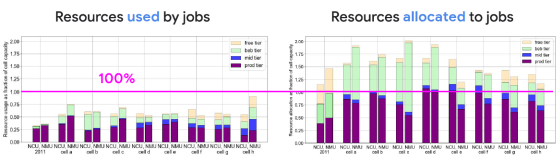
This time Google released various statistical information of the processing in Borg's Cell. The information released in 2011 is only information on one cell, but the 2019 version includes information collected from eight cells made up of 96,000 machines. There are mainly two metrics that are collected from Cell: 'Resource used by Job' and 'Resource allocated to Job = Allocated resource'.
First, let's take a look at 'Computing resources used by Job'. The vertical axis of the graph is the usage rate of computational resources in Cell and the horizontal axis is the number of days. You can see that compared to 2011, 2019 has a new priority called 'mid'.
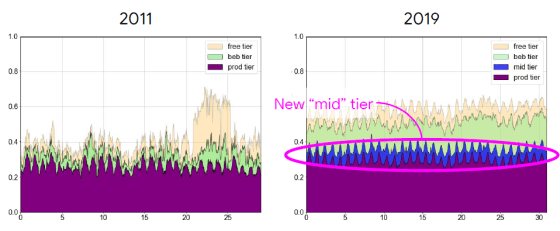
Jobs with the priority 'best-effort batch' are increasing. Since the job of 'best-effort batch' is a job that considers the possibility of stopping the processing by a job with a high priority, it can be seen that the processing capacity of Cell can be used efficiently.
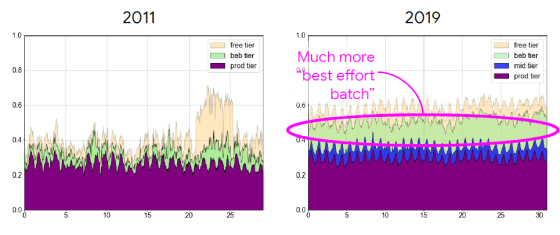
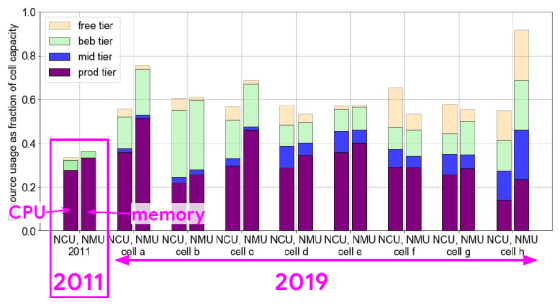
A similar trend can be seen by looking at the graph of CPU and memory used for Job in which the vertical axis is the processing capacity and the horizontal axis is the Cell.
Next, if you look at 'Resources allocated to Job', it is supposed that more Cell resources are allocated overall.
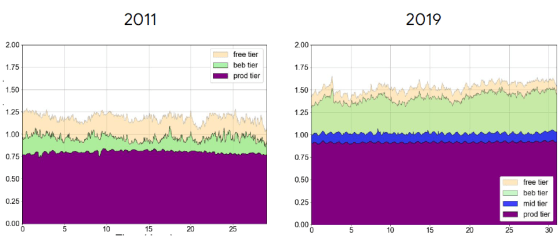
Comparing 'Resources used by Job' and 'Resources allocated to Job' looks like this. In 2019, it can be seen that Jobs with high priority are allocated efficiently so that the actual machine resources are used up.
The graph below is a cumulative frequency distribution curve with the vertical axis representing the cumulative rate and the horizontal axis representing the machine usage rate. There is a large difference in the curve between the machine usage rate of eight cells in 2019 and the machine usage rate of one cell in 2011.
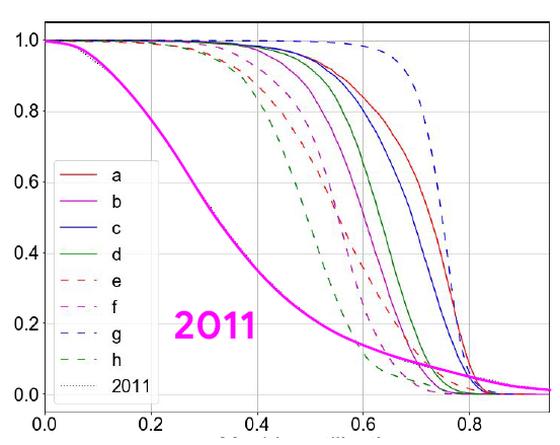
Looking at the median utilization rate, the utilization rate in 2011 was about 30%, while in 2019 we were able to improve the utilization rate from 50% to 77%.
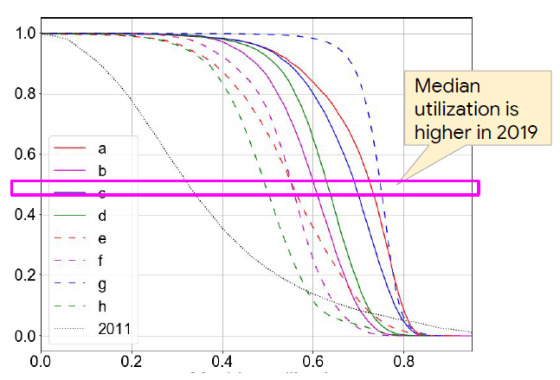
As a future issue, Google explains that jobs that consume a lot of machine resources are likely to hinder the processing of small jobs, and that scheduling of jobs is important.
Related Posts:
in Software, Posted by darkhorse_log